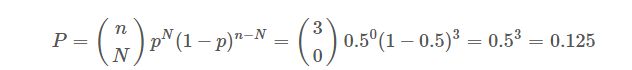numpy.where与numpy.random.multinomial用法
umpy.where() 有两种用法:
np.where(condition, x, y)满足条件(condition),输出x,不满足输出ynp.where(condition)只有条件(condition),没有x和y,则输出满足条件 (即非0) 元素的坐标 (等价于numpy.nonzero)。这里的坐标以tuple的形式给出,通常原数组有多少维,输出的tuple中就包含几个数组,分别对应符合条件元素的各维坐标。
1. np.where(condition, x, y)
满足条件(condition),输出x,不满足输出y。
import numpy as np
aa = np.arange(10)
Out[4]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
np.where(aa,1,-1)
Out[5]: array([-1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]) # 0为False,所以第一个输出-12. np.where(condition)
只有条件 (condition),没有x和y,则输出满足条件 (即非0) 元素的坐标 (等价于numpy.nonzero)。这里的坐标以tuple的形式给出,通常原数组有多少维,输出的tuple中就包含几个数组,分别对应符合条件元素的各维坐标。
np.where(aa > 5)
Out[6]: (array([6, 7, 8, 9], dtype=int64),)
aa[np.where(aa > 5)]
Out[7]: array([6, 7, 8, 9])numpy.random.multinomial函数
这是 numpy 提供的随机二项式分布实现,二项式分布(binomial distribution)如下表示:
函数原型如下:
numpy.random.RandomState.binomial(n, p, size=None)表示对一个二项分布进行采样,size表示采样的次数,参数中的n, p分别对应于公式中的n,pn,p,函数的返回值表示n中成功(success)的次数(也即NN)。 举个例子,比如掷骰子,一共3个硬币,每个都投一次,三个都是正面朝上的概率是多少?
这个使用简单的概率统计知识很容易计算得到:
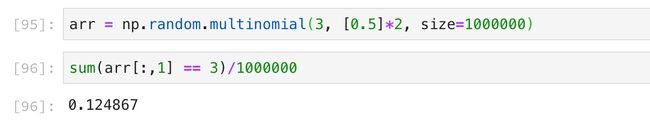
使用上述函数计算大概值则是做足够多次的试验,统计其中全为正面朝上的概率,通过频率计算概率,如下:
参考:
- https://www.cnblogs.com/massquantity/p/8908859.html
- https://suool.net/2018/12/14/Numpy-Where/