nnUnet肾脏肿瘤分割实战(KiTS19)
nnUnet肾脏肿瘤分割实战
KiTS19 Challenge Homepage
nnunet项目官方地址
MIC-DKFZ/nnUNet
使用nnunet之前,建议先阅读两篇论文
nnU-Net: Self-adapting Framework for U-Net-Based Medical Image Segmentation
nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation
1.数据获取
KiTS19是肾脏肿瘤分割挑战赛,包括300例病人。
其中有标签的210例作为训练样本(训练集),无标签的90例作为客观模型评估(测试集)。
原始数据集下载方法:
- github官网下载 – kits19: The official repository of the 2019 Kidney and Kidney Tumor Segmentation Challenge
- 百度飞桨的公共数据集 – Kits19肾脏肿瘤分割 - 飞桨AI Studio
找数据集的时候我校验过,百度飞桨和github上的数据集是一样的。
github官网下载比较慢,可使用wget命令直接从百度飞桨的数据集地址下载,网速非常快。
原始数据如下图所示,使用nnunet要求结构化的数据集,使用前进行一个简单处理
root@worker04:~/data# tree data/KiTS19/origin
data/KiTS19/origin
|-- case_00000
| |-- imaging.nii.gz
| `-- segmentation.nii.gz
|-- case_00001
| |-- imaging.nii.gz
| `-- segmentation.nii.gz
|-- case_00002
| |-- imaging.nii.gz
| `-- segmentation.nii.gz
|-- case_00003
| |-- imaging.nii.gz
| `-- segmentation.nii.gz
......
下面是我根据nnunet中的dataset_conversion/Task040_KiTS.py修改的代码
import os
import json
import shutil
def save_json(obj, file, indent=4, sort_keys=True):
with open(file, 'w') as f:
json.dump(obj, f, sort_keys=sort_keys, indent=indent)
def maybe_mkdir_p(directory):
directory = os.path.abspath(directory)
splits = directory.split("/")[1:]
for i in range(0, len(splits)):
if not os.path.isdir(os.path.join("/", *splits[:i+1])):
try:
os.mkdir(os.path.join("/", *splits[:i+1]))
except FileExistsError:
# this can sometimes happen when two jobs try to create the same directory at the same time,
# especially on network drives.
print("WARNING: Folder %s already existed and does not need to be created" % directory)
def subdirs(folder, join=True, prefix=None, suffix=None, sort=True):
if join:
l = os.path.join
else:
l = lambda x, y: y
res = [l(folder, i) for i in os.listdir(folder) if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(folder, i))
and (prefix is None or i.startswith(prefix))
and (suffix is None or i.endswith(suffix))]
if sort:
res.sort()
return res
base = "/root/data/data/KiTS19/origin"
out = "/root/data/nnUNet_raw_data_base/nnUNet_raw_data/Task040_KiTS"
cases = subdirs(base, join=False)
maybe_mkdir_p(out)
maybe_mkdir_p(os.path.join(out, "imagesTr"))
maybe_mkdir_p(os.path.join(out, "imagesTs"))
maybe_mkdir_p(os.path.join(out, "labelsTr"))
for c in cases:
case_id = int(c.split("_")[-1])
if case_id < 210:
shutil.copy(os.path.join(base, c, "imaging.nii.gz"), os.path.join(out, "imagesTr", c + "_0000.nii.gz"))
shutil.copy(os.path.join(base, c, "segmentation.nii.gz"), os.path.join(out, "labelsTr", c + ".nii.gz"))
else:
shutil.copy(os.path.join(base, c, "imaging.nii.gz"), os.path.join(out, "imagesTs", c + "_0000.nii.gz"))
print(case_id,' done!')
json_dict = {}
json_dict['name'] = "KiTS"
json_dict['description'] = "kidney and kidney tumor segmentation"
json_dict['tensorImageSize'] = "4D"
json_dict['reference'] = "KiTS data for nnunet"
json_dict['licence'] = ""
json_dict['release'] = "0.0"
json_dict['modality'] = {
"0": "CT",
}
json_dict['labels'] = {
"0": "background",
"1": "Kidney",
"2": "Tumor"
}
json_dict['numTraining'] = 210
json_dict['numTest'] = 90
json_dict['training'] = [{'image': "./imagesTr/%s.nii.gz" % i, "label": "./labelsTr/%s.nii.gz" % i} for i in
cases[:210]]
json_dict['test'] = ["./imagesTs/%s.nii.gz" % i for i in
cases[210:]]
save_json(json_dict, os.path.join(out, "dataset.json"))
这里只是对数据集进行一个拷贝和重命名,不对原始数据进行修改。
运行代码后,整理好的数据集结构如下:
nnUNet_raw_data_base/nnUNet_raw_data/Task040_KiTS
├── dataset.json
├── imagesTr
│ ├── case_00000_0000.nii.gz
│ ├── case_00001_0000.nii.gz
│ ├── ...
├── imagesTs
│ ├── case_00210_0000.nii.gz
│ ├── case_00211_0000.nii.gz
│ ├── ...
├── labelsTr
│ ├── case_00000.nii.gz
│ ├── case_00001.nii.gz
│ ├── ...
dataset.json文件保存了训练集图像、训练集标签、测试集图像等信息。
预处理阶段会根据dataset.json读取图像,如果想要剔除某个病例,直接在dataset.json修改就好。
{
"description": "kidney and kidney tumor segmentation",
"labels": {
"0": "background",
"1": "Kidney",
"2": "Tumor"
},
"licence": "",
"modality": {
"0": "CT"
},
"name": "KiTS",
"numTest": 90,
"numTraining": 210,
"reference": "KiTS data for nnunet",
"release": "0.0",
"tensorImageSize": "4D",
"test": [
"./imagesTs/case_00210.nii.gz",
"./imagesTs/case_00211.nii.gz",
.....
],
"training": [
{
"image": "./imagesTr/case_00000.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/case_00000.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/case_00001.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/case_00001.nii.gz"
},
......
]
}
提前准备三个文件夹,分别存放数据集、预处理数据和训练结果,配置好环境变量,具体细节可以参考我的第一篇博文。
2.数据预处理
nnUnet可以读取CT图像的模态信息、体素间距、灰度分布,自动进行重采样、裁剪以及归一化。
重采样
不同时期,不同仪器的CT扫描仪,采样得到的CT图像具有不同的空间分辨率,重采样的目的是将所有的病例采样到相同的空间分辨率(体素间距)。
nnUnet的数据预处理preprocess自带重采样,但我试过两次之后效果并不好,重采样之后的图像尺寸太大了,于是我按照冠军论文里的方法自己写了个重采样,将所有病例的体素间距重采样为 3.22 x 1.62 x 1.62.
另外,论文中有提到case15和case37标签的错误,本来打算去掉,不过后来我去KiTS19的github官网看了一下,官方已经作了修正。
import numpy as np
import SimpleITK as sitk
def transform(image,newSpacing, resamplemethod=sitk.sitkNearestNeighbor):
# 设置一个Filter
resample = sitk.ResampleImageFilter()
# 初始的体素块尺寸
originSize = image.GetSize()
# 初始的体素间距
originSpacing = image.GetSpacing()
newSize = [
int(np.round(originSize[0] * originSpacing[0] / newSpacing[0])),
int(np.round(originSize[1] * originSpacing[1] / newSpacing[1])),
int(np.round(originSize[2] * originSpacing[2] / newSpacing[2]))
]
print('current size:',newSize)
# 沿着x,y,z,的spacing(3)
# The sampling grid of the output space is specified with the spacing along each dimension and the origin.
resample.SetOutputSpacing(newSpacing)
# 设置original
resample.SetOutputOrigin(image.GetOrigin())
# 设置方向
resample.SetOutputDirection(image.GetDirection())
resample.SetSize(newSize)
# 设置插值方式
resample.SetInterpolator(resamplemethod)
# 设置transform
resample.SetTransform(sitk.Euler3DTransform())
# 默认像素值 resample.SetDefaultPixelValue(image.GetPixelIDValue())
return resample.Execute(image)
注意重采样的插值方法,我试过SimpleITK自带的多种插值方法,线性插值,三次插值以及B样条,比较发现B样条的效果是最好的。
因此,image采用sitk.sitkBSpline插值,segment采用sitk.sitkNearestNeighbor插值。
如果感兴趣可以自己尝试一下不同的插值方法,或者使用scipy等其他工具包进行重采样。
data_path = "/root/data/nnUNet_raw_data_base/nnUNet_raw_data/Task040_KiTS/imagesTr"
for path in sorted(os.listdir(data_path)):
print(path)
img_path = os.path.join(data_path,path)
img_itk = sitk.ReadImage(img_path)
print('origin size:', img_itk.GetSize())
new_itk = transform(img_itk, [3.22, 1.62, 1.62], sitk.sitkBSpline) # sitk.sitkLinear
sitk.WriteImage(new_itk, img_path)
print('images is resampled!')
print('-'*20)
label_path = "/root/data/nnUNet_raw_data_base/nnUNet_raw_data/Task040_KiTS/labelsTr"
for path in sorted(os.listdir(label_path)):
print(path)
img_path = os.path.join(label_path,path)
img_itk = sitk.ReadImage(img_path)
print('origin size:', img_itk.GetSize())
new_itk = transform(img_itk, [3.22, 1.62, 1.62])
sitk.WriteImage(new_itk, img_path)
print('labels is resampled!')
下面开始介绍nnUnet的数据预处理方法:
输入指令:
python nnunet/experiment_planning/nnUNet_plan_and_preprocess.py -t 40 --verify_dataset_integrity
verify_dataset_integrity这里不再赘述,主要是根据验证数据集结构,第一次运行的时候最好还是加上。
裁剪
裁剪的目的是裁去黑边,减少像素值为0的边缘区域,裁剪的时候保持空间分辨率等信息不变。
def crop(task_string, override=False, num_threads=default_num_threads):
# 输出目录:'/root/data/nnUNet_raw_data_base/nnUNet_cropped_data/Task040_KiTS'
cropped_out_dir = join(nnUNet_cropped_data, task_string)
maybe_mkdir_p(cropped_out_dir)
if override and isdir(cropped_out_dir):
shutil.rmtree(cropped_out_dir)
maybe_mkdir_p(cropped_out_dir)
splitted_4d_output_dir_task = join(nnUNet_raw_data, task_string)
lists, _ = create_lists_from_splitted_dataset(splitted_4d_output_dir_task) # 创建裁剪列表
imgcrop = ImageCropper(num_threads, cropped_out_dir)
imgcrop.run_cropping(lists, overwrite_existing=override)
shutil.copy(join(nnUNet_raw_data, task_string, "dataset.json"), cropped_out_dir)
create_lists_from_splitted_dataset加载所有的训练集的图像地址,lists一共有210个元素,每个元素包含图像和标签。
def create_lists_from_splitted_dataset(base_folder_splitted):
lists = []
json_file = join(base_folder_splitted, "dataset.json")
with open(json_file) as jsn:
d = json.load(jsn)
training_files = d['training']
num_modalities = len(d['modality'].keys())
for tr in training_files:
cur_pat = []
for mod in range(num_modalities):
cur_pat.append(join(base_folder_splitted, "imagesTr", tr['image'].split("/")[-1][:-7] +
"_%04.0d.nii.gz" % mod))
cur_pat.append(join(base_folder_splitted, "labelsTr", tr['label'].split("/")[-1]))
lists.append(cur_pat)
return lists, {int(i): d['modality'][str(i)] for i in d['modality'].keys()}
重点是这两个函数:
imgcrop = ImageCropper(num_threads, cropped_out_dir)
imgcrop.run_cropping(lists, overwrite_existing=override)
ImageCropper是一个类,包含10个方法。
重点是crop和run_cropping两个方法:
- crop:裁剪到非零区域,返回data, seg, properties
- run_cropping:执行裁剪操作,并且将结果保存为.npz文件(包含data和seg),将size, spacing, origin, classes, size_after_cropping 等属性保存在.pkl文件。
但是执行代码时,发现裁剪前后尺寸没有变化,可能是因为图像没有什么黑边
# 裁剪的时候seg!=None
def crop(data, properties, seg=None):
shape_before = data.shape # 原始尺寸
data, seg, bbox = crop_to_nonzero(data, seg, nonzero_label=-1) # 裁剪结果
shape_after = data.shape # 裁剪尺寸
print("before crop:", shape_before, "after crop:", shape_after, "spacing:",
np.array(properties["original_spacing"]), "\n")
properties["crop_bbox"] = bbox
properties['classes'] = np.unique(seg)
seg[seg < -1] = 0
properties["size_after_cropping"] = data[0].shape
return data, seg, properties
数据分析
收集上一步裁剪得到的图像信息(尺寸、体素间距、灰度分布),为当前任务制定合适的训练计划(plan)
# '/root/data/nnUNet_raw_data_base/nnUNet_cropped_data/Task040_KiTS'
cropped_out_dir = os.path.join(nnUNet_cropped_data, t)
# '/root/data/nnUNet_preprocessed/Task040_KiTS'
preprocessing_output_dir_this_task = os.path.join(preprocessing_output_dir, t)
# we need to figure out if we need the intensity propoerties. We collect them only if one of the modalities is CT
dataset_json = load_json(join(cropped_out_dir, 'dataset.json'))
modalities = list(dataset_json["modality"].values())
collect_intensityproperties = True if (("CT" in modalities) or ("ct" in modalities)) else False
dataset_analyzer = DatasetAnalyzer(cropped_out_dir, overwrite=False, num_processes=tf) # this class creates the fingerprint
_ = dataset_analyzer.analyze_dataset(collect_intensityproperties) # this will write output files that will be used by the ExperimentPlanner
maybe_mkdir_p(preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)
shutil.copy(join(cropped_out_dir, "dataset_properties.pkl"), preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)
shutil.copy(join(nnUNet_raw_data, t, "dataset.json"), preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)
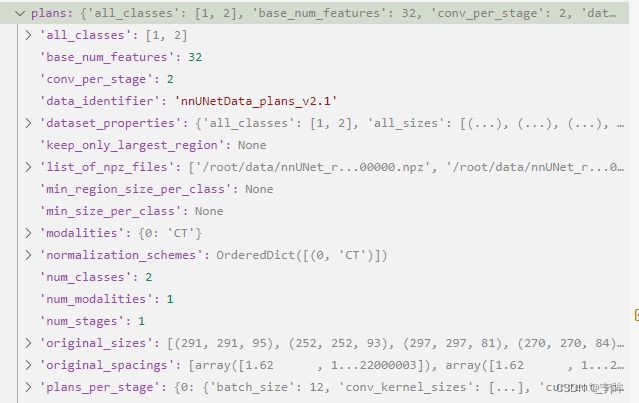
分析得到的dataset_properties.pkl结果如下:
创建数据指纹
根据上一步得到的数据集信息,针对不同的训练任务,制定合适的训练计划(plan)
if planner_3d is not None:
if args.overwrite_plans is not None:
assert args.overwrite_plans_identifier is not None, "You need to specify -overwrite_plans_identifier"
exp_planner = planner_3d(cropped_out_dir, preprocessing_output_dir_this_task, args.overwrite_plans,
args.overwrite_plans_identifier)
else:
exp_planner = planner_3d(cropped_out_dir, preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)
exp_planner.plan_experiment()
if not dont_run_preprocessing: # double negative, yooo
exp_planner.run_preprocessing(threads)
if planner_2d is not None:
exp_planner = planner_2d(cropped_out_dir, preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)
exp_planner.plan_experiment()
if not dont_run_preprocessing: # double negative, yooo
exp_planner.run_preprocessing(threads)
预处理执行完毕,得到如下处理结果:
nnUNet_preprocessed文件夹下
|-- Task040_KiTS
|-- dataset.json
|-- dataset_properties.pkl
|-- gt_segmentations
|-- nnUNetData_plans_v2.1_2D_stage0
|-- nnUNetData_plans_v2.1_stage0
|-- nnUNetPlansv2.1_plans_2D.pkl
|-- nnUNetPlansv2.1_plans_3D.pkl
`-- splits_final.pkl
这里生成的文件都可以打开来看看,对预处理方法和数据指纹有一个了解
-
dataset.json在数据获取阶段产生
-
daset_properties为数据的 size, spacing, origin, classes, size_after_cropping 等属性
-
gt_segmentations为图像分割标签
-
nnUNetData_plans_v2.1_2D_stage0和nnUNetData_plans_v2.1_stage0是预处理后的数据集
-
splits_final.pkl是五折交叉验证划分的结果,一共210个病人,42为一折
-
nnUNetPlansv2.1_plans*.pkl为训练计划,参考官方文档中的edit_plans_files.md可进行编辑
以nnUNetPlansv2.1_plans_3D.pkl为例,
3.模型训练
一行代码开始训练,执行过程以及调参可以参考我的博客nnUnet代码解读–模型训练
python nnunet/run/run_training.py CONFIGURATION TRAINER_CLASS_NAME TASK_NAME_OR_ID FOLD # 格式
python nnunet/run/run_training.py 3d_fullres nnUNetTrainerV2 40 1
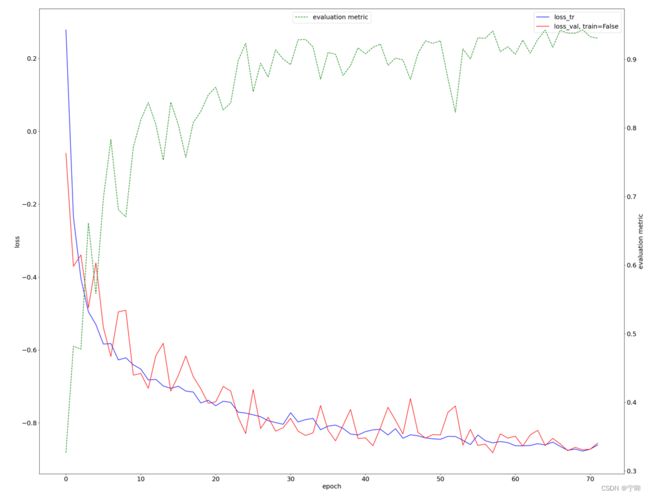
训练开始后,训练日志和训练结果记录在nnUNet_trained_models/nnUNet/3d_fullres/Task040_KiTS文件夹下
UNetTrainer__nnUNetPlansv2.1
├── fold_1
│ ├── debug.json
│ ├── model_best.model
│ ├── model_best.model.pkl
│ ├── model_final_checkpoint.model
│ ├── model_final_checkpoint.model.pkl
│ ├── postprocessing.json
│ ├── progress.png
│ ├── training_log_2022_5_4_12_06_14.txt
│ ├── training_log_2022_5_5_10_30_05.txt
│ ├── validation_raw
│ └── validation_raw_postprocessed
这里我想补充一下nnUnet的评价指标
在线评价
下面这段代码是nnUnet计算dice值的方法
先对每张图像中的每个类别分别计算tp, fp, fn,再对一个batch内的所有图像的tp, fp, fn求和,同时对一个batch求dice
import numpy as np
import torch
def sum_tensor(inp, axes, keepdim=False):
axes = np.unique(axes).astype(int)
if keepdim:
for ax in axes:
inp = inp.sum(int(ax), keepdim=True)
else:
for ax in sorted(axes, reverse=True):
inp = inp.sum(int(ax))
return inp
def run_online_evaluation(output, target):
# torch.Size([b,num_classes, 80, 160, 160]) torch.Size([b,1, 80, 160, 160])
with torch.no_grad():
num_classes = output.shape[1]
output_softmax = torch.softmax(output,dim=1)
output_seg = output_softmax.argmax(1) # [b,80,160,160]
target = target[:, 0] # [b,80,160,160]
axes = tuple(range(1, len(target.shape))) # (1,2,..,num_classes)
tp_hard = torch.zeros((target.shape[0], num_classes - 1)).to(output_seg.device.index) # [b,num_classes-1]
fp_hard = torch.zeros((target.shape[0], num_classes - 1)).to(output_seg.device.index) # [b,num_classes-1]
fn_hard = torch.zeros((target.shape[0], num_classes - 1)).to(output_seg.device.index) # [b,num_classes-1]
for c in range(1, num_classes):
tp_hard[:, c - 1] = sum_tensor((output_seg == c).float() * (target == c).float(), axes=axes)
fp_hard[:, c - 1] = sum_tensor((output_seg == c).float() * (target != c).float(), axes=axes)
fn_hard[:, c - 1] = sum_tensor((output_seg != c).float() * (target == c).float(), axes=axes)
# [b,num_classes-1] -> [num_classes-1,]
tp_hard = tp_hard.sum(0, keepdim=False).detach().cpu().numpy()
fp_hard = fp_hard.sum(0, keepdim=False).detach().cpu().numpy()
fn_hard = fn_hard.sum(0, keepdim=False).detach().cpu().numpy()
print(list((2 * tp_hard) / (2 * tp_hard + fp_hard + fn_hard + 1e-8)))
print(list(tp_hard))
print(list(fp_hard))
print(list(fn_hard))
if __name__ == '__main__':
outputs = torch.randn(4,3,80,160)
targets = torch.randint(0, 3, (4,1,80,160))
run_online_evaluation(outputs,targets)
但是我觉得直接对一个batch累加求dice不够准确,因为不同图像的目标区域大小不同,目标区域大的图像对目标区域小的图像影响太大了。
比较好的评价方法是应该对batch内的每张图像分别求dice,然后求平均。
下面这段代码中,作者也提到:
训练过程中的在线评价,只是对Dice值的一个估计,并不能代表最终的dice.
整体思路就是把每个batch当做一张图像去求的dice,迭代一个epoch之后,再对每个batch的dice求平均。
验证时,每个epoch中batch的数量取决于num_val_batches_per_epoch
def finish_online_evaluation(self):
self.online_eval_tp = np.sum(self.online_eval_tp, 0)
self.online_eval_fp = np.sum(self.online_eval_fp, 0)
self.online_eval_fn = np.sum(self.online_eval_fn, 0)
global_dc_per_class = [i for i in [2 * i / (2 * i + j + k) for i, j, k in
zip(self.online_eval_tp, self.online_eval_fp, self.online_eval_fn)]
if not np.isnan(i)]
self.all_val_eval_metrics.append(np.mean(global_dc_per_class))
self.print_to_log_file("Average global foreground Dice:", [np.round(i, 4) for i in global_dc_per_class])
self.print_to_log_file("(interpret this as an estimate for the Dice of the different classes. This is not "
"exact.)")
self.online_eval_foreground_dc = []
self.online_eval_tp = []
self.online_eval_fp = []
self.online_eval_fn = []
最终评价
模型训练完成后,对五折交叉验证的验证集进行评价
dataset_val存储了验证集的信息,包含data, seg, properties
for k in self.dataset_val.keys():
properties = load_pickle(self.dataset[k]['properties_file'])
fname = properties['list_of_data_files'][0].split("/")[-1][:-12]
if overwrite or (not isfile(join(output_folder, fname + ".nii.gz"))) or \
(save_softmax and not isfile(join(output_folder, fname + ".npz"))):
data = np.load(self.dataset[k]['data_file'])['data']
print(k, data.shape)
data[-1][data[-1] == -1] = 0
softmax_pred = self.predict_preprocessed_data_return_seg_and_softmax(data[:-1],
do_mirroring=do_mirroring, # True
mirror_axes=mirror_axes, # 0,1,2
use_sliding_window=use_sliding_window, # True
step_size=step_size, # 0.5
use_gaussian=use_gaussian, # True
all_in_gpu=all_in_gpu, # False
mixed_precision=self.fp16)[1] # fp16=True
在线评价时,每个epoch从训练集中取一定数量的batch,取样的patch_size为(80,160,160),计算dice以及tp,fp,fn
最终评价时,对划分的验证集的每个图像用patch_size大小的滑动窗口进行评价,每个图像是经过充分评价的。
核心是predict_preprocessed_data_return_seg_and_softmax函数,输出验证集的分割结果以及summary.json文件。
这里的dice等评价指标才是验证集的真实评价指标
"mean": {
"0": {
......
},
"1": {
"Accuracy": 0.9993829712065982,
"Dice": 0.9577956529884739,
"False Discovery Rate": 0.049338979474340974,
"False Negative Rate": 0.03426020473989496,
"False Omission Rate": 0.000264596006662038,
"False Positive Rate": 0.0003583155624936977,
"Jaccard": 0.9195569582759517,
"Negative Predictive Value": 0.9997354039933379,
"Precision": 0.950661020525659,
"Recall": 0.9657397952601052,
"Total Positives Reference": 50782.54761904762,
"Total Positives Test": 51469.26190476191,
"True Negative Rate": 0.9996416844375062
},
"2": {
"Accuracy": 0.9997035394427145,
"Dice": 0.818755367440307,
"False Discovery Rate": 0.1575802546022549,
"False Negative Rate": 0.1761964196424669,
"False Omission Rate": 0.00018421007671236777,
"False Positive Rate": 0.00011484654734425636,
"Jaccard": 0.7197449105231752,
"Negative Predictive Value": 0.9998157899232878,
"Precision": 0.8424197453977451,
"Recall": 0.823803580357533,
"Total Positives Reference": 19027.85714285714,
"Total Positives Test": 18542.309523809523,
"True Negative Rate": 0.9998851534526555
}
}
4.预测结果
nnUNet_predict -i INPUT_FOLDER -o OUTPUT_FOLDER -t TASK_NAME_OR_ID -m CONFIGURATION --save_npz # 格式
若以第二折交叉验证的结果进行预测,需要两个文件
fold_2/model_final_checkpoint.model为模型参数和权重fold_2/model_final_checkpoint.model.pkl包含模型类别,训练计划(plan)
nnunet包
nnUNet_predict -i $nnUNet_raw_data_base/nnUNet_raw_data/Task040_KiTS/imagesTs/ -o OUTPUT_DIRECTORY -t 40 -m 3d_fullres -f 2
使用代码
python /nnunet/inference/predict_simple.py -i $nnUNet_raw_data_base/nnUNet_raw_data/Task040_KiTS/imagesTs/ -o OUTPUT_DIRECTORY -t 40 -m 3d_fullres -f 2
- INPUT_FOLDER:测试集所在目录
- OUTPUT_FOLDER:输出目录,可自己指定
预测结果
KiTS19_predict/OUTPUT_DIRECTORY/
|-- plans.pkl
|-- case_00210.nii.gz
|-- case_00211.nii.gz
|-- ......
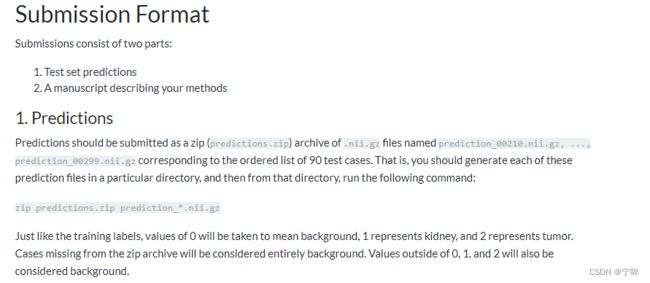
5.比赛提交
提交结果是有格式要求的,需要提交一个prediction.zip压缩包,其中的文件名为prediction_*.nii.gz
重命名
使用rename命令:
rename "s/case/prediction/" *
执行完毕,文件名中的case被批量替换为prediction
KiTS19_predict/OUTPUT_DIRECTORY/
|-- plans.pkl
|-- prediction_00210.nii.gz
|-- prediction_00211.nii.gz
|-- ......
打包文件
进入OUTPUT_DIRECTORY目录,命令行输入:
zip predictions.zip prediction_*.nii.gz
得到predictions.zip压缩包就可以提交了
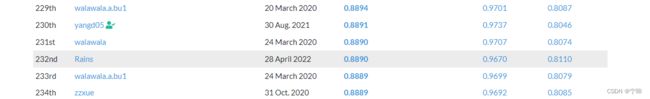
我用
nnUNetTrainerV2在第二折训练了90个epoch,当做最终训练结果预测测试集图像,提交了一次,排名200+,大家感兴趣的话也可以试试。
最近学会使用nnUnet训练自己的模型了,直接改网络确实比较麻烦,但还没想好怎么讲,后处理部分也还没看。