tensorflow2模型裁剪与量化示例讲解/以及模型的加载-1
主要参考文章:tensorflow2官网例程 链接
1、环境介绍
tensorflow : 2.4
tensorflow-model-optimization : 0.7
安装tensorflow2.4:
conda install tensorflow-gpu==2.4
安装模型优化:
python -m pip install --user --upgrade tensorflow-model-optimization
2、示例介绍
在这个示例中,我们将以一个mnist数据集进行分类做一个演示:
- 导入相关包
import tempfile
import os
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow import keras
- 通过不裁剪的方式训练Mnist数据集模型
#加载Mnist数据集
mnist = keras.datasets.mnist
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = mnist.load_data()
# Normalize the input image so that each pixel value is between 0 and 1.
train_images = train_images / 255.0
test_images = test_images / 255.0
#Define the model architecture.
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.InputLayer(input_shape=(28, 28)),
keras.layers.Reshape(target_shape=(28, 28, 1)),
keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=12, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation='relu'),
keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)),
keras.layers.Flatten(),
keras.layers.Dense(10)
])
#Train the digit classification model
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(
train_images,
train_labels,
epochs=4,
validation_split=0.1,
)
- 评估并保存模型(.h5)
#Returns the loss value & metrics values for the model in test mode
_, baseline_model_accuracy = model.evaluate(
test_images, test_labels, verbose=0)
print('Baseline test accuracy:', baseline_model_accuracy)
tf.keras.models.save_model(model, "./logs/1.h5", include_optimizer=False)
- 使用剪枝微调预训练模型
# Define the model
# 您将对整个模型应用修剪,并在模型摘要中看到这一点。
# 在此示例中,您以 50% 的稀疏度(50% 的权重为零)开始模型并以 80% 的稀疏度结束。
# 导入mot工具箱
import tensorflow_model_optimization as tfmot
prune_low_magnitude = tfmot.sparsity.keras.prune_low_magnitude # 定义一个优化函数对象
# 计算结束步长,2个epoch后完成剪枝。
batch_size = 128
epochs = 2
validation_split = 0.1 # 10% of training set will be used for validation set.
num_images = train_images.shape[0] * (1 - validation_split)
end_step = np.ceil(num_images / batch_size).astype(np.int32) * epochs # 这里计算一共需要进行训练多少次
# Define model for pruning. 定义裁剪层的参数
pruning_params = {
'pruning_schedule': tfmot.sparsity.keras.PolynomialDecay(initial_sparsity=0.50,
final_sparsity=0.80,
begin_step=0,
end_step=end_step)
}
- 使用定义的裁剪模型对模型进行包裹
model_for_pruning = prune_low_magnitude(model, **pruning_params)
- 裁剪模型需要重新编译,定以裁剪模型的编译参数
model_for_pruning.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
- 输出模型摘要
model_for_pruning.summary()
- 裁剪模型需要进行重新训练,这里进行训练
# 定义日志目录
logdir = './logs'
# 定义一些回调函数
# tfmot.sparsity.keras.UpdatePruningStep is required during training,
# and tfmot.sparsity.keras.PruningSummaries provides logs for tracking progress and debugging.
callbacks = [
tfmot.sparsity.keras.UpdatePruningStep(),
tfmot.sparsity.keras.PruningSummaries(log_dir=logdir),
]
# 再次进行训练
model_for_pruning.fit(train_images, train_labels,
batch_size=batch_size, epochs=epochs, validation_split=validation_split,
callbacks=callbacks)
- 进行裁剪模型的评估
_, model_for_pruning_accuracy = model_for_pruning.evaluate(
test_images, test_labels, verbose=0)
print('Baseline test accuracy:', baseline_model_accuracy)
print('Pruned test accuracy:', model_for_pruning_accuracy)
- 因为进行了模型的裁剪,因此权重有很多为0,如果直接进行模型保存,那么大小和之前还是一样,因此,对于裁剪模型,我们一般进行压缩导出,下面演示如何进行模型导出
# 首先,为 TensorFlow 创建一个可压缩模型。
# strip_pruning 是必要的,因为它删除了修剪仅在训练期间需要的每个 tf.Variable,否则会在推理期间增加模型大小
# 应用标准压缩算法是必要的,因为序列化的权重矩阵与修剪前的大小相同。然而,剪枝使大部分权重为零,这是算法可以利用的额外冗余来进一步压缩模型
model_for_export = tfmot.sparsity.keras.strip_pruning(model_for_pruning)
pruned_keras_file = 'yasuo.h5'
# 进行不压缩保存,可以看到此时保存的.h5模型大小和原始模型大小相同,这是因为还没有执行压缩算法
tf.keras.models.save_model(model_for_export, pruned_keras_file, include_optimizer=False)
# 创建一个tflite压缩模型
# 首先创建一个模型转换器
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model(model_for_export)
pruned_tflite_model = converter.convert() # 进行压缩转换
# 定义保存模型的名字
pruned_tflite_file = "tflitemodel.tflite"
# 进行模型保存
with open(pruned_tflite_file, 'wb') as f:
f.write(pruned_tflite_model)
- 定义一个帮助函数以通过gzip实际压缩模型并测量压缩后的大小(这个函数不需要了解其中原理,使用的时候只需要将文件路径输入即可打出模型大小)
def get_gzipped_model_size(file):
# Returns size of gzipped model, in bytes.
import os
import zipfile
_, zipped_file = tempfile.mkstemp('.zip')
with zipfile.ZipFile(zipped_file, 'w', compression=zipfile.ZIP_DEFLATED) as f:
f.write(file)
return os.path.getsize(zipped_file)
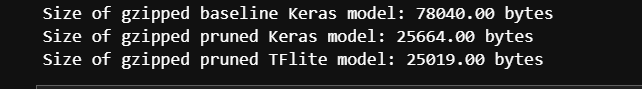
- 查看模型大小
print("Size of gzipped baseline Keras model: %.2f bytes" % (get_gzipped_model_size("./logs/1.h5")))
print("Size of gzipped pruned Keras model: %.2f bytes" % (get_gzipped_model_size(pruned_keras_file)))
print("Size of gzipped pruned TFlite model: %.2f bytes" % (get_gzipped_model_size(pruned_tflite_file)))
- 进行模型量化和裁剪,这样可以使得模型更加的小(这里量化+裁剪其实很简单,上面模型我们定义了一个转换器,但是这个只是进行裁剪转换,并没有应用任何优化,因此,要进行量化,我们只需要在优化器后面再定义一个优化器即可)
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model(model_for_export)
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT] # 使用默认优化器
quantized_and_pruned_tflite_model = converter.convert() # 量化和裁剪tflite模型
# 模型保存文件
quantized_and_pruned_tflite_file = 'quantized_and_pruned.tflite'
# 进行量化后的模型保存
with open(quantized_and_pruned_tflite_file, 'wb') as f:
f.write(quantized_and_pruned_tflite_model)
# 输出模型大小
print("Size of gzipped pruned and quantized TFlite model: %.2f bytes" % (get_gzipped_model_size(quantized_and_pruned_tflite_file)))
可以看到进行量化和裁剪一起作用,使得模型大小减小了近10倍
3、tflite模型的使用
上面的操作我们已经对模型进行了裁剪和量化,使得模型变得很小了,并已经保存为了tflite形式的模型,那么这种tflite形式的模型我们该如何进行使用呢?下面进行介绍
- 导入相关库
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
- 定义解释器进行预测
# 定义解释器
interpreter = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_path="./quantized_and_pruned.tflite")
# 分配内存
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
# 获取输入索引
input_index = interpreter.get_input_details()[0]["index"]
# 获取输出索引
output_index = interpreter.get_output_details()[0]["index"]
# 加载数据集
# Load MNIST dataset
mnist = keras.datasets.mnist
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = mnist.load_data()
# 定义保存数字识别的数组
prediction_digits = []
# 进行输入图片预测
prediction_digits = []
for i, test_image in enumerate(test_images): # 10000,28,28
if i % 1000 == 0:
print('Evaluated on {n} results so far.'.format(n=i))
# Pre-processing: add batch dimension and convert to float32 to match with
# # the model's input data format.
test_image = np.expand_dims(test_image, axis=0).astype(np.float32)
interpreter.set_tensor(input_index, test_image)
# Run inference. 进行推理
interpreter.invoke() # 调用解释器 ,
# Post-processing: remove batch dimension and find the digit with highest
# 获取输出有两种方式
## 第一种方式 使用get_tensor方法,这个输入参数为输出的层的索引,返回直接就是预测结果
output = interpreter.get_tensor(output_index) #
digit = np.argmax(output)
## 第二种方式 ,使用tensor方法,这个返回一个函数对象,需要进行调用才可以得到输出,返回的参数为【batch,预测结果】,因此需要使用下面这个方式才可以获得输出
# output = interpreter.tensor(output_index)
# digit = np.argmax(output()[0])
prediction_digits.append(digit)
- 打印准确率
# # 将预测结果与真实标签进行比较以计算准确度。
prediction_digits = np.array(prediction_digits)
accuracy = (prediction_digits == test_labels).mean()
print("准确率为:",accuracy)
![]()
可以看到,压缩了10倍之后的模型准确率从0.9降到了0.7左右,因此,在进行模型压缩的时候,我们需要进行合理裁剪量化。不能一昧的盲目进行裁剪和压缩。