UI thread client callback和UI thread WCF Service一起工作时死锁的形成原因及解决方法
前言:
当WCF service和WCF client都是基于UI时,当服务器端callback客户端时,此时若想对于Service端或者Client端的UI进行update,例如某个控件的状态的改变,需要进行严格的同步管理,否则Service|Client UI thread就会陷入deadlock。
deaklock形成原因:
假设有以下一个scenario:
1个windows forms client已经建立了UI的同步上下文信息(UI SynchronizationContext)和回调对象(callback object)之间的姻联。然后该基于UI的客户端调用一个WCF service,连同其callback reference一起传送至service。 假设WCF service的ConcurrencyMode配置为ReEntrant。那么service在收到这个request之后开始callback 客户端。这就形成了一个死锁!因为对客户端的回调请求是执行在客户端的UI thread中的,而此时该UI thread在等待刚刚发出去的service call的结果。
有人可能想:将callback operation的MEP(Message Exchange Pattern)配置为IsOneWay可以吗? 还是不行。因为service对client 的callback request还是首先需要被marshaled到client UI thread.
题外话:如果将service operation和callback operation都设置为IsOneWay可以解决deadlock吗? 您自己去想吧:)
解决方法:
解决方法是将service端对client的callback请求设置成异步地(asynchronously)marshal到client UI thread即可
例如:服务器端operation 请求callback的正确代码如下:
1 public string DoSomething(int value)
2 {
3 MyForm form = System.Windows.Forms.Application.OpenForms[0] as MyForm;
4 SendOrPostCallback del = delegate
5 {
6 form.ServiceLable = callback.OnCallBack();
7 };
8
9 System.Diagnostics.Debug.Assert(form.MySynchronizationContext != null);
10 form.MySynchronizationContext.Post(del, null);
//form.MySynchronizationContext.Send(del,null)就会死锁!!
11
12 return "The string is returned from WCF service";
13 }
source code:
1. service contract and callback contract
client UI source code:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.Threading;
namespace UICallBack_DeadLock_Client
{
public partial class CallBackForm : Form,IMyContractCallback
{
private MyContractClient proxy;
private SynchronizationContext m_ClientCallBackSynchronizationContext;
private string returnValue = String.Empty;
public CallBackForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
m_ClientCallBackSynchronizationContext = SynchronizationContext.Current;
}
public string OnCallBack()
{
SendOrPostCallback setText = delegate
{
m_ClientLabel.Text = returnValue;
};
DialogResult result = MessageBox.Show( " please select one answer " , " callback test " , MessageBoxButtons.YesNo, MessageBoxIcon.Question);
m_ClientCallBackSynchronizationContext.Post(setText, null );
return result == DialogResult.Yes ? " client answer via Callback is YES " : " client answer via Callback is NO " ;
}
private void CallBackForm_Load( object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void button1_Click( object sender, EventArgs e)
{
InstanceContext instanceContext = new InstanceContext( this );
proxy = new MyContractClient(instanceContext);
proxy.Connect();
returnValue = proxy.DoSomething( 2 );
}
}
}
运行screenshot
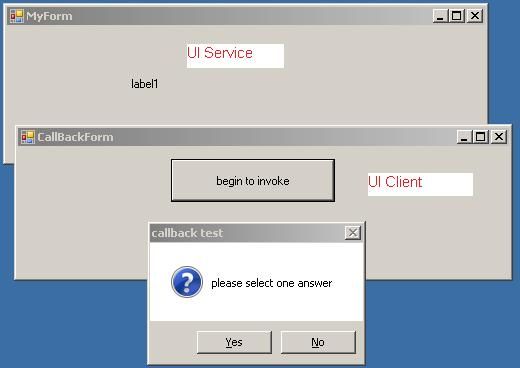 :
:
For all source code regarding to this article, please press here to download