java网络编程基础—Netty框架应用基础
缘由:
在最近的一段时间中,一直没有对java网络编程有了解,只知道socket的大概却又说不清楚,但常规的socket编程已经不适合现在的开发了,于是我去了解了有什么java网络框架能减少网络编程的难度。其实有2个,Mina与Netty,热门的rpc框架dubbo的网络通信部分就是用这2者实现的(使用时选择使用其中一个)。但Netty的社区还在活跃,所以还是选择去了解了Netty框架,把《Netty实战》这本书粗略地看了一遍,其实netty能实现的东西有很多,对tcp,udp,http,websocket有着很好的封装与支持,通过把socket抽象成channel,把数据流通过不同的编解码与处理器,能玩的花样可多了,甚至还能支持自己设计的协议,只要自己设计好Netty的编解码器就行,如dubbo进行rpc时的协议,性能还不赖,所以,可以通过netty去了解什么是网络编程,bio,nio,aio(但好像Netty不支持aio,原因是linux对aio不怎么支持),边学边用。但最近比较忙,忙中偷闲抽一天来总结一下netty的基础用法。
Netty进行tcp通信:
Server端引导代码:
NioEventLoopGroup bosseventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup childeventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bosseventLoopGroup,childeventLoopGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
p.addLast(new StringDecoder());
p.addLast(new StringEncoder());
p.addLast(new HelloServerHandler());
}
});
bootstrap.bind(port).sync().channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// Shut down the event loop to terminate all threads.
bosseventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
childeventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
} HelloServerHandler代码:
public class HelloServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
if (msg.toString().startsWith("get")) {
String result = new HelloServiceImpl()
.hello(msg.toString());
ctx.writeAndFlush(result);
}
}
}server端的思路是,当收到client端发来的信息头带有get字样时,将调用hello方法返回响应字符。
Client端引导代码
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
p.addLast(new StringDecoder());
p.addLast(new StringEncoder());
p.addLast(new HelloClientHandler());
}
});
try {
b.connect("localhost",14567).sync().channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// Shut down the event loop to terminate all threads.
group.shutdownGracefully();
} Client思路是与Server端连接完成后将发送"gethello Server!"到服务器,服务器做出响应,handler将采用channelRead方法进行读取,读取时再发送测试字符到服务器端,直到count大于10。
Netty进行Udp通信:
由于Udp是无连接的,所以服务器端需要一直绑定监听端口等待客户端发来Udp数据包,客户端也需要绑定端口对指定地址进行发送Udp数据包,但发送是不需要进行连接,等待一段时间放弃绑定端口即可。Netty对Udp也有很好的支持,把Udp的数据包用DatagramPacket进行了一次封装,所以。。服务器客户端只需要对DatagramPacket进行解析即可,不用去面对烦人的二进制数据流了。
Server端引导代码:
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioDatagramChannel.class)
.handler(new UdpServerHandler());
// 服务端监听在9999端口
try {
b.bind(9999).sync().channel().closeFuture().await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}因为是服务器,不能绑定接口后就直接跑路了,需要用await方法阻塞起来,不指定时间参数将永久阻塞,谁叫你是服务器呢!
UdpServerHandler代码:
public class UdpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, DatagramPacket msg) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String req = msg.content().toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
System.out.println(req);
if ("get".equals(req)) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(new DatagramPacket(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(
"服务器时间:"+System.currentTimeMillis(), CharsetUtil.UTF_8), msg.sender()));
}
}
} 为了简单,服务器收到udp数据将直接发送服务器时间到客户端。
client端引导:
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioDatagramChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BROADCAST, true)
.handler(new UdpClientHandler());
Channel ch = b.bind(0).sync().channel();
ch.writeAndFlush(new DatagramPacket(
Unpooled.copiedBuffer("get", CharsetUtil.UTF_8),
new InetSocketAddress("255.255.255.255", 9999))).sync();
if (!ch.closeFuture().await(15000)) {
System.out.println("Search request timed out.");
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
client端进行广播发送,发送完数据后等待15秒后关闭。
UdpClientHandler代码:
public class UdpClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, DatagramPacket msg) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String req = msg.content().toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
System.out.println(req);
}
} 还是为了方便,直接读取返回数据即可。
Netty对http与Websocket的使用(转载):
不多说先上代码:
HttpRequestHandler代码:
public class HttpRequestHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler { //1
private final String wsUri;
private static final File INDEX;
static {
URL location = HttpRequestHandler.class.getProtectionDomain().getCodeSource().getLocation();
try {
String path = location.toURI()+"text.html";
path = !path.contains("file:") ? path : path.substring(5);
INDEX = new File(path);
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to locate text.html", e);
}
}
public HttpRequestHandler(String wsUri) {
this.wsUri = wsUri;
}
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest request) throws Exception {
if (wsUri.equalsIgnoreCase(request.getUri())) {
ctx.fireChannelRead(request.retain()); //2
} else {
if (HttpHeaders.is100ContinueExpected(request)) {
send100Continue(ctx); //3
}
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile(INDEX, "r");//4
HttpResponse response = new DefaultHttpResponse(request.getProtocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK);
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/html; charset=UTF-8");
boolean keepAlive = HttpHeaders.isKeepAlive(request);
if (keepAlive) { //5
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_LENGTH, file.length());
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONNECTION, HttpHeaders.Values.KEEP_ALIVE);
}
ctx.write(response); //6
if (ctx.pipeline().get(SslHandler.class) == null) { //7
ctx.write(new DefaultFileRegion(file.getChannel(), 0, file.length()));
} else {
ctx.write(new ChunkedNioFile(file.getChannel()));
}
ChannelFuture future = ctx.writeAndFlush(LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT); //8
if (!keepAlive) {
future.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); //9
}
file.close();
}
}
private static void send100Continue(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.CONTINUE);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
System.out.println("Client:"+incoming.remoteAddress()+"异常");
// 当出现异常就关闭连接
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
} TextWebSocketFrameHandler 代码:
public class TextWebSocketFrameHandler extends
SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
public static ChannelGroup channels = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception { // (1)
Channel incoming = (Channel) ctx.channel();
for (io.netty.channel.Channel channel : channels) {
if (channel != incoming){
channel.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("[" + incoming.remoteAddress() + "]" + msg.text()));
} else {
channel.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("[you]" + msg.text() ));
}
}
}
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // (2)
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
for (Channel channel : channels) {
channel.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("[SERVER] - " + incoming.remoteAddress() + " 加入"));
}
channels.add(ctx.channel());
System.out.println("Client:"+incoming.remoteAddress() +"加入");
}
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // (3)
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
for (Channel channel : channels) {
channel.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("[SERVER] - " + incoming.remoteAddress() + " 离开"));
}
System.out.println("Client:"+incoming.remoteAddress() +"离开");
channels.remove(ctx.channel());
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // (5)
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
System.out.println("Client:"+incoming.remoteAddress()+"在线");
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // (6)
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
System.out.println("Client:"+incoming.remoteAddress()+"掉线");
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
System.out.println("Client:"+incoming.remoteAddress()+"异常");
// 当出现异常就关闭连接
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
} 流处理器WebsocketChatServerInitializer代码:
public class WebsocketChatServerInitializer extends
ChannelInitializer { //1
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {//2
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(64*1024));
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpRequestHandler("/ws"));
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/ws"));
pipeline.addLast(new TextWebSocketFrameHandler());
}
} 最后引导实现:
public class WebsocketChatServer {
private int port;
public WebsocketChatServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void run() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // (1)
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); // (2)
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // (3)
.childHandler(new WebsocketChatServerInitializer()) //(4)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // (5)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); // (6)
System.out.println("WebsocketChatServer 启动了");
// 绑定端口,开始接收进来的连接
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync(); // (7)
// 等待服务器 socket 关闭 。
// 在这个例子中,这不会发生,但你可以优雅地关闭你的服务器。
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
System.out.println("WebsocketChatServer 关闭了");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new WebsocketChatServer(8080).run();
}
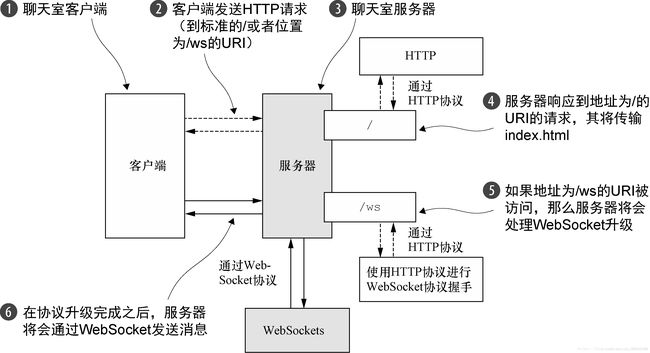
}根据Netty实战这本书的说法,在从标准的HTTP或者HTTPS协议切换到WebSocket时,将会使用一种称为升级握手的机制。因此,使用WebSocket的应用程序将始终以HTTP/S作为开始,然后再执行升级。这个升级动作发生的确切时刻特定于应用程序它可能会发生在启动时,也可能会发生在请求了某个特定的URL之后。我们的应用程序将采用下面的约定:如果被请求的URL 以/ws 结尾,那么我们将会把该协议升级为WebSocket;否则,服务器将使用基本的HTTP/S。在连接已经升级完成之后,所有数据都将会使用WebSocket 进行传输。
一开始将以http/s的方式获取聊天室html页面,但在html页面中支持了websocket的使用,所以说,获取静态网页是http,websocket去支持多人聊天,原理是某一用户加入,离开,发言后服务器都将通过websocket发送给其他用户。
静态页面:
WebSocket Chat
最后的运行结果:
其实网络编程只是学到了皮毛,能深入总归是好事,还需要在未来的时间好好去研究。
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「nullguo」的原创文章。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36642340/article/details/80374139