React 实战
一、React 视图层
项目创建
Create React App
npx create-react-app my-app
cd my-app
npm start / yarn start
JSX
如何将 React 元素渲染到DOM中?
const element = Hello,world
;
ReactDOM.render(element,document.getElementById('root'))
组件
React 应用组成和复用的基本单元
component = (props) => element
函数组件
import React from 'react';
function Welcome(props) {
return Hello, {props.name}
}
export default Welcome;
类组件
必须有一个 render() 方法
import React from 'react';
class Welcome extends React.Component {
render() {
return Hello, {this.props.name}
}
}
export default Welcome;
列表中的 key
只需要保证,在同一个数组中的兄弟元素之间的 key 是唯一的。而不需要在整个应用程序甚至单个组件中保持唯一。
理想情况下,key 应该从数据中获取,对应着唯一且固定的标识符,例如 post.id。
state
创建 Clock 时钟组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class Clock extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { date: new Date() };
}
// 组件被挂载到 DOM 节点时会调用
componentDidMount() {
// setInterval 循环任务 API
this.timerID = setInterval(() => this.tick(), 1000);
}
// 组件从 DOM 卸载时会调用
componentWillUnmount() {
// 清除 setInterval 创建的定时任务
clearInterval(this.timerID);
}
tick() {
this.setState({
date: new Date()
});
}
render() {
return (
Current Time:{this.state.date.toLocaleTimeString()}
);
}
}
export default Clock;
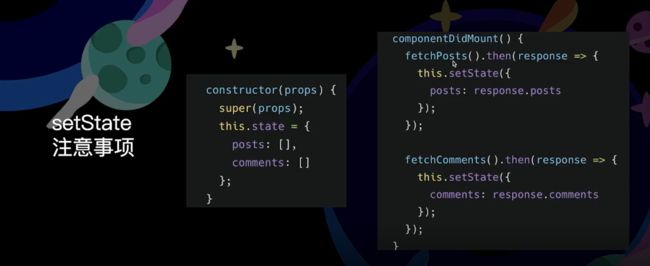
setState 注意事项
不能通过 this.state 直接赋值
// Wrong
this.state.comment = 'Hello';
使用 this.setState 方法赋值
// Correct
this.setState({comment: 'Hello'});
如果新的状态需要依赖当前状态得到
// Wrong
this.setState({
counter: this.state.counter + this.props.increment
})
// Correct
this.setState((state, props) => ({
counter:satae.counter + props.increment
}))
setState 对 state 的修改是部分修改,而不是对整个 state 全量替换
state 总结
- Props:父组件传递给子组件的属性,在子组件内部只读
- State:组件内部自己维护的状态,可以被修改
生命周期方法
针对类组件是有意义的,而函数组件没有这些生命周期方法
Form
受控组件
input 的值受 react 组件控制
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class NameForm extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { value: '' };
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this);
this.handleSubmit = this.handleSubmit.bind(this);
}
handleChange(event) {
this.setState({ value: event.target.value })
}
handleSubmit(event) {
alert('A name was submitted:' + this.state.value);
event.preventDefault();
}
render() {
return (
);
}
}
export default NameForm;
非受控组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class NameForm extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleSubmit = this.handleSubmit.bind(this);
this.input = React.createRef();
}
handleSubmit(event) {
alert('A name was submitted:' + this.input.current.value);
event.preventDefault();
}
render() {
return (
);
}
}
export default NameForm;
组件的组合用法
一般用法
import React from 'react';
function FanctBorder(props) {
return (
{props.children}
)
}
function WelcomeDialog() {
return (
Welcome
Thank you for visiting our spacecraft!
)
}
export default WelcomeDialog;
更加灵活的组合方式
import React from 'react';
function FanctBorder(props) {
return (
{props.left}
this is line!
{props.right}
)
}
function Left(props) {
return (
this is a Left!
)
}
function Right(props) {
return (
this is a Right!
)
}
function WelcomeDialog() {
return (
React Hooks
React 16.8 以后,新的组件开发方法
React Hooks 编写形式对比
先来写一个最简单的组件,点我们点击按钮时,点击数量不断增加。
有状态组件写法:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class Example extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
count: 0
}
this.addCount = this.addCount.bind(this)
}
render() {
return (
);
}
addCount() {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1
})
}
}
export default Example;
React Hooks 写法
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function Example() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
useEffect(() => {
console.log(`useEffect=> You clicked ${count}`);
return () => {
console.log('解绑生命周期函数!')
}
}, [count]) // count 发生变化,就会执行解绑
return (
)
}
export default Example;
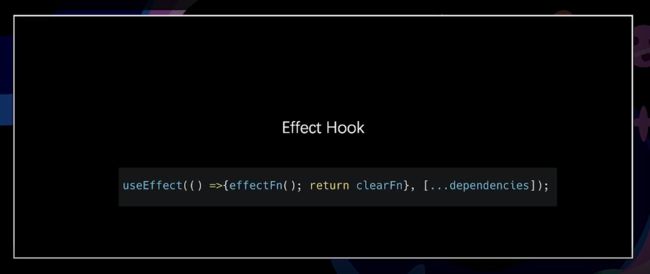
const [state, setState] = useState(initialState);
useEffect(() =>{ effectFn(); return clearFn},[...dependencies])
一般用法
useEffect(() => {
const getUserInfo = async () => {
try {
const userInfo = await fetch('https://api.github.com/users/hzjsj');
console.log(userInfo)
} catch (err) {
console.error(err)
}
}
getUserInfo();
}, [])
二、React Router 路由层
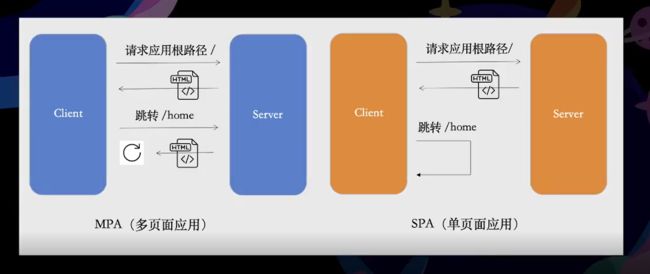
路由分类
1.服务端路由
请求发送到服务端,服务端返回对应的页面内容
2.客户端路由
请求不发送到服务端,有客户端代码更新页面内容
MPA 和 SPA
React Router是什么
React 应用中的客户端路由解决方案
基础示例
import React from "react";
import {
BrowserRouter as Router,
// HashRouter as Router,
Switch,
Route,
Link,
useHistory,
useParams
} from "react-router-dom";
export default function BasicExample() {
return (
-
Home
-
About
-
Dashboard
);
}
// You can think of these components as "pages"
// in your app.
function Home() {
const history = useHistory();
return (
Home
);
}
function About() {
return (
About
);
}
function Dashboard() {
return (
Dashboard
);
}
function User() {
const params = useParams();
const username = params.username;
return Welcome: {username};
}
Router
browserrouter:根据 URL 中的 path 做路由跳转
HashRouter:根据 URL 中的 hash 部分做路由
Route
当 url 和 Route 中定义的 path 匹配时,渲染对应的组件
重要 props:path、exact
Switch
当找到Switch组件内的第一个路由规则匹配的Route组件后,立即停止后续的查找
路由跳转
声明式的组件方式:Link
命令式的 API 调用方式:history.push
Hooks
useHistory:获取 history 对象
useParams:获取路由中的参数