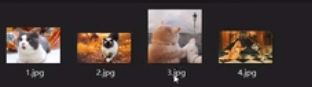
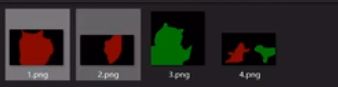
语义分割重制版1——Pytorch 搭建自己的Unet语义分割平台
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44791964/article/details/108866828?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
对应b站视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1rz4y117rR?p=5&spm_id_from=pageDriver
转载+自己的笔记
目录
注意事项
学习前言
代码下载
Unet实现思路
一、预测部分
1、主干网络介绍
2、加强特征提取结构
3、利用特征获得预测结果
4.prediction processs-预测过程详解
二、训练部分
1、训练文件详解
2、LOSS解析
三、训练自己的Unet模型
1.整个Unet的文件构架为:
1)voc数据集
2)自己制作数据集
3)修改参数——训练参数详解
4)开始训练voc
如何制作自己的数据集
predict_利用自己训练好的模型进行预测
如果用自己训练好的模型进行miou测试
注意事项
这是重新构建了的Unet语义分割网络,主要是文件框架上的构建,还有代码的实现,和之前的语义分割网络相比,更加完整也更清晰一些。建议还是学习这个版本的Unet。
学习前言
还是快乐的pytorch人。
什么是Unet模型
Unet是一个优秀的语义分割模型,其主要执行过程与其它语义分割模型类似。
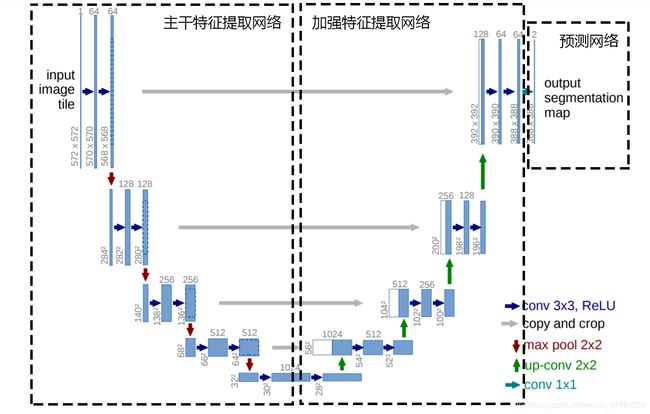
Unet可以分为三个部分,如下图所示:
第一部分是主干特征提取部分,我们可以利用主干部分获得一个又一个的特征层,Unet的主干特征提取部分与VGG相似,为卷积和最大池化的堆叠。利用主干特征提取部分我们可以获得五个初步有效特征层,在第二步中,我们会利用这五个有效特征层可以进行特征融合。
第二部分是加强特征提取部分,我们可以利用主干部分获取到的五个初步有效特征层进行上采样,并且进行特征融合,获得一个最终的,融合了所有特征的有效特征层。
第三部分是预测部分,我们会利用最终获得的最后一个有效特征层对每一个特征点进行分类,相当于对每一个像素点进行分类。(将最后特征层调整通道数,也就是我们要分类个数)
代码下载
Github源码下载地址为:
https://github.com/bubbliiiing/unet-pytorch
Unet实现思路
一、预测部分
1、主干网络介绍
![]()
Unet的主干特征提取部分由卷积+最大池化组成,整体结构与VGG类似。
本文所采用的主干特征提取网络为VGG16,这样也方便使用imagnet上的预训练权重。
VGG是由Simonyan 和Zisserman在文献《Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large Scale Image Recognition》中提出卷积神经网络模型,其名称来源于作者所在的牛津大学视觉几何组(Visual Geometry Group)的缩写。
该模型参加2014年的 ImageNet图像分类与定位挑战赛,取得了优异成绩:在分类任务上排名第二,在定位任务上排名第一。
它的结构如下图所示:
(红色为最大池化、黑色为卷积+激活函数)VGG16只进行四次最大池化
![]()
这是一个VGG16被用到烂的图,但确实很好的反应了VGG16的结构。
当我们使用VGG16作为主干特征提取网络的时候,我们只会用到两种类型的层,分别是卷积层和最大池化层。
当输入的图像大小为512x512x3的时候,具体执行方式如下:
1、conv1:进行两次[3,3]的64通道的卷积,获得一个[512,512,64]的初步有效特征层(对应图上第一条横线),再进行2X2最大池化,获得一个[256,256,64]的特征层(通道数不变)。
2、conv2:进行两次[3,3]的128通道的卷积,获得一个[256,256,128]的初步有效特征层(对应图上第二条横线),再进行2X2最大池化,获得一个[128,128,128]的特征层。
3、conv3:进行三次[3,3]的256通道的卷积,获得一个[128,128,256]的初步有效特征层(对应图上第三条横线),再进行2X2最大池化,获得一个[64,64,256]的特征层。
4、conv4:进行三次[3,3]的512通道的卷积,获得一个[64,64,512]的初步有效特征层(对应图上第四条横线),再进行2X2最大池化,获得一个[32,32,512]的特征层。
5、conv5:进行三次[3,3]的512通道的卷积,获得一个[32,32,512]的初步有效特征层(对应图上第五条横线)。
最后获得的是五个有效特征层,即对应图上的五条横线。
![]()
E:\深度学习\学习材料\unet-pytorch-main\nets\vgg.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision.models.utils import load_state_dict_from_url
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, num_classes=1000):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
self.features = features #仅用feature ,即后面的卷积+池化
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((7, 7))
self.classifier = nn.Sequential( #后面全连接没有使用
nn.Linear(512 * 7 * 7, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),
)
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def make_layers(cfg, batch_norm=False, in_channels = 3):
layers = []
for v in cfg: #对列表进行循环
if v == 'M':
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
else:
conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if batch_norm:
layers += [conv2d, nn.BatchNorm2d(v), nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
else:
layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
in_channels = v
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
#当输入的图像大小为512x512x3的时候,具体执行方式如下:
#1、conv1:64通道的卷积, [512,512,64]特征层,再进行2X2最大池化,得[256,256,64]的特征层。
#2、conv2:128通道的卷积,[256,256,128]特征层,再进行2X2最大池化,得[128,128,128]的特征层。
#3、conv3:256通道的卷积,[128,128,256]特征层,再进行2X2最大池化,得[64,64,256]的特征层。
#4、conv4:512通道的卷积,[64,64,512]特征层,再进行2X2最大池化,得[32,32,512]的特征层。
#5、conv5:512通道的卷积,[32,32,512]特征层。
cfgs = {
'D': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M']
} #判断输入的是数字还是M,如果是M则要进行最大池化;如果是数字的话,就代表通道数是多少
def VGG16(pretrained, in_channels, **kwargs):
model = VGG(make_layers(cfgs["D"], batch_norm = False, in_channels = in_channels), **kwargs)
if pretrained:
state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url("https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg16-397923af.pth", model_dir="./model_data")
model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
del model.avgpool
del model.classifier
return model
2、加强特征提取结构
Unet所使用的加强特征提取网络是一个U的形状。
利用第一步我们可以获得五个初步的有效特征层,在加强特征提取网络这里,我们会利用这五个初步的有效特征层进行特征融合,特征融合的方式就是对特征层进行上采样并且进行堆叠。
为了方便网络的构建与更好的通用性,我们的Unet和上图的Unet结构有些许不同,在上采样时直接进行两倍上采样再进行特征融合,最终获得的特征层和输入图片的高宽相同。
具体示意图如下:即对初步获得有效特征层,进行一次上采样,堆叠,二次卷积
当输入的图像大小为512x512x3的时候,具体执行方式如下:
最后一次卷积池化后获得的有效特征层为[32,32,512],因此,即为上采样的第一个数
1、unetup1:进行上采样后,获得结果为[64,64,512]
2、unetup2:进行上采样后,获得结果为[128,128,256]
3、unetup3:进行上采样后,获得结果为[256,256,128]
4、unetup4:进行上采样后,获得结果为[512,512,64],为最后的特征层,用于预测
![]()
E:\深度学习\学习材料\unet-pytorch-main\nets\unet.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchsummary import summary
from nets.vgg import VGG16
class unetUp(nn.Module): #使用unetup可将5个有效特征层进行上采样,融合
def __init__(self, in_size, out_size):
super(unetUp, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_size, out_size, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_size, out_size, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.up = nn.UpsamplingBilinear2d(scale_factor=2)
def forward(self, inputs1, inputs2): #输入2个,如input1= f4,input2=f5
outputs = torch.cat([inputs1, self.up(inputs2)], 1) #input2上采样,高和宽加长,可以和input1进行堆叠
outputs = self.conv1(outputs) #两次卷积
outputs = self.conv2(outputs)
return outputs
class Unet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=21, in_channels=3, pretrained=False):
super(Unet, self).__init__()
self.vgg = VGG16(pretrained=pretrained,in_channels=in_channels)
in_filters = [192, 384, 768, 1024]
out_filters = [64, 128, 256, 512] #对应每次上采样结果对应的通道数,倒过来看
# upsampling #因为获得的初步特征层最后一个为[32,32,512],即为上采样的第一个
self.up_concat4 = unetUp(in_filters[3], out_filters[3]) #结果为[64,64,512]
self.up_concat3 = unetUp(in_filters[2], out_filters[2]) #结果为[128,128,256]
self.up_concat2 = unetUp(in_filters[1], out_filters[1]) #结果为[256,256,128]
self.up_concat1 = unetUp(in_filters[0], out_filters[0]) #结果为[512,512,64],为最后的特征层,用于预测,最后与输入图片的高宽一致
# final conv (without any concat)
self.final = nn.Conv2d(out_filters[0], num_classes, 1)
def forward(self, inputs):
feat1 = self.vgg.features[ :4 ](inputs)
feat2 = self.vgg.features[4 :9 ](feat1)
feat3 = self.vgg.features[9 :16](feat2)
feat4 = self.vgg.features[16:23](feat3)
feat5 = self.vgg.features[23:-1](feat4)
up4 = self.up_concat4(feat4, feat5)
up3 = self.up_concat3(feat3, up4)
up2 = self.up_concat2(feat2, up3)
up1 = self.up_concat1(feat1, up2)
final = self.final(up1)
return final
def _initialize_weights(self, *stages):
for modules in stages:
for module in modules.modules():
if isinstance(module, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(module.weight)
if module.bias is not None:
module.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm2d):
module.weight.data.fill_(1)
module.bias.data.zero_()
3、利用特征获得预测结果
利用1、2步,我们可以获取输入进来的图片的特征,此时,我们需要利用特征获得预测结果。
利用特征获得预测结果的过程为:
利用一个1x1卷积进行通道调整,将最终特征层的通道数调整成num_classes。(即对每一个像素点进行分类)
![]()
E:\深度学习\学习材料\unet-pytorch-main\nets\unet.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchsummary import summary
from nets.vgg import VGG16
class unetUp(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_size, out_size):
super(unetUp, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_size, out_size, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_size, out_size, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.up = nn.UpsamplingBilinear2d(scale_factor=2)
def forward(self, inputs1, inputs2):
outputs = torch.cat([inputs1, self.up(inputs2)], 1)
outputs = self.conv1(outputs)
outputs = self.conv2(outputs)
return outputs
class Unet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=21, in_channels=3, pretrained=False):
super(Unet, self).__init__()
self.vgg = VGG16(pretrained=pretrained,in_channels=in_channels)
in_filters = [192, 384, 768, 1024]
out_filters = [64, 128, 256, 512]
# upsampling
self.up_concat4 = unetUp(in_filters[3], out_filters[3])
self.up_concat3 = unetUp(in_filters[2], out_filters[2])
self.up_concat2 = unetUp(in_filters[1], out_filters[1])
self.up_concat1 = unetUp(in_filters[0], out_filters[0])
# final conv (without any concat) #最后进行1*1卷积
self.final = nn.Conv2d(out_filters[0], num_classes, 1) #将最终特征层的通道数调整成num_classes。(即对每一个像素点进行分类)
def forward(self, inputs): #forward也是这样子做的
feat1 = self.vgg.features[ :4 ](inputs)
feat2 = self.vgg.features[4 :9 ](feat1)
feat3 = self.vgg.features[9 :16](feat2)
feat4 = self.vgg.features[16:23](feat3)
feat5 = self.vgg.features[23:-1](feat4)
up4 = self.up_concat4(feat4, feat5)
up3 = self.up_concat3(feat3, up4)
up2 = self.up_concat2(feat2, up3)
up1 = self.up_concat1(feat1, up2)
final = self.final(up1)
return final
def _initialize_weights(self, *stages):
for modules in stages:
for module in modules.modules():
if isinstance(module, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(module.weight)
if module.bias is not None:
module.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm2d):
module.weight.data.fill_(1)
module.bias.data.zero_()
4.prediction processs-预测过程详解
先看看预测效果, 运行predict.py文件即可,载入模型,加入图片,选用street.img
unet= Unet(),使用了unet中重要的detect_imge,—— 备份、计算图片高宽、letterbox保证图片不失真、归一化、转到bugsize的后一维度、图片传入网络预测、通道数转为最后一维、 permute将获取的 预测结果转到最后一维、softmax取出每一个像素点的种类、灰条裁剪、分类赋予颜色、分割图与原图混合
具体如下:
E:\深度学习\学习材料\unet-pytorch-main\unet.py
# 预测从这里开始
# 备份、计算图片高宽、保证图片不失真、归一化、转到第一维度为bugsize的第一维度、图片传入网络预测、通道数转为最后一维、
# permute将获取的 预测结果转到最后一维、softmax取出每一个像素点的种类、灰条裁剪、分类赋予颜色、与原图混合
# ---------------------------------------------------#
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 检测图片
#---------------------------------------------------#
def detect_image(self, image): #输入的是一张图片
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image = image.convert('RGB')
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 对输入图像进行一个备份,后面用于绘图
#---------------------------------------------------#
old_img = copy.deepcopy(image) #对图片备份
orininal_h = np.array(image).shape[0] #计算图片的高
orininal_w = np.array(image).shape[1] #计算图片的宽
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 进行不失真的resize,添加灰条,进行图像归一化
#---------------------------------------------------#
image, nw, nh = self.letterbox_image(image,(self.model_image_size[1],self.model_image_size[0])) # 处理的图片为正方形图片,如果输入的是长方形则会压缩变形,用letterbox则会添加灰条,保持不变不变,不失真
images = [np.array(image)/255] #对输入图片归一化,再加上bugsize的维度
images = np.transpose(images,(0,3,1,2)) #将通道转为第一维度,即为bugsize的后一维度
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 图片传入网络进行预测
#---------------------------------------------------#
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(images).type(torch.FloatTensor) #图片传入网络进行预测
if self.cuda:
images =images.cuda()
pr = self.net(images)[0] #通道数转为最后一维
#---------------------------------------------------#
# softmax取出每一个像素点的种类,permute将获取的预测结果转到最后一维
#---------------------------------------------------#
pr = F.softmax(pr.permute(1,2,0),dim = -1).cpu().numpy().argmax(axis=-1)
#--------------------------------------#
# 将灰条部分截取掉
#--------------------------------------#
pr = pr[int((self.model_image_size[0]-nh)//2):int((self.model_image_size[0]-nh)//2+nh), int((self.model_image_size[1]-nw)//2):int((self.model_image_size[1]-nw)//2+nw)]
#------------------------------------------------#
# 创建一副新图,并根据每个像素点的种类赋予颜色
#------------------------------------------------#
seg_img = np.zeros((np.shape(pr)[0],np.shape(pr)[1],3))
for c in range(self.num_classes):
seg_img[:,:,0] += ((pr[:,: ] == c )*( self.colors[c][0] )).astype('uint8')
seg_img[:,:,1] += ((pr[:,: ] == c )*( self.colors[c][1] )).astype('uint8')
seg_img[:,:,2] += ((pr[:,: ] == c )*( self.colors[c][2] )).astype('uint8')
#------------------------------------------------#
# 将新图片转换成Image的形式
#------------------------------------------------#
image = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(seg_img)).resize((orininal_w,orininal_h))
#------------------------------------------------#
# 将新图片和原图片混合
#------------------------------------------------#
if self.blend:
image = Image.blend(old_img,image,0.7)
return image二、训练部分
1、训练文件详解
我们使用的训练文件采用VOC的格式。
语义分割模型训练的文件分为两部分。
第一部分是原图,像这样:
![]()
第二部分标签,像这样:
![]()
原图就是普通的RGB图像,标签就是灰度图或者8位彩色图。
原图的shape为[height, width, 3],标签的shape就是[height, width],对于标签而言,每个像素点的内容是一个数字,比如0、1、2、3、4、5……,代表这个像素点所属的类别。
语义分割的工作就是对原始的图片的每一个像素点进行分类,所以通过预测结果中每个像素点属于每个类别的概率与标签对比,可以对网络进行训练。
2、LOSS解析
本文所使用的LOSS由两部分组成:
1、Cross Entropy Loss。
2、Dice Loss。
Cross Entropy Loss就是普通的交叉熵损失,当语义分割平台利用Softmax对像素点进行分类的时候,进行使用。
Dice loss将语义分割的评价指标作为Loss,Dice系数是一种集合相似度度量函数,通常用于计算两个样本的相似度,取值范围在[0,1]。
计算公式如下:
![]()
就是预测结果和真实结果的交乘上2,除上预测结果加上真实结果。其值在0-1之间。越大表示预测结果和真实结果重合度越大。所以Dice系数是越大越好。
如果作为LOSS的话是越小越好,所以使得Dice loss = 1 - Dice,就可以将Loss作为语义分割的损失了。
实现代码如下:
E:\深度学习\学习材料\unet-pytorch-main\nets\unet_training.py
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
from torch import nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
from random import shuffle
from matplotlib.colors import rgb_to_hsv, hsv_to_rgb
from PIL import Image
import cv2
def CE_Loss(inputs, target, num_classes=21):
n, c, h, w = inputs.size()
nt, ht, wt = target.size()
if h != ht and w != wt:
inputs = F.interpolate(inputs, size=(ht, wt), mode="bilinear", align_corners=True)
temp_inputs = inputs.transpose(1, 2).transpose(2, 3).contiguous().view(-1, c)
temp_target = target.view(-1)
CE_loss = nn.NLLLoss(ignore_index=num_classes)(F.log_softmax(temp_inputs, dim = -1), temp_target)
return CE_loss
def Dice_loss(inputs, target, beta=1, smooth = 1e-5):
n, c, h, w = inputs.size()
nt, ht, wt, ct = target.size()
if h != ht and w != wt:
inputs = F.interpolate(inputs, size=(ht, wt), mode="bilinear", align_corners=True)
temp_inputs = torch.softmax(inputs.transpose(1, 2).transpose(2, 3).contiguous().view(n, -1, c),-1)
temp_target = target.view(n, -1, ct)
#--------------------------------------------#
# 计算dice loss
#--------------------------------------------#
tp = torch.sum(temp_target[...,:-1] * temp_inputs, axis=[0,1])
fp = torch.sum(temp_inputs , axis=[0,1]) - tp
fn = torch.sum(temp_target[...,:-1] , axis=[0,1]) - tp
score = ((1 + beta ** 2) * tp + smooth) / ((1 + beta ** 2) * tp + beta ** 2 * fn + fp + smooth)
dice_loss = 1 - torch.mean(score)
return dice_loss
三、训练自己的Unet模型
1.整个Unet的文件构架为:
![]()
在训练模型之前,我们需要首先准备好数据集。
1)voc数据集
大家可以下载我上传的voc数据集,也可以根据voc数据集格式进行数据集制作。imageset\Segmentiation存放train.txt(用于训练的文件名称)、 val.txt(用于验证的文件名称)、JPEGImage存放原图片、SegmentiationClass存放标签文件
voc数据集详细介绍见:https://haoji007.blog.csdn.net/article/details/80361587
![]()
如果大家下载的是我上传的voc数据集,那么就不需要运行VOCdevkit文件夹下面的voc2unet.py。
2)自己制作数据集
如果是自己制作的数据集,那么需要运行VOCdevkit文件夹下面的voc2unet.py,从而生成train.txt和val.txt。
![]()
注意参数的修改
trainval_percent=1
# 9:1 训练集为9,验证集为1
train_percent=0.9
3)修改参数——训练参数详解
生成后,修改参数。修改train.py文件下的num_classes,使其为分的类的个数+1。
E:\深度学习\学习材料\unet-pytorch-main\train.py
###模型训练参数的修改
if __name__ == "__main__":
log_dir = "logs/"
#------------------------------#
# 输入图片的大小
#------------------------------#
inputs_size = [512,512,3] #修改高宽,一定是32的倍数,网络才能正常训练
#---------------------#
# 分类个数+1
# 区分猫和狗,则为2+1,1是背景
#---------------------#
NUM_CLASSES = 21
#--------------------------------------------------------------------#
# dice_loss建议选项:
# 种类少(几类)时,设置为True
# 种类多(十几类)时,如果batch_size比较大(10以上),那么设置为True
# 种类多(十几类)时,如果batch_size比较小(10以下),那么设置为False
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
dice_loss = False
#-------------------------------#
# 主干网络预训练权重的使用
#-------------------------------#
pretrained = False #如要重头到尾使用,为true,则下面的weight不执行
#-------------------------------#
# Cuda的使用
#-------------------------------#
Cuda = True
#------------------------------#
# 数据集路径
#------------------------------#
dataset_path = "VOCdevkit/VOC2007/"
model = Unet(num_classes=NUM_CLASSES, in_channels=inputs_size[-1], pretrained=pretrained).train()
loss_history = LossHistory("logs/")
#-------------------------------------------#
# 权值文件的下载请看README
# 权值和主干特征提取网络一定要对应
#-------------------------------------------#
#如果pretrained = True,这一段不运行
model_path = r"model_data/unet_voc.pth" #unet预训练权重,默认用voc数据集训练好的权重
print('Loading weights into state dict...')
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model_dict = model.state_dict()
pretrained_dict = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
pretrained_dict = {k: v for k, v in pretrained_dict.items() if np.shape(model_dict[k]) == np.shape(v)}
model_dict.update(pretrained_dict)
model.load_state_dict(model_dict)
print('Finished!')
# -------------------------------------------#
if Cuda:
net = torch.nn.DataParallel(model)
cudnn.benchmark = True
net = net.cuda()
# 打开数据集的txt
with open(os.path.join(dataset_path, "ImageSets/Segmentation/train.txt"),"r") as f:
train_lines = f.readlines()
# 打开数据集的txt
with open(os.path.join(dataset_path, "ImageSets/Segmentation/val.txt"),"r") as f:
val_lines = f.readlines()
#------------------------------------------------------#
# 主干特征提取网络特征通用,冻结训练可以加快训练速度
# 也可以在训练初期防止权值被破坏。
# Init_Epoch为起始世代
# Interval_Epoch为冻结训练世代:训练50次
# Epoch总训练世代
# 提示OOM或者显存不足请调小Batch_size :每次训练输入多少数据,显存大可以设为8,小设为2
#------------------------------------------------------#
if True:
lr = 1e-4
Init_Epoch = 0
Interval_Epoch = 50
Batch_size = 2
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr)
lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer,step_size=1,gamma=0.92)
train_dataset = DeeplabDataset(train_lines, inputs_size, NUM_CLASSES, True, dataset_path)
val_dataset = DeeplabDataset(val_lines, inputs_size, NUM_CLASSES, False, dataset_path)
gen = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=Batch_size, num_workers=4, pin_memory=True,
drop_last=True, collate_fn=deeplab_dataset_collate)
gen_val = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=Batch_size, num_workers=4,pin_memory=True,
drop_last=True, collate_fn=deeplab_dataset_collate)
epoch_size = len(train_lines) // Batch_size
epoch_size_val = len(val_lines) // Batch_size
if epoch_size == 0 or epoch_size_val == 0:
raise ValueError("数据集过小,无法进行训练,请扩充数据集。")
for param in model.vgg.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
for epoch in range(Init_Epoch,Interval_Epoch):
fit_one_epoch(model,epoch,epoch_size,epoch_size_val,gen,gen_val,Interval_Epoch,Cuda)
lr_scheduler.step()
if True:
lr = 1e-5
Interval_Epoch = 50 #建议和前面的数值一样,否则在终端代数的显示不太正常
Epoch = 100 #模型结冻后训练的次数,
Batch_size = 2
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr)
lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer,step_size=1,gamma=0.92)
train_dataset = DeeplabDataset(train_lines, inputs_size, NUM_CLASSES, True, dataset_path)
val_dataset = DeeplabDataset(val_lines, inputs_size, NUM_CLASSES, False, dataset_path)
gen = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=Batch_size, num_workers=4, pin_memory=True,
drop_last=True, collate_fn=deeplab_dataset_collate)
gen_val = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=Batch_size, num_workers=4,pin_memory=True,
drop_last=True, collate_fn=deeplab_dataset_collate)
epoch_size = len(train_lines) // Batch_size
epoch_size_val = len(val_lines) // Batch_size
if epoch_size == 0 or epoch_size_val == 0:
raise ValueError("数据集过小,无法进行训练,请扩充数据集。")
for param in model.vgg.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
for epoch in range(Interval_Epoch,Epoch):
fit_one_epoch(model,epoch,epoch_size,epoch_size_val,gen,gen_val,Epoch,Cuda)
lr_scheduler.step()4)开始训练voc
之后就可以开始训练了。如果想从头开始训练,则把
pretrained = True #则下面的weight不执行E:\深度学习\学习材料\unet-pytorch-main\train.py
![]()
如何制作自己的数据集
1.把数据集存放在根目录,E:\深度学习\学习材料\unet-pytorch-main\datasets\before
2.安装软件:(cmd)激活环境TensorFlow,安装软件labelme
active TensorFlow
!pip install labelme == 3.16.7 #bug会少一点
labelme #即可打开
3.copa dir 选择文件夹目录,即可导入
4.file——save automilicaly 保存更方便
5.create polygine 开始标注,输入种类名称
#点击图片的A D 可以实现图片切换 Ctrl+z可以撤回一个点
6.结果,before目录下会生成json文件
7.回到pycharm界面,运行json_to_dataset.py
8.修改参数 classes = ["_background_","aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat"],即需要分的类
9.然后即可运行,转换图片完成
结果如下:
训练图片:与原图一致 标签文件:
然后复制到 unet-pytorch-main\VOCdevkit\VOC2007对应文件夹,即可训练
predict_利用自己训练好的模型进行预测
unet.py
# 使用自己训练好的模型预测需要修改2个参数
# model_path和num_classes都需要修改
然后运行predict.py,输入图片,img/street.jpg
import colorsys
import copy
import time
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from PIL import Image
from torch import nn
from nets.unet import Unet as unet
#--------------------------------------------#
# 使用自己训练好的模型预测需要修改2个参数
# model_path和num_classes都需要修改!
# 如果出现shape不匹配
# 一定要注意训练时的model_path和num_classes数的修改
#--------------------------------------------#
class Unet(object):
_defaults = {
"model_path" : 'model_data/unet_voc.pth', #指向训练好的权重,一般保存在logs文件夹
"model_image_size" : (512, 512, 3),
"num_classes" : 21, #需要区分个数的+1
"cuda" : True,
#--------------------------------#
# blend参数用于控制是否
# 让识别结果和原图混合
#--------------------------------#
"blend" : True
}
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 初始化UNET
#---------------------------------------------------#
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults)
self.generate()
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得所有的分类
#---------------------------------------------------#
def generate(self):
self.net = unet(num_classes=self.num_classes, in_channels=self.model_image_size[-1]).eval()
state_dict = torch.load(self.model_path)
self.net.load_state_dict(state_dict)
if self.cuda:
self.net = nn.DataParallel(self.net)
self.net = self.net.cuda()
print('{} model loaded.'.format(self.model_path))
if self.num_classes <= 21:
self.colors = [(0, 0, 0), (128, 0, 0), (0, 128, 0), (128, 128, 0), (0, 0, 128), (128, 0, 128), (0, 128, 128),
(128, 128, 128), (64, 0, 0), (192, 0, 0), (64, 128, 0), (192, 128, 0), (64, 0, 128), (192, 0, 128),
(64, 128, 128), (192, 128, 128), (0, 64, 0), (128, 64, 0), (0, 192, 0), (128, 192, 0), (0, 64, 128), (128, 64, 12)]
else:
# 画框设置不同的颜色
hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(
map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
self.colors))
def letterbox_image(self ,image, size):
image = image.convert("RGB")
iw, ih = image.size
w, h = size
scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
nw = int(iw*scale)
nh = int(ih*scale)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
new_image = Image.new('RGB', size, (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, ((w-nw)//2, (h-nh)//2))
return new_image,nw,nh
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 预测从这里开始
# 备份、计算图片高宽、保证图片不失真、归一化、转到第一维度为bugsize的第一维度、图片传入网络预测、通道数转为最后一维、
# permute将获取的 预测结果转到最后一维、softmax取出每一个像素点的种类、灰条裁剪、分类赋予颜色、与原图混合
# ---------------------------------------------------#
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 检测图片
#---------------------------------------------------#
def detect_image(self, image):
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image = image.convert('RGB')
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 对输入图像进行一个备份,后面用于绘图
#---------------------------------------------------#
old_img = copy.deepcopy(image) #对图片备份
orininal_h = np.array(image).shape[0] #计算图片的高
orininal_w = np.array(image).shape[1] #计算图片的宽
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 进行不失真的resize,添加灰条,进行图像归一化
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 处理的图片为正方形图片,如果输入的是长方形则会压缩变形,用letterbox则会添加灰条,保持不变不变,不失真
image, nw, nh = self.letterbox_image(image,(self.model_image_size[1],self.model_image_size[0]))
images = [np.array(image)/255] #对输入图片归一化,再加上bugsize的维度
images = np.transpose(images,(0,3,1,2)) #将通道转为第一维度,即为bugsize的第一维度
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 图片传入网络进行预测
#---------------------------------------------------#
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(images).type(torch.FloatTensor) #图片传入网络进行预测
if self.cuda:
images =images.cuda()
pr = self.net(images)[0] #通道数转为最后一维
#---------------------------------------------------#
# softmax取出每一个像素点的种类
#---------------------------------------------------#
pr = F.softmax(pr.permute(1,2,0),dim = -1).cpu().numpy().argmax(axis=-1) #permute将获取的 预测结果转到最后一维
#--------------------------------------#
# 将灰条部分截取掉
#--------------------------------------#
pr = pr[int((self.model_image_size[0]-nh)//2):int((self.model_image_size[0]-nh)//2+nh), int((self.model_image_size[1]-nw)//2):int((self.model_image_size[1]-nw)//2+nw)]
#------------------------------------------------#
# 创建一副新图,并根据每个像素点的种类赋予颜色
#------------------------------------------------#
seg_img = np.zeros((np.shape(pr)[0],np.shape(pr)[1],3))
for c in range(self.num_classes):
seg_img[:,:,0] += ((pr[:,: ] == c )*( self.colors[c][0] )).astype('uint8')
seg_img[:,:,1] += ((pr[:,: ] == c )*( self.colors[c][1] )).astype('uint8')
seg_img[:,:,2] += ((pr[:,: ] == c )*( self.colors[c][2] )).astype('uint8')
#------------------------------------------------#
# 将新图片转换成Image的形式
#------------------------------------------------#
image = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(seg_img)).resize((orininal_w,orininal_h))
#------------------------------------------------#
# 将新图片和原图片混合
#------------------------------------------------#
if self.blend:
image = Image.blend(old_img,image,0.7)
return image
def get_FPS(self, image, test_interval):
orininal_h = np.array(image).shape[0]
orininal_w = np.array(image).shape[1]
image, nw, nh = self.letterbox_image(image,(self.model_image_size[1],self.model_image_size[0]))
images = [np.array(image)/255]
images = np.transpose(images,(0,3,1,2))
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(images).type(torch.FloatTensor)
if self.cuda:
images =images.cuda()
pr = self.net(images)[0]
pr = F.softmax(pr.permute(1,2,0),dim = -1).cpu().numpy().argmax(axis=-1)
pr = pr[int((self.model_image_size[0]-nh)//2):int((self.model_image_size[0]-nh)//2+nh), int((self.model_image_size[1]-nw)//2):int((self.model_image_size[1]-nw)//2+nw)]
t1 = time.time()
for _ in range(test_interval):
with torch.no_grad():
pr = self.net(images)[0]
pr = F.softmax(pr.permute(1,2,0),dim = -1).cpu().numpy().argmax(axis=-1)
pr = pr[int((self.model_image_size[0]-nh)//2):int((self.model_image_size[0]-nh)//2+nh), int((self.model_image_size[1]-nw)//2):int((self.model_image_size[1]-nw)//2+nw)]
t2 = time.time()
tact_time = (t2 - t1) / test_interval
return tact_time
如果用自己训练好的模型进行miou测试
1.修改pspent.py文件,修改参数 model_path, num_classes
2.运行get.miou_prediction.py 计算的是验证集的miou,,运行中将一张张图片送到网络中,计算预测结果
3.如果要计算训练的miou,后面的路径文件修改为test.txt
import os
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
from unet import Unet
class miou_Unet(Unet):
def detect_image(self, image):
orininal_h = np.array(image).shape[0]
orininal_w = np.array(image).shape[1]
image, nw, nh = self.letterbox_image(image,(self.model_image_size[1],self.model_image_size[0]))
images = [np.array(image)/255]
images = np.transpose(images,(0,3,1,2))
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(images).type(torch.FloatTensor)
if self.cuda:
images =images.cuda()
pr = self.net(images)[0]
pr = F.softmax(pr.permute(1,2,0),dim = -1).cpu().numpy().argmax(axis=-1)
pr = pr[int((self.model_image_size[0]-nh)//2):int((self.model_image_size[0]-nh)//2+nh), int((self.model_image_size[1]-nw)//2):int((self.model_image_size[1]-nw)//2+nw)]
image = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(pr)).resize((orininal_w,orininal_h),Image.NEAREST)
return image
unet = miou_Unet()
image_ids = open("VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets/Segmentation/val.txt",'r').read().splitlines() #如要计算训练集的miou,则换为test.txt
if not os.path.exists("./miou_pr_dir"):
os.makedirs("./miou_pr_dir")
for image_id in tqdm(image_ids):
image_path = "VOCdevkit/VOC2007/JPEGImages/"+image_id+".jpg"
image = Image.open(image_path)
image = unet.detect_image(image)
image.save("miou_pr_dir/" + image_id + ".png")
4. 运行结束后,打开miou.py,设置参数num_classes、name_classes、、、以及前面提及的test.txt。
5.运算得到miou值,得出的权重为71.04,结果还阔以
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「Bubbliiiing」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44791964/article/details/108866828