RestFul风格详解
文章目录
- 一、前言
- 二、什么是RestFul风格
- 三、传统风格与RestFul风格对比
-
- 1. 传统方式操作资源
- 2. RestFul方式操作资源
- 四、RestFul代码演示
-
- 1.代码展示
- 2.拓展情景
- 五、使用method属性指定请求类型
- 六、总结
一、前言
该技术博客总结与狂神说SpringMVC课程
二、什么是RestFul风格
Restful就是一个资源定位、资源操作的风格。不是标准也不是协议,只是一种风格。基于这个风格设计的软件可以更简洁,更有层次,更易于实现缓存等机制。
资源:互联网所有的事物都可以被抽象为资源
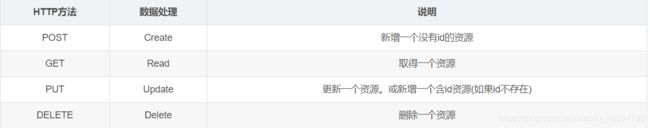
资源操作:分为POST、DELETE、PUT、GET四种方法,使用不同方法对资源进行操作(增、删、改、查)
三、传统风格与RestFul风格对比
1. 传统方式操作资源
通过不同的参数来实现不同的效果!方法单一!
http://127.0.0.1/item/queryItem.action?id=1 (查询,GET)
http://127.0.0.1/item/saveItem.action (新增,POST)
http://127.0.0.1/item/updateItem.action (更新,POST)
http://127.0.0.1/item/deleteItem.action?id=1 (删除,GET或POST)
2. RestFul方式操作资源
可以通过不同的请求方式来实现不同的效果!
如下:请求地址一样,但是功能可以不同!
http://127.0.0.1/item/1 (查询,GET)
http://127.0.0.1/item (新增,POST)
http://127.0.0.1/item (更新,PUT)
http://127.0.0.1/item/1 (删除,DELETE)
四、RestFul代码演示
1.代码展示
在进行代码演示之前,需要配置好环境!
首先导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvcartifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
接着创建springmvc.xml配置文件:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.xu.controller"/>
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
bean>
beans>
接着配置web.xml文件:
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServletservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServletservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
web-app>
然后在WEB-INF下创建jsp/test.jsp文件,用于接收值:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Testtitle>
head>
<body>
${msg}
body>
html>
最后创建RestFulController类:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
@Controller
public class RestFulController {
//映射访问路径
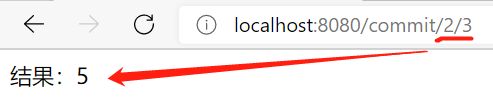
@RequestMapping("/commit/{p1}/{p2}")
//在SpringMVC中可以使用 @PathVariable,让方法参数的值对应绑定到一个URI模板变量上
public ModelAndView index(@PathVariable int p1, @PathVariable int p2, ModelAndView mv){
int result = p1 + p2;
//实例化一个ModelAndView对象用于向视图中传值
mv.addObject("msg","结果:" + result);
//返回视图
mv.setViewName("test");
return mv;
}
}
2.拓展情景
通过路径变量的类型可以约束访问参数,如果类型不一样,则访问不到对应的请求方法,如果这里访问是的路径是 /commit/1/a,则路径与方法不匹配,而不会是参数转换失败。
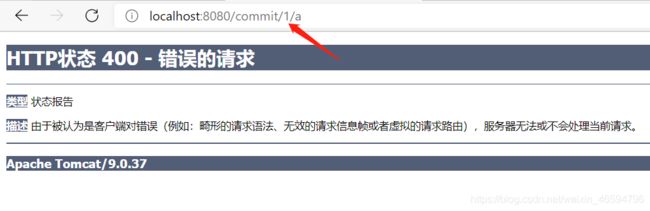
解决方式:将RestFulController类中方法第二个参数类型改成String
五、使用method属性指定请求类型
用于约束请求的类型,可以收窄请求范围。
指定请求谓词的类型如:GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE等
代码展示:
//在RestFulController类中增加一个方法
//映射访问路径,必须是POST请求
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = {RequestMethod.POST})
public String index2(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg", "hello!");
return "test";
}
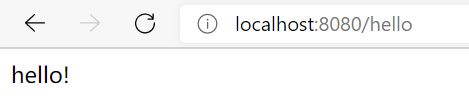
发送请求后,显示如下结果:
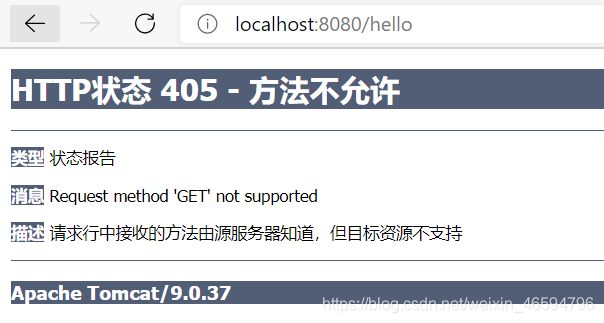
原因:我们使用浏览器地址栏进行访问默认是Get请求,会报错405!
解决方式:将POST修改为GET就正常了
//映射访问路径,必须是Get请求
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = {RequestMethod.GET})
//我们一般采用这种方式:@GetMapping("/hello")
public String index2(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg", "hello!");
return "test";
}
六、总结
所有的地址栏请求默认都会是GET类型的。
针对章节五的问题,我们也可以通过组合注解来解决:
@GetMapping:扮演的是@RequestMapping(method =RequestMethod.GET) 的快捷方式。
@PostMapping
@PutMapping
@DeleteMapping
@PatchMapping