月亮数据预测(决策树和随机森林算法)
资料:https://download.csdn.net/download/m0_61504367/85399409
一、问题描述
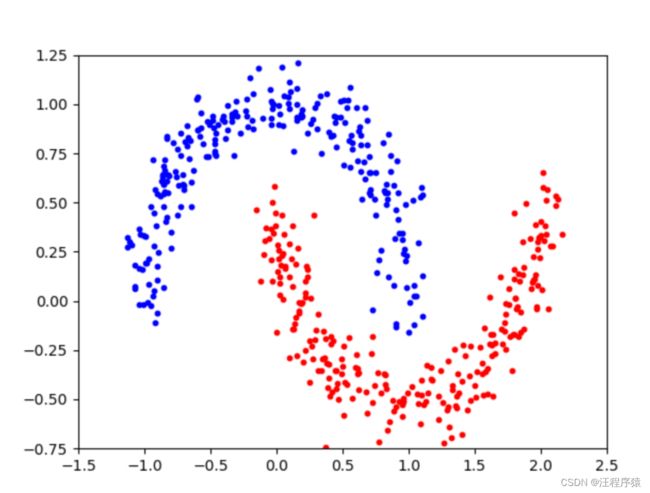
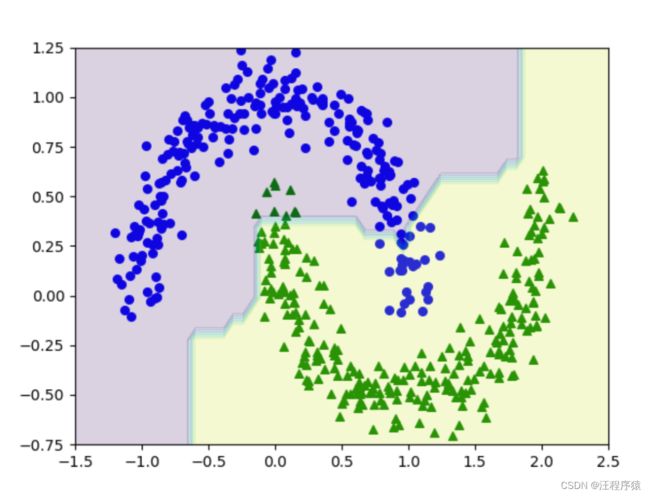
月亮数据是sklearn工具库提供的一个数据集。它上用于分类和聚类算法的实践实验。图中每一个点是一条数据。其中(x1,x2)是特征组,颜色是标签值。如图所示。
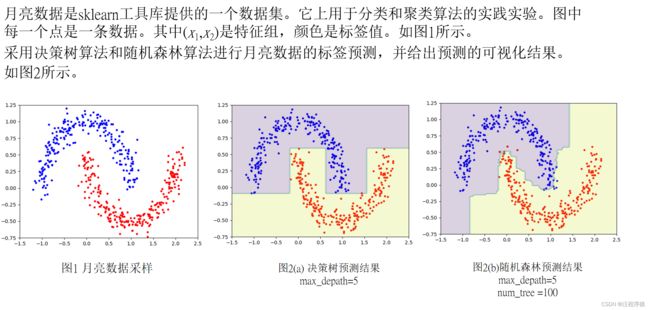
采用决策树算法和随机森林算法进行月亮数据的标签预测,并给出预测的可视化结果。
二、实验目的
学习决策树算法和随机森林算法。
三、实验内容
3.1数据导入
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
3.2数据预处理
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=1000, noise=0.1)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.5, random_state=0)
plt.figure(0)
plt.axis([-1.5, 2.5, -0.75, 1.25])
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0][y_train == 0], X_train[:, 1][y_train == 0], c='b', marker='o', s=10)
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0][y_train == 1], X_train[:, 1][y_train == 1], c='r', marker='o', s=10)
plt.show()
3.3算法描述
决策树算法:
决策树(decision tree)是一个树结构(可以是二叉树或非二叉树)。其每个非叶节点表示一个特征属性上的测试,每个分支代表这个特征属性在某个值域上的输出,而每个叶节点存放一个类别。决策树学习的关键在于寻找最优划分特征和阈值。决策树回归算法用方差值来划分数据,最小化均方误差;决策树分类算法则用熵值来划分数据,最小化交叉熵。本实验是决策树分类问题,分值函数是使用交叉熵CE。
1.遍历所有可能的特征j与阈值
2.对每一组j和阈值, 由分值函数get_score计算score1和score2,
计算score。
3.选出score最小的一组j和阈值,样本的划分。
随机森林算法:
随机森林分类算法是一个包含多棵决策树的分类器。其输出的类别是由森林中的所有决策树输出类别的众数来确定的。
随机森林分类算法的基本思想依据:
1.虽然森林中的每一棵树都有一定的预测错误的概率,但是它们同时都出错的概率却是较低的。
2.在随机森林算法中,要求森林中的决策树相互独立。由于生成决策树的数据子集取自同一训练数据集,因此这些数据子集具有相同的分布。这使得所生成的决策树都比较相似。这就导致生成的决策树相互不独立。
3.增加森林中决策树之间完全相互独立的可能性的方法:随机森林算法在训练每一棵决策树时,要增加以下的额外步骤:在CART算法中作每一次数据划分时,随机地选取一部分特征进行遍历,而不是遍历全部特征。
3.4主要代码
moon.py
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from lib.decision_tree_classifier import DecisionTreeClassifier
from lib.random_forest_classifier import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
import numpy as np
def convert_to_vector(y):
m = len(y)
k = np.max(y) + 1
v = np.zeros(m * k).reshape(m, k)
for i in range(m):
v[i][y[i]] = 1
return v
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=1000, noise=0.1)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.5, random_state=0)
plt.figure(0)
plt.axis([-1.5, 2.5, -0.75, 1.25])
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0][y_train == 0], X_train[:, 1][y_train == 0], c='b', marker='o', s=10)
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0][y_train == 1], X_train[:, 1][y_train == 1], c='r', marker='o', s=10)
plt.show()
tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=50)
tree.fit(X_train, convert_to_vector(y_train))
y_pred = tree.predict(X_test)
print("decision tree accuracy= {}".format(accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)))
plt.figure(1)
x0s = np.linspace(-3, 4, 100)
x1s = np.linspace(-1, 6, 100)
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(x0s, x1s)
W = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
u = tree.predict(W).reshape(x0.shape)
plt.axis([-1.5, 2.5, -0.75, 1.25])
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0][y_train == 0], X_train[:, 1][y_train == 0], c='b', marker='o', s=30)
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0][y_train == 1], X_train[:, 1][y_train == 1], c='g', marker='^', s=30)
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0][y_train == 2], X_train[:, 1][y_train == 2], c='y', marker='s', s=30)
plt.contourf(x0, x1, u, c=u, alpha=0.2)
plt.show()
forest = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=50, num_trees=100, feature_sample_rate=0.5, data_sample_rate=0.15)
forest.fit(X_train, convert_to_vector(y_train))
y_pred = forest.predict(X_test)
print("random forest accuracy= {}".format(accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)))
plt.figure(2)
u = forest.predict(W).reshape(x0.shape)
plt.axis([-1.5, 2.5, -0.75, 1.25])
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0][y_train == 0], X_train[:, 1][y_train == 0], c='b', marker='o', s=30)
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0][y_train == 1], X_train[:, 1][y_train == 1], c='g', marker='^', s=30)
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0][y_train == 2], X_train[:, 1][y_train == 2], c='y', marker='s', s=30)
plt.contourf(x0, x1, u, c=u, alpha=0.2)
plt.show()
决策树算法主要代码
import numpy as np
class Node:
j = None
theta = None
p = None
left = None
right = None
class DecisionTreeBase:
def __init__(self, max_depth, feature_sample_rate, get_score):
self.max_depth = max_depth
self.feature_sample_rate = feature_sample_rate
self.get_score = get_score
def split_data(self, j, theta, X, idx):
idx1, idx2 = list(), list()
for i in idx:
value = X[i][j]
if value <= theta:
idx1.append(i)
else:
idx2.append(i)
return idx1, idx2
def get_random_features(self, n):
shuffled = np.random.permutation(n)
size = int(self.feature_sample_rate * n)
selected = shuffled[:size]
return selected
def find_best_split(self, X, y, idx):
m, n = X.shape
best_score = float("inf")
best_j = -1
best_theta = float("inf")
best_idx1, best_idx2 = list(), list()
selected_j = self.get_random_features(n)
for j in selected_j:
thetas = set([x[j] for x in X])
for theta in thetas:
idx1, idx2 = self.split_data(j, theta, X, idx)
if min(len(idx1), len(idx2)) == 0:
continue
score1, score2 = self.get_score(y, idx1), self.get_score(y, idx2)
w = 1.0 * len(idx1) / len(idx)
score = w * score1 + (1 - w) * score2
if score < best_score:
best_score = score
best_j = j
best_theta = theta
best_idx1 = idx1
best_idx2 = idx2
return best_j, best_theta, best_idx1, best_idx2, best_score
def generate_tree(self, X, y, idx, d):
r = Node()
r.p = np.average(y[idx], axis=0)
if d == 0 or len(idx) < 2:
return r
current_score = self.get_score(y, idx)
j, theta, idx1, idx2, score = self.find_best_split(X, y, idx)
if score >= current_score:
return r
r.j = j
r.theta = theta
r.left = self.generate_tree(X, y, idx1, d - 1)
r.right = self.generate_tree(X, y, idx2, d - 1)
return r
def fit(self, X, y):
self.root = self.generate_tree(X, y, range(len(X)), self.max_depth)
def get_prediction(self, r, x):
if r.left == None and r.right == None:
return r.p
value = x[r.j]
if value <= r.theta:
return self.get_prediction(r.left, x)
else:
return self.get_prediction(r.right, x)
def predict(self, X):
y = list()
for i in range(len(X)):
y.append(self.get_prediction(self.root, X[i]))
return np.array(y)
def get_impurity(y, idx):
p = np.average(y[idx], axis=0)
return 1 - p.dot(p.T)
def get_entropy(y, idx):
_, k = y.shape
p = np.average(y[idx], axis=0)
return - np.log(p + 0.001 * np.random.rand(k)).dot(p.T)
class DecisionTreeClassifier(DecisionTreeBase):
def __init__(self, max_depth=0, feature_sample_rate=1.0):
super().__init__(max_depth = max_depth,
feature_sample_rate = feature_sample_rate,
get_score = get_entropy)
def predict_proba(self, X):
return super().predict(X)
def predict(self, X):
proba = self.predict_proba(X)
return np.argmax(proba,axis=1)
随机森林算法主要代码
import numpy as np
class Node:
j = None
theta = None
p = None
left = None
right = None
class DecisionTreeBase:
def __init__(self, max_depth, feature_sample_rate, get_score):
self.max_depth = max_depth
self.feature_sample_rate = feature_sample_rate
self.get_score = get_score
def split_data(self, j, theta, X, idx):
idx1, idx2 = list(), list()
for i in idx:
value = X[i][j]
if value <= theta:
idx1.append(i)
else:
idx2.append(i)
return idx1, idx2
def get_random_features(self, n):
shuffled = np.random.permutation(n)
size = int(self.feature_sample_rate * n)
selected = shuffled[:size]
return selected
def find_best_split(self, X, y, idx):
m, n = X.shape
best_score = float("inf")
best_j = -1
best_theta = float("inf")
best_idx1, best_idx2 = list(), list()
selected_j = self.get_random_features(n)
for j in selected_j:
thetas = set([x[j] for x in X])
for theta in thetas:
idx1, idx2 = self.split_data(j, theta, X, idx)
if min(len(idx1), len(idx2)) == 0:
continue
score1, score2 = self.get_score(y, idx1), self.get_score(y, idx2)
w = 1.0 * len(idx1) / len(idx)
score = w * score1 + (1 - w) * score2
if score < best_score:
best_score = score
best_j = j
best_theta = theta
best_idx1 = idx1
best_idx2 = idx2
return best_j, best_theta, best_idx1, best_idx2, best_score
def generate_tree(self, X, y, idx, d):
r = Node()
r.p = np.average(y[idx], axis=0)
if d == 0 or len(idx) < 2:
return r
current_score = self.get_score(y, idx)
j, theta, idx1, idx2, score = self.find_best_split(X, y, idx)
if score >= current_score:
return r
r.j = j
r.theta = theta
r.left = self.generate_tree(X, y, idx1, d - 1)
r.right = self.generate_tree(X, y, idx2, d - 1)
return r
def fit(self, X, y):
self.root = self.generate_tree(X, y, range(len(X)), self.max_depth)
def get_prediction(self, r, x):
if r.left == None and r.right == None:
return r.p
value = x[r.j]
if value <= r.theta:
return self.get_prediction(r.left, x)
else:
return self.get_prediction(r.right, x)
def predict(self, X):
y = list()
for i in range(len(X)):
y.append(self.get_prediction(self.root, X[i]))
return np.array(y)
def get_impurity(y, idx):
p = np.average(y[idx], axis=0)
return 1 - p.dot(p.T)
def get_entropy(y, idx):
_, k = y.shape
p = np.average(y[idx], axis=0)
return - np.log(p + 0.001 * np.random.rand(k)).dot(p.T)
class DecisionTreeClassifier(DecisionTreeBase):
def __init__(self, max_depth=0, feature_sample_rate=1.0):
super().__init__(max_depth=max_depth,
feature_sample_rate=feature_sample_rate,
get_score=get_entropy)
def predict_proba(self, X):
return super().predict(X)
def predict(self, X):
proba = self.predict_proba(X)
return np.argmax(proba, axis=1)
def get_impurity(y, idx):
p = np.average(y[idx], axis=0)
return 1 - p.dot(p.T)
def get_entropy(y, idx):
_, k = y.shape
p = np.average(y[idx], axis=0)
return - np.log(p + 0.001 * np.random.rand(k)).dot(p.T)
class DecisionTreeClassifier(DecisionTreeBase):
def __init__(self, max_depth=0, feature_sample_rate=1.0):
super().__init__(max_depth=max_depth,
feature_sample_rate=feature_sample_rate,
get_score=get_entropy)
def predict_proba(self, X):
return super().predict(X)
def predict(self, X):
proba = self.predict_proba(X)
return np.argmax(proba, axis=1)
class RandomForestClassifier:
def __init__(self, num_trees,max_depth, feature_sample_rate,
data_sample_rate, random_state = 0):
self.max_depth, self.num_trees = max_depth, num_trees
self.feature_sample_rate = feature_sample_rate
self.data_sample_rate = data_sample_rate
self.trees = []
np.random.seed(random_state)
def get_data_samples(self, X, y):
shuffled_indices = np.random.permutation(len(X))
size = int(self.data_sample_rate * len(X))
selected_indices = shuffled_indices[:size]
return X[selected_indices], y[selected_indices]
def fit(self, X, y):
for t in range(self.num_trees):
X_t, y_t = self.get_data_samples(X, y)
model = DecisionTreeClassifier(
max_depth = self.max_depth,
feature_sample_rate = self.feature_sample_rate)
model.fit(X_t, y_t)
self.trees.append(model)
def predict_proba(self, X):
probas = np.array([tree.predict_proba(X) for tree in self.trees])
return np.average(probas, axis=0)
def predict(self, X):
proba = self.predict_proba(X)
return np.argmax(proba, axis=1)
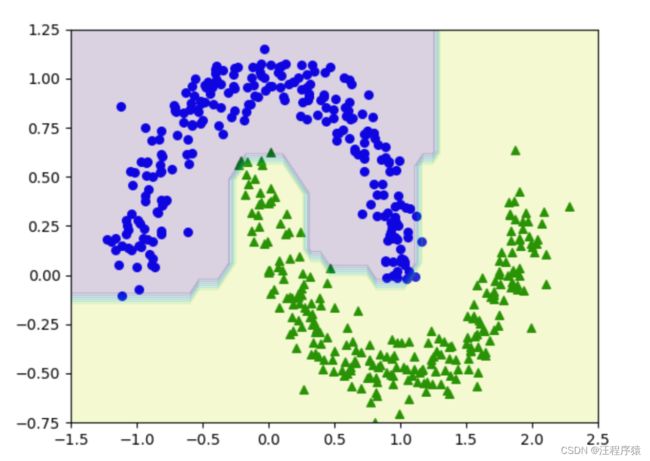
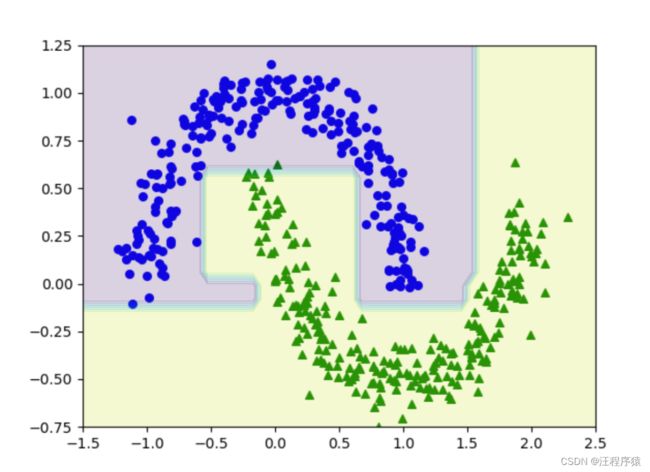
四、实验结果及分析
(2)max_depath=3
(3)max_depath=50
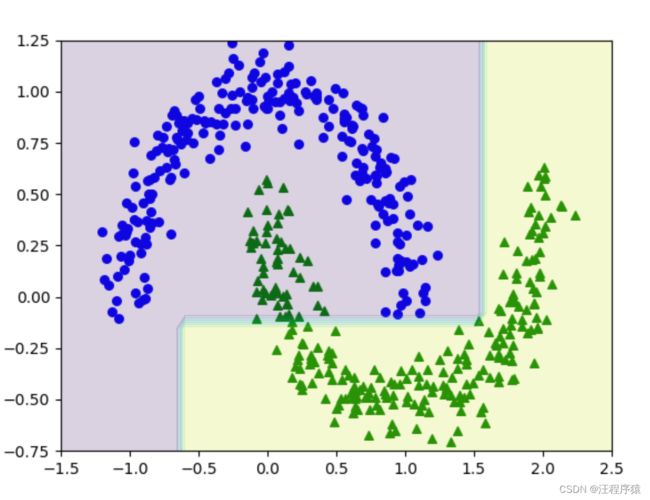
随机森林预测结果
(1)max_depath=5,num_tree =100
(2)max_depath=3,num_tree =100
(3)max_depath=50,num_tree =100