Oracle19c 定制脚本runstats
runstats 工具, 能对做同一件事的两个不同方法进行比较。得出孰优孰劣的结果。
只需要提供两个不同的方法。
runstats只是测量3个要素。
- 墙上时钟(wall clock)或耗用时间(elapsed time):
- 系统统计结果:会并排地显示每个方法做某件事(如执行解析调用)的次数,并展示出二者之差。
- 闩定(latching):这是这个报告的关键输出。
闩(latch)是一种轻量级的锁。锁(lock)是一种串行化设备,而串行化设备不支持并发。应用中使用闩越少,性能就越好。
Runstats最好独立使用。最好在一个单用户数据库上运行。Runstat在运行过程中,不希望其他任务对系统的负载或闩产生影响。
要使用runstats,需要能访问几个V$视图,并创建一个表来存储统计结果。还要创建runstats包。
需要访问4个V$表(动态性能表):V$STATNAME,V$MYSTAT,V$LATCH,V$TIMER
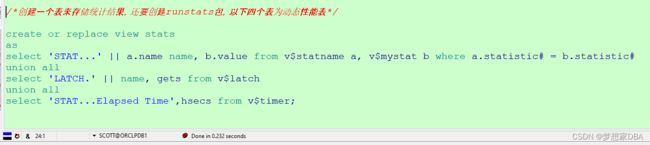
/*创建一个表来存储统计结果,还要创建runstats包,以下四个表为动态性能表*/
create or replace view stats
as
select 'STAT...' || a.name name, b.value from v$statname a, v$mystat b where a.statistic# = b.statistic#
union all
select 'LATCH.' || name, gets from v$latch;
union all
select 'STAT...Elapsed Time',hsecs from v$timer;注意: 需要授权访问的具体对象名应该是v_$statname ,v_$latch,v_$timer,v_$mystat, 而 V$名只是同义词,它们分别指向以V_$开头的底层视图。
[oracle@MaxwellDBA ~]$
[oracle@MaxwellDBA ~]$ sqlplus sys/sys as sysdba
SQL*Plus: Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on Wed Sep 28 16:46:25 2022
Version 19.3.0.0.0
Copyright (c) 1982, 2019, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connected to:
Oracle Database 19c Enterprise Edition Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production
Version 19.3.0.0.0
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb>
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb>
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb> ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=ORCLPDB1;
Session altered.
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb> show user;
USER is "SYS"
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb> show con_name
CON_NAME
------------------------------
ORCLPDB1
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb> grant select on v_$statname to SCOTT;
Grant succeeded.
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb> grant select on v_$latch to SCOTT;
Grant succeeded.
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb> grant select on v_$timer to SCOTT;
Grant succeeded.
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb> grant select on v_$mystat to SCOTT;
Grant succeeded.
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb>Step 1: 创建视图。
/*创建一个表来存储统计结果,还要创建runstats包,以下四个表为动态性能表*/
create or replace view stats
as
select 'STAT...' || a.name name, b.value from v$statname a, v$mystat b where a.statistic# = b.statistic#
union all
select 'LATCH.' || name, gets from v$latch;
union all
select 'STAT...Elapsed Time',hsecs from v$timer;Step2: 接下来只需要一个小表来收集统计结果。
/*创建一个临时表来收集统计结果*/
create global temporary table run_stats
(runid varchar2(15),
name varchar2(80),
value int)
on commit preserve rows;Step 3: 需要创建runstats包。其中包含3个简单的API调用
- runstats测试开始时调用RS_START(runstats开始)。
- RS_MIDDLE会在测试中间调用。
- 完成时调用RS_STOP,打印报告。
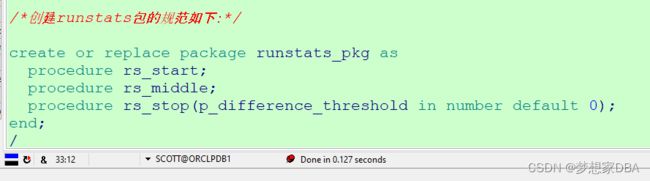
创建runstats包的规范如下:
- 参数p_difference_threshold用于控制最后打印的数据量。runstats会收集并得到每次运行的统计结果和闩信息,然后打印一个报告,说明每次测试(每个方法)使用了多少资源,以及不同测试(不同方法)的结果之差。可以使用这个输入参数来控制只查看差值大于这个数的统计结果和闩信息。参数默认值为0.默认情况下可以看到所有输出。
/*创建runstats包的规范如下:*/
create or replace package runstats_pkg as
procedure rs_start;
procedure rs_middle;
procedure rs_stop(p_difference_threshold in number default 0);
end;
/create or replace package body runstats_pkg
as
/*global variables : be used to record cost time in every running*/
g_start number;
g_run1 number;
g_run2 number;
procedure rs_start is
begin
/*clear up table run_stats, and then insert last time get stats information and latch lock information */
delete from run_stats;
insert into run_stats
select 'before', stats.* from stats;
g_start := dbms_utility.get_cpu_time;
end;
procedure rs_middle is
begin
/*把第一次测试运行的耗用时间记录在G_RUN1中,然后插入当前的一组统计结果和闩信息。最后记录一下运行的开始时间*/
g_run1 := (dbms_utility.get_cpu_time - g_start);
insert into run_stats
select 'after 1', stats.* from stats;
g_start := dbms_utility.get_cpu_time;
end;
procedure rs_stop(p_difference_threshold in number default 0)
is
/*打印每次运行的累加CPU时间,然后分别打印两次运行的统计/闩值之差(只打印差值超出阀值时的结果。)*/
begin
g_run2:=(dbms_utility.get_cpu_time-g_start);
dbms_output.put_line('Run1 ran in ' || g_run1 || 'cpu hsecs' );
dbms_output.put_line('Run2 ran in ' || g_run2 || 'cpu hsecs' );
if(g_run2 <> 0) then
dbms_output.put_line('run1 ran in ' || round(g_run1/g_run2*100,2) || '% of the time' );
end if;
dbms_output.put_line(chr(9));
insert into run_stats select 'after 2', stats.* from stats;
dbms_output.put_line(rpad('Name', 30) || lpad('Run1', 12) || lpad('Run2', 12) || lpad('Diff',12));
for x in
(select rpad(a.name,30) ||
to_char(b.value-a.value,'999,999,999')||
to_char(c.value-b.value,'999,999,999')||
to_char(((c.value-b.value)-(b.value-a.value)),'999,999,999') data
from run_stats a, run_stats b, run_stats c
where a.name = b.name
and b.name = c.name
and a.runid = 'before'
and b.runid = 'after 1'
and c.runid = 'after 2'
and abs((c.value-b.value)-(b.value-a.value)) > p_difference_threshold
order by abs((c.value-b.value)-(b.value-a.value))
)loop
dbms_output.put_line(x.data);
end loop;
dbms_output.put_line(chr(9));
dbms_output.put_line('Run1 latches total versus runs -- difference and pct');
dbms_output.put_line(lpad('Run1', 12) || lpad('Run2', 12)||lpad('Diff',12) || lpad('Pct',10));
for x in (select to_char(run1, '999,999,999')||
to_char(run2, '999,999,999')||
to_char(diff, '999,999,999')||
to_char(round(run1/decode(run2,0,to_number(0),run2)*100,2), '99,999.99')||'%' data
from (select sum(b.value-a.value) run1, sum(c.value-b.value) run2,
sum((c.value-b.value)-(b.value-a.value)) diff
from run_stats a , run_stats b, run_stats c
where a.name = b.name
and b.name = c.name
and a.runid = 'before'
and b.runid = 'after 1'
and c.runid = 'after 2'
and a.name like 'LATCH%'
)
) loop
dbms_output.put_line(x.data);
end loop;
end;
end;
下面通过例子来说明如何使用runstats对批量插入(INSERT)和逐行处理的进行比较,看看哪种方法效率更高。
Step 1 建表,插入50000行记录。
Step2 使用第一种方法插入记录,使用单独一条SQL语句完成批量插入。首先调用RUNSTATS_PKG.RS_START;
Step3:准备执行第二种方法,逐行插入数据。
Step4:最后生成报告。
[root@MaxwellDBA ~]# su - oracle
Last login: Wed Sep 28 18:50:50 CST 2022 on pts/2
[oracle@MaxwellDBA ~]$ sqlplus sys/sys as sysdba
SQL*Plus: Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on Thu Sep 29 06:00:32 2022
Version 19.3.0.0.0
Copyright (c) 1982, 2019, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connected to:
Oracle Database 19c Enterprise Edition Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production
Version 19.3.0.0.0
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb> ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=ORCLPDB1;
Session altered.
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb> show user;
USER is "SYS"
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb> show con_name
CON_NAME
------------------------------
ORCLPDB1
sys@cdb$root:orclcdb>
scott@orclpdb1:orclcdb>
scott@orclpdb1:orclcdb> drop table t1;
Table dropped.
scott@orclpdb1:orclcdb> drop table t2;
Table dropped.
scott@orclpdb1:orclcdb> create table t1 as select * from big_table where 1=0;
Table created.
scott@orclpdb1:orclcdb> create table t2 as select * from big_table where 1=0;
Table created.
scott@orclpdb1:orclcdb> exec runstats_pkg.rs_start;
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
scott@orclpdb1:orclcdb> insert into t1 select * from big_table where rownum <= 50000;
50000 rows created.
scott@orclpdb1:orclcdb> exec runstats_pkg.rs_middle;
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
scott@orclpdb1:orclcdb> beigin
SP2-0042: unknown command "beigin" - rest of line ignored.
scott@orclpdb1:orclcdb> begin
2 for x in (select * from big_table where rownum <= 50000)
3 loop
4 insert into t2 values x;
5 end loop;
6 commit;
7 end;
8 /
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
scott@orclpdb1:orclcdb> exec runstats_pkg.rs_stop(50000)
Run1 ran in 11cpu hsecs
Run2 ran in 83cpu hsecs
run1 ran in 13.25% of the time
Name Run1 Run2 Diff
STAT...opened cursors cumulati 34 50,042 50,008
STAT...session cursor cache hi 22 50,030 50,008
STAT...db block gets from cach 9,101 59,493 50,392
STAT...db block gets 9,101 59,493 50,392
STAT...recursive calls 193 50,660 50,467
STAT...session logical reads 11,160 62,225 51,065
STAT...session uga memory 0 -65,480 -65,480
STAT...Client Path Maximum Tra 0 65,535 65,535
LATCH.enqueue hash chains 21,816 104,658 82,842
STAT...db block changes 8,436 106,562 98,126
STAT...Client Time (usec) Last 0 140,354 140,354
STAT...Client Time (usec) Last 0 140,354 140,354
STAT...Client Time (usec) Last 0 140,355 140,355
STAT...session pga memory -131,072 65,536 196,608
LATCH.cache buffers chains 33,983 301,790 267,807
STAT...Client Time (usec) Busy 0 320,000 320,000
STAT...physical read total byt 9,043,968 8,699,904 -344,064
STAT...cell physical IO interc 9,043,968 8,699,904 -344,064
STAT...physical read bytes 9,043,968 8,699,904 -344,064
STAT...KTFB alloc space (block 9,437,184 11,534,336 2,097,152
STAT...undo change vector size 246,320 3,410,532 3,164,212
STAT...redo size 8,479,584 23,470,344 14,990,760
STAT...logical read bytes from 82,976,768 509,747,200 426,770,432
Run1 latches total versus runs -- difference and pct
Run1 Run2 Diff Pct
82,704 533,412 450,708 15.50%
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
scott@orclpdb1:orclcdb>