【一起学数据结构与算法】深度学习队列
目录
- 一、什么是队列?
- 二、 队列的基本操作
-
- 2.1 offer - 入队
- 2.2 poll - 出队
- 2.3 peek - 获取队头元素
- 2.4 isEmpty - 判断队列是否为空
- 2.5 size - 获取队列长度
- 三、队列的模拟实现
-
- 3.1 isEmpty
- 3.2 offer
- 3.3 poll
- 3.4 peek
- 3.5 MyQueue.java
- 四、循环队列
-
- 4.1 isEmpty - 判空
- 4.2 isFull - 判满
- 4.3 front - 队头
- 4.4 rear - 队尾
- 4.5 enQueue - 入队
- 4.6 deQueue - 出队
- 4.7 MyCircularQueue.java
- 五、双端队列
- 六、面试题
-
- 6.1 用队列实现栈
-
- 6.1.1 解题思路
- 6.1.2 代码
- 6.2 用栈实现队列
-
- 6.2.1 解题思路
- 6.2.2 代码
一、什么是队列?
队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作,和栈一样,队列是一种操作受限制的线性表。进行插入操作的端称为队尾,进行删除操作的端称为队头。 – 来源百度

队头(front):允许删除的一端,称为队首
队尾(rear):允许插入的一端
空队列:不包含任何元素的空表
二、 队列的基本操作
在Java中,Queue是个接口,底层是通过链表来实现的。
- offer:入队若队列未满,将x加入,使之称为新的队尾。
- poll:出队,若队列未空,删除队头元素,并用x返回。
- peek:获取队头元素,若队列未空,则将队头元素赋值给x。
- isEmpty:判断队列是否为空,若队列为空返回true,否则返回false。
- size:获取队列中有效元素个数
2.1 offer - 入队
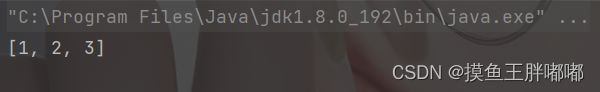
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(1); queue.offer(2); queue.offer(3); System.out.println(queue); } }2.2 poll - 出队
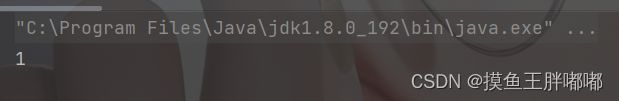
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(1); queue.offer(2); queue.offer(3); System.out.println(queue); queue.poll(); queue.poll(); System.out.println(queue); } }2.3 peek - 获取队头元素
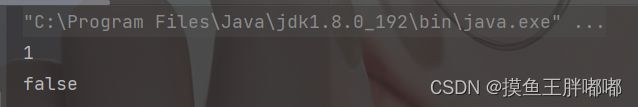
public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(1); queue.offer(2); queue.offer(3); System.out.println(queue.peek()); }2.4 isEmpty - 判断队列是否为空
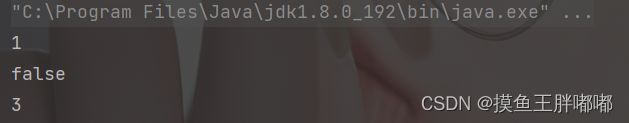
public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(1); queue.offer(2); queue.offer(3); System.out.println(queue.peek()); System.out.println(queue.isEmpty()); }2.5 size - 获取队列长度
public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(1); queue.offer(2); queue.offer(3); System.out.println(queue.peek()); System.out.println(queue.isEmpty()); System.out.println(queue.size()); }三、队列的模拟实现
3.1 isEmpty
public boolean isEmpty() { return this.head == null; }3.2 offer
/** * 尾插法 * @param val */ public void offer(int val) { Node node = new Node(val); if (head == null) { head = node; last = node; } else { last.next = node; last = last.next; } }3.3 poll
/** * 出队 * @return */ public int poll() { if (isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("队列为空"); } int oldVal = head.val; this.head = head.next; return oldVal; }3.4 peek
public int peek() { if (isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("队列为空"); } return head.val; }3.5 MyQueue.java
@SuppressWarnings({"all"}) class Node { public int val; public Node next; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; } } public class MyQueue { public Node head; public Node last; /** * 尾插法 * @param val */ public void offer(int val) { Node node = new Node(val); if (head == null) { head = node; last = node; } else { last.next = node; last = last.next; } } /** * 出队 * @return */ public int poll() { if (isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("队列为空"); } int oldVal = head.val; this.head = head.next; return oldVal; } public boolean isEmpty() { return this.head == null; } public int peek() { if (isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("队列为空"); } return head.val; } }四、循环队列
为充分利用向量空间,克服"假溢出"现象的方法是:将向量空间想象为一个首尾相接的圆环,并称这种向量为循环向量。存储在其中的队列称为循环队列(Circular Queue)。循环队列是把顺序队列首尾相连,把存储队列元素的表从逻辑上看成一个环,成为循环队列。 - 来源百度
队列头尾相连的顺序存储结构称为循环队列。
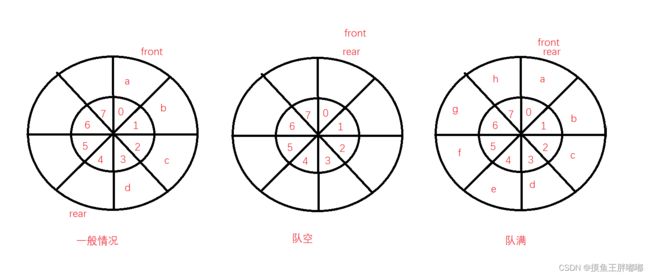
使用循环队列的时候,我们会发现一个问题,如何去区分空与满?其实是有三种解决方法的
- 通过添加size属性记录
- 保留一个位置
- 使用flag标记
我们使用第二种方法来实现
4.1 isEmpty - 判空
public boolean isEmpty() { return front == rear; }4.2 isFull - 判满
public boolean isFull() { if ((this.rear+1) % elem.length == front) { return true; } return false; }4.3 front - 队头
public int front() { if (isEmpty()) return -1; return elem[front]; }4.4 rear - 队尾
public int rear() { if (isEmpty()) return -1; int index = -1; if (rear == 0) { index = elem.length-1; } else { index = rear-1; } return elem[index]; }4.5 enQueue - 入队
public boolean enQueue(int value) { if (isFull()) return false; this.elem[rear] = value; rear = (rear + 1) % elem.length; return true; }4.6 deQueue - 出队
public boolean deQueue() { if (isEmpty()) return false; front = (front+1) % elem.length; return true; }4.7 MyCircularQueue.java
public class MyCircularQueue { public int[] elem; public int front;//队头下标 public int rear;//队尾下标 public MyCircularQueue(int k) { this.elem = new int[k+1]; } /** * 入队 * * @param value * @return */ public boolean enQueue(int value) { if (isFull()) return false; this.elem[rear] = value; rear = (rear + 1) % elem.length; return true; } public boolean deQueue() { if (isEmpty()) return false; front = (front+1) % elem.length; return true; } /** * 得到队头元素 * @return */ public int front() { if (isEmpty()) return -1; return elem[front]; } public int rear() { if (isEmpty()) return -1; int index = -1; if (rear == 0) { index = elem.length-1; } else { index = rear-1; } return elem[index]; } public boolean isEmpty() { return front == rear; } public boolean isFull() { if ((this.rear+1) % elem.length == front) { return true; } return false; } }五、双端队列
deque(double-ended queue,双端队列)是一种具有队列和栈的性质的数据结构。双端队列中的元素可以从两端弹出,相比list增加[]运算符重载。

在双端队列进队时,前端进的元素排列在队列中后端进的元素的前面,后端进的元素排列在队列中前端进的元素的后面。在双端队列出队时,无论是前端还是后端出队,先出的元素排列在后出的元素的前面。Deque是一个接口,使用时必须创建LinkedList的对象。由于在实际开发中Deque使用的并不是非常多,所以大家只需了解一下即可!
六、面试题
6.1 用队列实现栈
6.1.1 解题思路
因为栈是后进先出结构,而我们的队列是先进先出结构,我们可以用两个队列来模拟实现栈的结构,qu1用来进栈,当我们需要出栈时,将qu1里面的元素出栈size-1个元素,就能得到我们的栈顶元素,注意,进栈的时候先判断两个队列谁不为空往哪个队列进,只有两个队列都为空的时候我们的栈也为空。
6.1.2 代码
class MyStack { private Queue<Integer> qu1; private Queue<Integer> qu2; public MyStack() { qu1 = new LinkedList<>(); qu2 = new LinkedList<>(); } public void push(int x) { if (!qu1.isEmpty()) { qu1.offer(x); } else if (!qu2.isEmpty()) { qu2.offer(x); } else { qu1.offer(x); } } public int pop() { if(empty()) return -1; if (!qu1.isEmpty()) { int size = qu1.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++) { int val = qu1.poll(); qu2.offer(val); } return qu1.poll(); } if (!qu2.isEmpty()) { int size = qu2.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++) { int val = qu2.poll(); qu1.offer(val); } return qu2.poll(); } return -1; } public int top() { if(empty()) return -1; if (!qu1.isEmpty()) { int val = -1; int size = qu1.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { val = qu1.poll(); qu2.offer(val); } return val; } if (!qu2.isEmpty()) { int val = -1; int size = qu2.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { val = qu2.poll(); qu1.offer(val); } return val; } return -1; } public boolean empty() { return qu2.isEmpty() && qu1.isEmpty(); } }6.2 用栈实现队列
6.2.1 解题思路
- 用两个栈实现队列,先将元素全部入栈到第一个栈s1当中。
- pop()操作,先判断s1是否为空,如果为空则返回-1,接着判断条件为s2为空,s1不为空,将s1中的元素全部进栈到s2当中,然后return s2.pop()便是出队操作。
- 跟操作2类似,最后返回s2.peek()便可!
6.2.2 代码
class MyQueue { public Stack<Integer> stack1; public Stack<Integer> stack2; public MyQueue() { stack1 = new Stack<>(); stack2 = new Stack<>(); } public void push(int x) { stack1.push(x); } public int pop() { if (empty()) return -1; if (stack2.isEmpty()) { while (!stack1.isEmpty()) { stack2.push(stack1.pop()); } } return stack2.pop(); } public int peek() { if (empty()) return -1; if (stack2.isEmpty()) { while (!stack1.isEmpty()) { stack2.push(stack1.pop()); } } return stack2.peek(); } public boolean empty() { return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty(); } } /** * Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such: * MyQueue obj = new MyQueue(); * obj.push(x); * int param_2 = obj.pop(); * int param_3 = obj.peek(); * boolean param_4 = obj.empty(); */