TinyRenderer学习笔记
一、从画线开始
TinyRenderer项目用tga文件来查看渲染出的图片,引入tgaimage.h与.cpp
#ifndef __IMAGE_H__
#define __IMAGE_H__
#include
#pragma pack(push,1)
struct TGA_Header {
char idlength;
char colormaptype;
char datatypecode;
short colormaporigin;
short colormaplength;
char colormapdepth;
short x_origin;
short y_origin;
short width;
short height;
char bitsperpixel;
char imagedescriptor;
};
#pragma pack(pop)
struct TGAColor {
union {
struct {
unsigned char b, g, r, a;
};
unsigned char raw[4];
unsigned int val;
};
int bytespp;
TGAColor() : val(0), bytespp(1) {
}
TGAColor(unsigned char R, unsigned char G, unsigned char B, unsigned char A) : b(B), g(G), r(R), a(A), bytespp(4) {
}
TGAColor(int v, int bpp) : val(v), bytespp(bpp) {
}
TGAColor(const TGAColor &c) : val(c.val), bytespp(c.bytespp) {
}
TGAColor(const unsigned char *p, int bpp) : val(0), bytespp(bpp) {
for (int i=0; i #include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "tgaimage.h"
TGAImage::TGAImage() : data(NULL), width(0), height(0), bytespp(0) {
}
TGAImage::TGAImage(int w, int h, int bpp) : data(NULL), width(w), height(h), bytespp(bpp) {
unsigned long nbytes = width*height*bytespp;
data = new unsigned char[nbytes];
memset(data, 0, nbytes);
}
TGAImage::TGAImage(const TGAImage &img) {
width = img.width;
height = img.height;
bytespp = img.bytespp;
unsigned long nbytes = width*height*bytespp;
data = new unsigned char[nbytes];
memcpy(data, img.data, nbytes);
}
TGAImage::~TGAImage() {
if (data) delete [] data;
}
TGAImage & TGAImage::operator =(const TGAImage &img) {
if (this != &img) {
if (data) delete [] data;
width = img.width;
height = img.height;
bytespp = img.bytespp;
unsigned long nbytes = width*height*bytespp;
data = new unsigned char[nbytes];
memcpy(data, img.data, nbytes);
}
return *this;
}
bool TGAImage::read_tga_file(const char *filename) {
if (data) delete [] data;
data = NULL;
std::ifstream in;
in.open (filename, std::ios::binary);
if (!in.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "can't open file " << filename << "\n";
in.close();
return false;
}
TGA_Header header;
in.read((char *)&header, sizeof(header));
if (!in.good()) {
in.close();
std::cerr << "an error occured while reading the header\n";
return false;
}
width = header.width;
height = header.height;
bytespp = header.bitsperpixel>>3;
if (width<=0 || height<=0 || (bytespp!=GRAYSCALE && bytespp!=RGB && bytespp!=RGBA)) {
in.close();
std::cerr << "bad bpp (or width/height) value\n";
return false;
}
unsigned long nbytes = bytespp*width*height;
data = new unsigned char[nbytes];
if (3==header.datatypecode || 2==header.datatypecode) {
in.read((char *)data, nbytes);
if (!in.good()) {
in.close();
std::cerr << "an error occured while reading the data\n";
return false;
}
} else if (10==header.datatypecode||11==header.datatypecode) {
if (!load_rle_data(in)) {
in.close();
std::cerr << "an error occured while reading the data\n";
return false;
}
} else {
in.close();
std::cerr << "unknown file format " << (int)header.datatypecode << "\n";
return false;
}
if (!(header.imagedescriptor & 0x20)) {
flip_vertically();
}
if (header.imagedescriptor & 0x10) {
flip_horizontally();
}
std::cerr << width << "x" << height << "/" << bytespp*8 << "\n";
in.close();
return true;
}
bool TGAImage::load_rle_data(std::ifstream &in) {
unsigned long pixelcount = width*height;
unsigned long currentpixel = 0;
unsigned long currentbyte = 0;
TGAColor colorbuffer;
do {
unsigned char chunkheader = 0;
chunkheader = in.get();
if (!in.good()) {
std::cerr << "an error occured while reading the data\n";
return false;
}
if (chunkheader<128) {
chunkheader++;
for (int i=0; ipixelcount) {
std::cerr << "Too many pixels read\n";
return false;
}
}
} else {
chunkheader -= 127;
in.read((char *)colorbuffer.raw, bytespp);
if (!in.good()) {
std::cerr << "an error occured while reading the header\n";
return false;
}
for (int i=0; ipixelcount) {
std::cerr << "Too many pixels read\n";
return false;
}
}
}
} while (currentpixel < pixelcount);
return true;
}
bool TGAImage::write_tga_file(const char *filename, bool rle) {
unsigned char developer_area_ref[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0};
unsigned char extension_area_ref[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0};
unsigned char footer[18] = {'T','R','U','E','V','I','S','I','O','N','-','X','F','I','L','E','.','\0'};
std::ofstream out;
out.open (filename, std::ios::binary);
if (!out.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "can't open file " << filename << "\n";
out.close();
return false;
}
TGA_Header header;
memset((void *)&header, 0, sizeof(header));
header.bitsperpixel = bytespp<<3;
header.width = width;
header.height = height;
header.datatypecode = (bytespp==GRAYSCALE?(rle?11:3):(rle?10:2));
header.imagedescriptor = 0x20; // top-left origin
out.write((char *)&header, sizeof(header));
if (!out.good()) {
out.close();
std::cerr << "can't dump the tga file\n";
return false;
}
if (!rle) {
out.write((char *)data, width*height*bytespp);
if (!out.good()) {
std::cerr << "can't unload raw data\n";
out.close();
return false;
}
} else {
if (!unload_rle_data(out)) {
out.close();
std::cerr << "can't unload rle data\n";
return false;
}
}
out.write((char *)developer_area_ref, sizeof(developer_area_ref));
if (!out.good()) {
std::cerr << "can't dump the tga file\n";
out.close();
return false;
}
out.write((char *)extension_area_ref, sizeof(extension_area_ref));
if (!out.good()) {
std::cerr << "can't dump the tga file\n";
out.close();
return false;
}
out.write((char *)footer, sizeof(footer));
if (!out.good()) {
std::cerr << "can't dump the tga file\n";
out.close();
return false;
}
out.close();
return true;
}
// TODO: it is not necessary to break a raw chunk for two equal pixels (for the matter of the resulting size)
bool TGAImage::unload_rle_data(std::ofstream &out) {
const unsigned char max_chunk_length = 128;
unsigned long npixels = width*height;
unsigned long curpix = 0;
while (curpix=width || y>=height) {
return TGAColor();
}
return TGAColor(data+(x+y*width)*bytespp, bytespp);
}
bool TGAImage::set(int x, int y, TGAColor c) {
if (!data || x<0 || y<0 || x>=width || y>=height) {
return false;
}
memcpy(data+(x+y*width)*bytespp, c.raw, bytespp);
return true;
}
int TGAImage::get_bytespp() {
return bytespp;
}
int TGAImage::get_width() {
return width;
}
int TGAImage::get_height() {
return height;
}
bool TGAImage::flip_horizontally() {
if (!data) return false;
int half = width>>1;
for (int i=0; i>1;
for (int j=0; j=(int)width) {
errx -= width;
nx += bytespp;
memcpy(tdata+nscanline+nx, data+oscanline+ox, bytespp);
}
}
erry += h;
oscanline += olinebytes;
while (erry>=(int)height) {
if (erry>=(int)height<<1) // it means we jump over a scanline
memcpy(tdata+nscanline+nlinebytes, tdata+nscanline, nlinebytes);
erry -= height;
nscanline += nlinebytes;
}
}
delete [] data;
data = tdata;
width = w;
height = h;
return true;
}
有了以上的头文件支持,就可以输出到tga图片了!
#include
#include"tgaimage.h"
using namespace std;
const TGAColor white = TGAColor(255, 255, 255, 255);
const TGAColor red = TGAColor(255, 0, 0, 255);
void Line(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1, TGAImage& image, TGAColor color) {
for (int x = x0; x <= x1; x++) {
float t =(float)(x - x0) / (x1 - x0); //t是一个比例
int y = y0 + t * (y1 - y0);
image.set(x, y, color); //画点
}
}
int main() {
TGAImage image(100, 100, TGAImage::RGB); //创建一个tga图片
//Line(13, 20, 80, 40, image, white); //线段A
//Line(20, 13, 40, 80, image, red); //线段B
Line(80, 40, 13, 20, image, red);//线段C
//输出到图片
image.flip_vertically(); //左下角做原点
image.write_tga_file("output.tga");
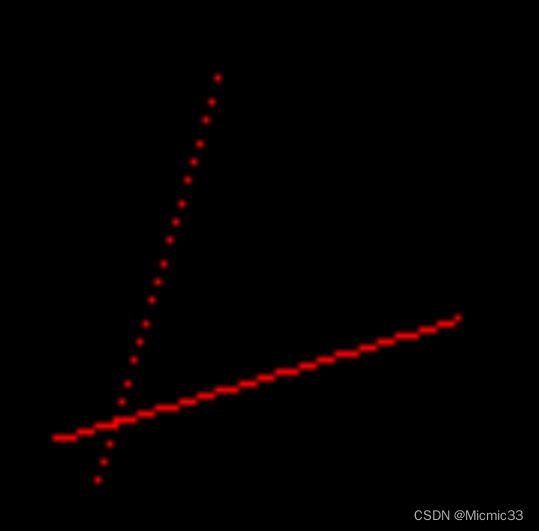
} 运行。此时,发现线段C并没有显示在图片里,为什么呢——其实它和A是一条线,但是现在的画线代码,只有x0,y0比x1,y1小时才管用,否则t算出来是<0的
添加代码:
if (x0 > x1)swap(x0, x1);
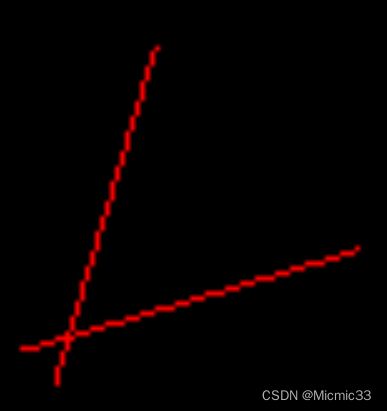
if (y0 > y1)swap(y0, y1);现在,C能正确绘制了,AC也是正确的覆盖关系(C后画,红线理应盖住白线)
问题是B画出来不是连续的线
为什么?因为它的k>1~~~
解决方式是,把这条线转换成根据y=x对称的线,这样,这条线的k就<0,实现了连续
在画点时,去画(y,x)点,不就刚好画出了原来要画的线吗
bool steep = false; //k>1?
if (abs(x0 - x1) < abs(y0 - y1)) {
swap(x0, y0);
swap(x1, y1);
steep = true;
}
if (steep)
image.set(y, x, color); //若k>1画根据y=x对称的点因此获得了画线算法的正确代码
#include
#include"tgaimage.h"
using namespace std;
const TGAColor white = TGAColor(255, 255, 255, 255);
const TGAColor red = TGAColor(255, 0, 0, 255);
void Line(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1, TGAImage& image, TGAColor color) {
if (x0 > x1)swap(x0, x1);
if (y0 > y1)swap(y0, y1);
bool steep = false; //k>1?
if (abs(x0 - x1) < abs(y0 - y1)) {
swap(x0, y0);
swap(x1, y1);
steep = true;
}
for (int x = x0; x <= x1; x++) {
float t =(float)(x - x0) / (x1 - x0); //t是一个比例
int y = y0 + t * (y1 - y0);
if (steep)
image.set(y, x, color); //若k>1画根据y=x对称的点
else
image.set(x, y, color); //画点
}
}
int main() {
TGAImage image(100, 100, TGAImage::RGB); //创建一个tga图片
Line(13, 20, 80, 40, image, white); //线段A
Line(20, 13, 40, 80, image, red); //线段B
Line(80, 40, 13, 20, image, red);//线段C
//输出到图片
image.flip_vertically(); //左下角做原点
image.write_tga_file("output.tga");
} 二、渲染模型线框
再引入关于向量等的geometry头文件
#ifndef __GEOMETRY_H__
#define __GEOMETRY_H__
#include
///
template struct Vec2 {
union {
struct { t u, v; };
struct { t x, y; };
t raw[2];
};
Vec2() : u(0), v(0) {}
Vec2(t _u, t _v) : u(_u), v(_v) {}
inline Vec2 operator +(const Vec2& V) const { return Vec2(u + V.u, v + V.v); }
inline Vec2 operator -(const Vec2& V) const { return Vec2(u - V.u, v - V.v); }
inline Vec2 operator *(float f) const { return Vec2(u * f, v * f); }
template friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& s, Vec2& v);
};
template struct Vec3 {
union {
struct { t x, y, z; };
struct { t ivert, iuv, inorm; };
t raw[3];
};
Vec3() : x(0), y(0), z(0) {}
Vec3(t _x, t _y, t _z) : x(_x), y(_y), z(_z) {}
inline Vec3 operator ^(const Vec3& v) const { return Vec3(y * v.z - z * v.y, z * v.x - x * v.z, x * v.y - y * v.x); }
inline Vec3 operator +(const Vec3& v) const { return Vec3(x + v.x, y + v.y, z + v.z); }
inline Vec3 operator -(const Vec3& v) const { return Vec3(x - v.x, y - v.y, z - v.z); }
inline Vec3 operator *(float f) const { return Vec3(x * f, y * f, z * f); }
inline t operator *(const Vec3& v) const { return x * v.x + y * v.y + z * v.z; }
float norm() const { return std::sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z); }
Vec3& normalize(t l = 1) { *this = (*this) * (l / norm()); return *this; }
template friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& s, Vec3& v);
};
typedef Vec2 Vec2f;
typedef Vec2 Vec2i;
typedef Vec3 Vec3f;
typedef Vec3 Vec3i;
template std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& s, Vec2& v) {
s << "(" << v.x << ", " << v.y << ")\n";
return s;
}
template std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& s, Vec3& v) {
s << "(" << v.x << ", " << v.y << ", " << v.z << ")\n";
return s;
}
#endif //__GEOMETRY_H__
以及处理模型的model文件
#ifndef __MODEL_H__
#define __MODEL_H__
#include
#include "geometry.h"
class Model {
private:
std::vector verts_;
std::vector > faces_;
public:
Model(const char *filename);
~Model();
int nverts();
int nfaces();
Vec3f vert(int i);
std::vector face(int idx);
};
#endif //__MODEL_H__
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "model.h"
Model::Model(const char *filename) : verts_(), faces_() {
std::ifstream in;
in.open (filename, std::ifstream::in);
if (in.fail()) return;
std::string line;
while (!in.eof()) {
std::getline(in, line);
std::istringstream iss(line.c_str());
char trash;
if (!line.compare(0, 2, "v ")) {
iss >> trash;
Vec3f v;
for (int i=0;i<3;i++) iss >> v.raw[i];
verts_.push_back(v);
} else if (!line.compare(0, 2, "f ")) {
std::vector f;
int itrash, idx;
iss >> trash;
while (iss >> idx >> trash >> itrash >> trash >> itrash) {
idx--; // in wavefront obj all indices start at 1, not zero
f.push_back(idx);
}
faces_.push_back(f);
}
}
std::cerr << "# v# " << verts_.size() << " f# " << faces_.size() << std::endl;
}
Model::~Model() {
}
int Model::nverts() {
return (int)verts_.size();
}
int Model::nfaces() {
return (int)faces_.size();
}
std::vector Model::face(int idx) {
return faces_[idx];
}
Vec3f Model::vert(int i) {
return verts_[i];
}
如何渲染线框?——连接模型中顶点组成的面的边就好了
遍历所有面,对于每个面,用刚刚的画线算法连三条线
(连的线需要在屏幕空间画,所以要进行一下坐标的转换)
(这里应该是TinyRenderer项目进行了一些简化,直接认为已经是一个标准立方体)
//模型的面作为循环控制变量
for (int i = 0; i < model->nfaces(); i++) {
//face数组:存储一个面的三个顶点坐标
std::vectorface = model->face(i);
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Vec3f v0 = model->vert(face[j]);
Vec3f v1 = model->vert(face[(j + 1) % 3]);
//分别找每个点和它的下一个点(可能越界,所以对3取模)
//对这两个点进行画线算法(不过首先要从世界坐标映射到屏幕坐标)
//这里直接默认把[-1,1]标准立方体的x,y映射到屏幕了
int x0 = (v0.x + 1.) * width / 2.;
int y0 = (v0.y + 1.) * height / 2.;
int x1 = (v1.x + 1.) * width / 2.;
int y1 = (v1.y + 1.) * height / 2.;
//画线
Line(x0, y0, x1, y1, image, white);
}
}
同时发现刚刚的画线算法有点错误
先处理斜率,再处理点哪个大哪个小
完整的线框渲染代码:
#include
#include
#include "tgaimage.h" //tga画图库
#include "model.h" //模型类,主要实现模型的读取
#include "geometry.h" //几何库,主要定义了Vec2和Vec3类型
#include
const TGAColor white = TGAColor(255, 255, 255, 255);
const TGAColor red = TGAColor(255, 0, 0, 255);
Model* model = NULL;
//定义宽度高度
const int width = 800;
const int height = 800;
//画线算法
void Line(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1, TGAImage& image, TGAColor color) {
bool steep = false; //k>1?
if (abs(x0 - x1) < abs(y0 - y1)) {
std::swap(x0, y0);
std::swap(x1, y1);
steep = true;
}
if (x0 > x1) {
std::swap(x0, x1);
std::swap(y0, y1);
}
for (int x = x0; x <= x1; x++) {
float t =(x - x0) / (float)(x1 - x0); //t是一个比例
int y = y0 + t * (y1 - y0);
if (steep)
image.set(y, x, color); //若k>1画根据y=x对称的点
else
image.set(x, y, color); //画点
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
//命令行控制方式和代码方式构造model
//构造模型(obj文件路径)
if (2 == argc) {
model = new Model(argv[1]);
}
else {
model = new Model("obj/african_head.obj");
}
//构造tga(宽,高,指定颜色空间)
TGAImage image(width, height, TGAImage::RGB);
//模型的面作为循环控制变量
for (int i = 0; i < model->nfaces(); i++) {
//face数组:存储一个面的三个顶点坐标
std::vectorface = model->face(i);
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Vec3f v0 = model->vert(face[j]);
Vec3f v1 = model->vert(face[(j + 1) % 3]);
//分别找每个点和它的下一个点(可能越界,所以对3取模)
//对这两个点进行画线算法(不过首先要从世界坐标映射到屏幕坐标)
//这里直接默认把[-1,1]标准立方体的x,y映射到屏幕了
int x0 = (v0.x + 1.) * width / 2.;
int y0 = (v0.y + 1.) * height / 2.;
int x1 = (v1.x + 1.) * width / 2.;
int y1 = (v1.y + 1.) * height / 2.;
//画线
Line(x0, y0, x1, y1, image, white);
}
}
//输出到图片
image.flip_vertically(); //左下角做原点
image.write_tga_file("output.tga");
delete model;
} 三、对三角形着色
利用二的知识,已经可以画出三角形线框,下一步,我们对三角形进行着色
//对三角形着色
//参数:3个顶点+tga指针+颜色
void triangle(Vec2i t0, Vec2i t1, Vec2i t2, TGAImage& image, TGAColor color) {
//三角形面积为0
if (t0.y == t1.y && t0.y == t2.y)return;
//把该三角形做成从下到上t0,t1,t2的三角形
if (t0.y > t1.y)std::swap(t0, t1);
if (t0.y > t2.y)std::swap(t0, t2);
if (t1.y > t2.y)std::swap(t1, t2);
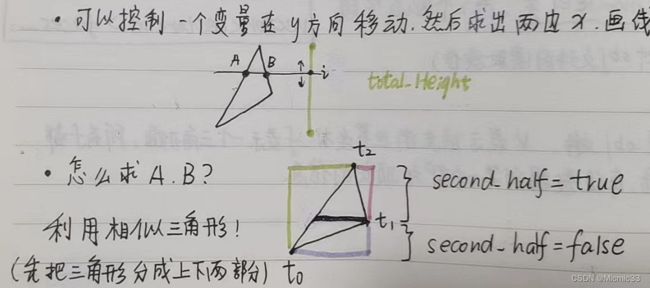
int total_height = t2.y - t0.y; //总高度差
//以i在y方向移动,横着画线,交点用相似三角形求
for (int i = 0; i < total_height; i++) {
//根据t1将三角形分割成上下两部分
bool second_half = i > t1.y - t0.y || t1.y == t0.y; //要么是过了t1,要么是平底三角形
//所在这一半三角形的高度
int segment_height = second_half ? t2.y - t1.y : t1.y - t0.y;
//相似三角形的比例
float alpha = (float)i / total_height; //左半边三角形比例
float beta = (float)(i - (second_half ? t1.y - t0.y : 0))/segment_height; //右半边三角形比例
//计算AB的坐标
Vec2i A = t0 + (t2 - t0) * alpha;
Vec2i B = second_half ? t1 + (t2 - t1) * beta : t0 + (t1 - t0) * beta;
//还要保证此算法A在B的左边
if (A.x > B.x)std::swap(A, B);
//根据当前i和它与三角形交出的边界点AB一条一条划横线着色
for (int j = A.x; j <= B.x; j++)
image.set(j, t0.y + i, color);
}
}对模型线框着色的完整代码:
#include
#include
#include "tgaimage.h" //tga画图库
#include "model.h" //模型类,主要实现模型的读取
#include "geometry.h" //几何库,主要定义了Vec2和Vec3类型
#include
const TGAColor white = TGAColor(255, 255, 255, 255);
const TGAColor red = TGAColor(255, 0, 0, 255);
const TGAColor green = TGAColor(0, 255, 0, 255);
Model* model = NULL;
//定义宽度高度
const int width = 800;
const int height = 800;
画线算法1.0
//void Line(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1, TGAImage& image, TGAColor color) {
// bool steep = false; //k>1?
// if (abs(x0 - x1) < abs(y0 - y1)) {
// std::swap(x0, y0);
// std::swap(x1, y1);
// steep = true;
// }
//
// if (x0 > x1) {
// std::swap(x0, x1);
// std::swap(y0, y1);
// }
//
// for (int x = x0; x <= x1; x++) {
// float t =(x - x0) / (float)(x1 - x0); //t是一个比例
// int y = y0 + t * (y1 - y0);
// if (steep)
// image.set(y, x, color); //若k>1画根据y=x对称的点
// else
// image.set(x, y, color); //画点
// }
//
//}
//画线算法2.0(事实上只是把原来四个参数xy换成了两个参数p,p有xy成员)
void Line(Vec2i p0, Vec2i p1, TGAImage& image, TGAColor color) {
bool steep=false;
if (abs(p0.x - p1.x) < abs(p0.y - p1.y)) {
std::swap(p0.x, p0.y);
std::swap(p1.x, p1.y);
steep = true;
}
if (p0.x > p1.x) {
std::swap(p0.x, p1.x);
std::swap(p0.y, p1.y);
}
for (int x = p0.x; x <= p1.x; x++) {
float t = (x - p0.x) / (float)(p1.x - p0.x);
int y = p0.y + t * (p1.y - p0.y);
if (steep)
image.set(y, x, color);
else
image.set(x, y, color);
}
}
//对三角形着色
//参数:3个顶点+tga指针+颜色
void triangle(Vec2i t0, Vec2i t1, Vec2i t2, TGAImage& image, TGAColor color) {
//三角形面积为0
if (t0.y == t1.y && t0.y == t2.y)return;
//把该三角形做成从下到上t0,t1,t2的三角形
if (t0.y > t1.y)std::swap(t0, t1);
if (t0.y > t2.y)std::swap(t0, t2);
if (t1.y > t2.y)std::swap(t1, t2);
int total_height = t2.y - t0.y; //总高度差
//以i在y方向移动,横着画线,交点用相似三角形求
for (int i = 0; i < total_height; i++) {
//根据t1将三角形分割成上下两部分
bool second_half = i > t1.y - t0.y || t1.y == t0.y; //要么是过了t1,要么是平底三角形
//所在这一半三角形的高度
int segment_height = second_half ? t2.y - t1.y : t1.y - t0.y;
//相似三角形的比例
float alpha = (float)i / total_height; //左半边三角形比例
float beta = (float)(i - (second_half ? t1.y - t0.y : 0))/segment_height; //右半边三角形比例
//计算AB的坐标
Vec2i A = t0 + (t2 - t0) * alpha;
Vec2i B = second_half ? t1 + (t2 - t1) * beta : t0 + (t1 - t0) * beta;
//还要保证此算法A在B的左边
if (A.x > B.x)std::swap(A, B);
//根据当前i和它与三角形交出的边界点AB一条一条划横线着色
for (int j = A.x; j <= B.x; j++)
image.set(j, t0.y + i, color);
}
}
//本人很闲的绘制三角形测试代码
void DrawYuanShi(TGAImage&image) {
Vec2i V0[3] = { Vec2i(100,400),Vec2i(400,400),Vec2i(250,500) };
Vec2i V1[3] = { Vec2i(250,500),Vec2i(400,400),Vec2i(400,700) };
Vec2i V2[3] = { Vec2i(550,500),Vec2i(400,400),Vec2i(400,700) };
Vec2i V3[3] = { Vec2i(550,500),Vec2i(400,400),Vec2i(700,400) };
Vec2i V4[3] = { Vec2i(550,300),Vec2i(400,400),Vec2i(700,400) };
Vec2i V5[3] = { Vec2i(550,300),Vec2i(400,400),Vec2i(400,100) };
Vec2i V6[3] = { Vec2i(250,300),Vec2i(400,400),Vec2i(400,100) };
Vec2i V7[3] = { Vec2i(100,400),Vec2i(400,400),Vec2i(250,300) };
triangle(V0[0], V0[1], V0[2], image, TGAColor(255, 182, 193, 0));
triangle(V1[0], V1[1], V1[2], image, TGAColor(255, 192, 203, 0));
triangle(V2[0], V2[1], V2[2], image, TGAColor(255, 182, 193, 0));
triangle(V3[0], V3[1], V3[2], image, TGAColor(135, 206, 250, 0));
triangle(V4[0], V4[1], V4[2], image, TGAColor(0, 191, 255, 0));
triangle(V5[0], V5[1], V5[2], image, TGAColor(30, 144, 255, 0));
triangle(V6[0], V6[1], V6[2], image, TGAColor(135, 206, 250, 0));
triangle(V7[0], V7[1], V7[2], image, TGAColor(0, 191, 255, 0));
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
//命令行控制方式和代码方式构造model
//构造模型(obj文件路径)
if (2 == argc) {
model = new Model(argv[1]);
}
else {
model = new Model("obj/african_head.obj");
}
//构造tga(宽,高,指定颜色空间)
TGAImage image(width, height, TGAImage::RGB);
//画画三角形试试:
//DrawYuanShi(image);
//(添加的模型变换、光照模型部分并不严谨!)
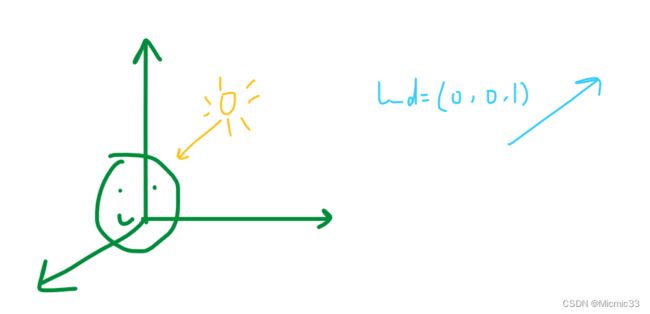
//指定光照方向
Vec3f light_dir(0, 0, -1);
//模型面作为循环控制变量
for (int i = 0; i < model->nfaces(); i++) {
std::vectorface = model->face(i);
Vec2i screen_coords[3]; //屏幕坐标
Vec3f world_coords[3]; //世界坐标
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Vec3f v = model->vert(face[j]);
screen_coords[j] = Vec2i((v.x + 1.) * width / 2., (v.y + 1.) * height / 2.);
world_coords[j] = v;
}
//用世界坐标计算这个面的法向量
Vec3f n = (world_coords[2] - world_coords[0]) ^ (world_coords[1] - world_coords[0]);
n.normalize();
float intensity = n * light_dir;
if (intensity > 0)
//注意这里的颜色乘上了光照强度
triangle(screen_coords[0], screen_coords[1], screen_coords[2], image, TGAColor(intensity * 255, intensity * 255, intensity * 255, 255));
}
//输出到图片
image.flip_vertically(); //左下角做原点
image.write_tga_file("output.tga");
delete model;
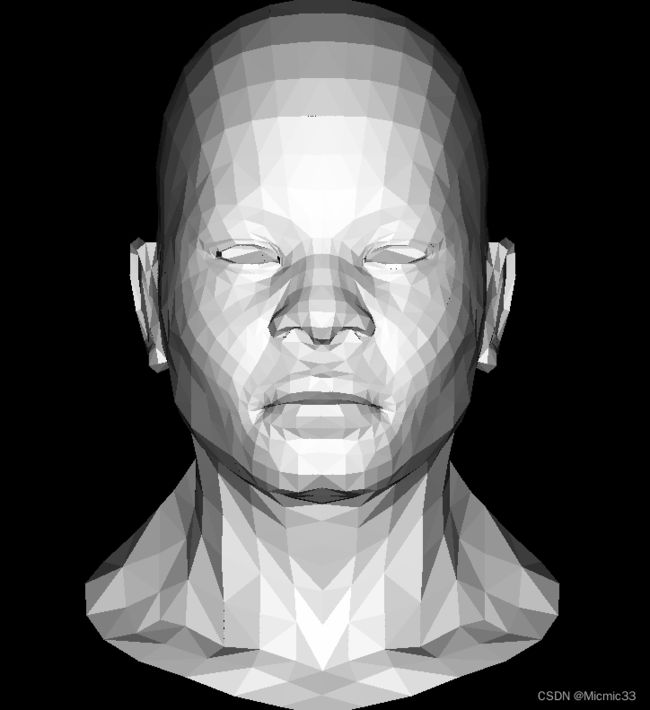
} 并不严谨,这里的法向量是直接用顶点的世界坐标叉乘得出每个面的法向量,再用法向量和光照相乘。
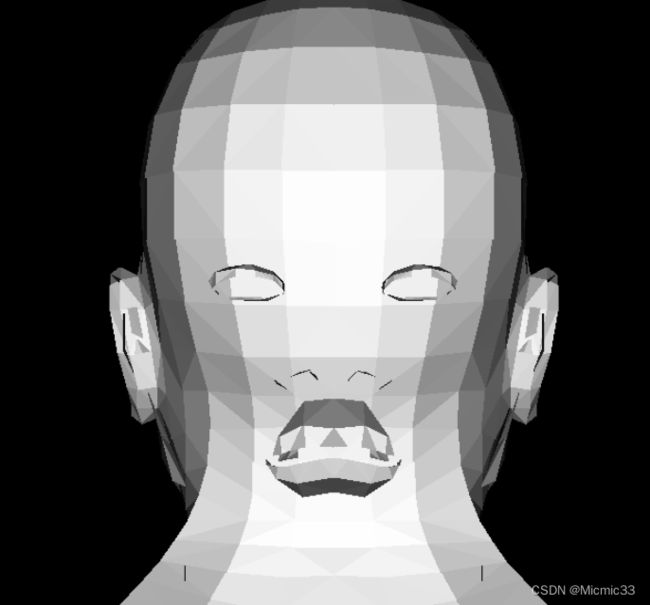
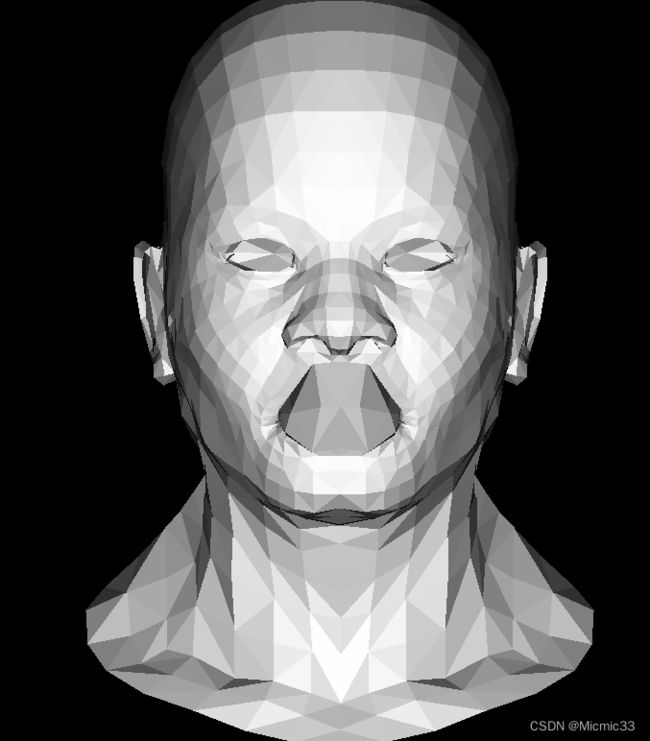
(结合后边zbuffer,应该是右手坐标系,因为把光线方向负方向改成(0,0,1)后就会变成下图这样)
(是没有添加zbuffer导致的,这种情况应该是后边被照亮了)
(光线方向和zbuffer似乎还是很别扭。。。)
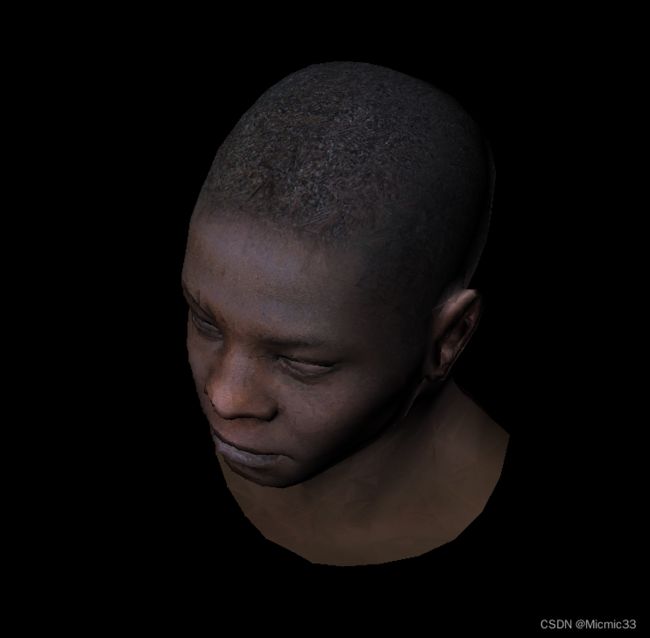
至此达到的效果:
四、添加zBuffer
this part要实现深度缓存,我们要离摄像机近的画面
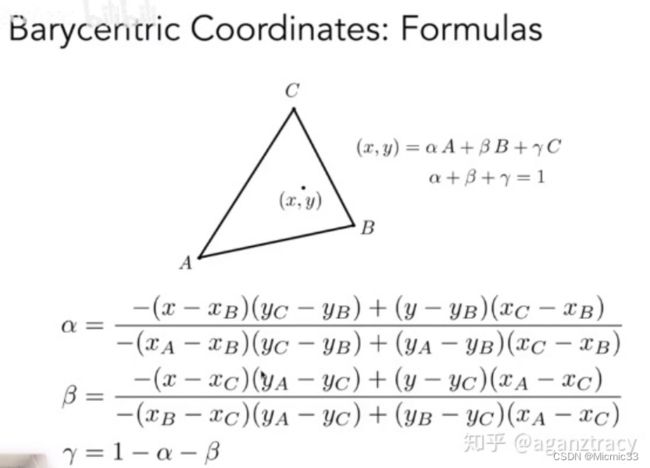
知道顶点深度,怎么求每个像素的深度?——引入了重心坐标进行插值(不只是深度,顶点的许多属性都是通过重心坐标插值去计算的)
重心坐标的计算:
推导过程大概是这样
加入zbuffer后的完整代码:
(不过这既不是games101中的phong光照模型,也没有mvp变换,很不标准。只需理解这个zbuffer就好)
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "tgaimage.h"
#include "model.h"
#include "geometry.h"
#include
const TGAColor white = TGAColor(255, 255, 255, 255);
const TGAColor red = TGAColor(255, 0, 0, 255);
const TGAColor green = TGAColor(0, 255, 0, 255);
Model* model = NULL;
//定义宽度高度
const int width = 800;
const int height = 800;
画线算法1.0
//void Line(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1, TGAImage& image, TGAColor color) {
// bool steep = false; //k>1?
// if (abs(x0 - x1) < abs(y0 - y1)) {
// std::swap(x0, y0);
// std::swap(x1, y1);
// steep = true;
// }
//
// if (x0 > x1) {
// std::swap(x0, x1);
// std::swap(y0, y1);
// }
//
// for (int x = x0; x <= x1; x++) {
// float t =(x - x0) / (float)(x1 - x0); //t是一个比例
// int y = y0 + t * (y1 - y0);
// if (steep)
// image.set(y, x, color); //若k>1画根据y=x对称的点
// else
// image.set(x, y, color); //画点
// }
//
//}
//画线算法2.0(事实上只是把原来四个参数xy换成了两个参数p,p有xy成员)
void Line(Vec2i p0, Vec2i p1, TGAImage& image, TGAColor color) {
bool steep=false;
if (abs(p0.x - p1.x) < abs(p0.y - p1.y)) {
std::swap(p0.x, p0.y);
std::swap(p1.x, p1.y);
steep = true;
}
if (p0.x > p1.x) {
std::swap(p0.x, p1.x);
std::swap(p0.y, p1.y);
}
for (int x = p0.x; x <= p1.x; x++) {
float t = (x - p0.x) / (float)(p1.x - p0.x);
int y = p0.y + t * (p1.y - p0.y);
if (steep)
image.set(y, x, color);
else
image.set(x, y, color);
}
}
//计算重心坐标
Vec3f barycentric(Vec3f v1, Vec3f v2, Vec3f v3, Vec3f p)
{
//别丢了分母等于0的情况
if ((-(v1.x - v2.x) * (v3.y - v2.y) + (v1.y - v2.y) * (v3.x - v2.x)) == 0)
return Vec3f(1, 0, 0);
if (-(v2.x - v3.x) * (v1.y - v3.y) + (v2.y - v3.y) * (v1.x - v3.x) == 0)
return Vec3f(1, 0, 0);
float alpha = (-(p.x - v2.x) * (v3.y - v2.y) + (p.y - v2.y) * (v3.x - v2.x)) / (-(v1.x - v2.x) * (v3.y - v2.y) + (v1.y - v2.y) * (v3.x - v2.x));
float beta = (-(p.x - v3.x) * (v1.y - v3.y) + (p.y - v3.y) * (v1.x - v3.x)) / (-(v2.x - v3.x) * (v1.y - v3.y) + (v2.y - v3.y) * (v1.x - v3.x));
float gamma = 1 - alpha - beta;
return Vec3f(alpha, beta, gamma);
}
//对三角形着色
//参数:3个顶点+tga指针+颜色
void triangle(Vec3f*pts, float *zbuffer,TGAImage& image, TGAColor color) {
//如何判断像素在三角形内--先看是否在包围盒内,如果在,看是否在三角形内
Vec2f bboxmin(std::numeric_limits::max(), std::numeric_limits::max());
Vec2f bboxmax(-std::numeric_limits::max(), -std::numeric_limits::max());
Vec2f clamp(image.get_width() - 1, image.get_height() - 1); //不能超过图像的大小
//确定boundingBox
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { //per Vertex
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) { //per x,y
bboxmin[j] = std::max(0.f, std::min(bboxmin[j], pts[i][j])); //左上边界
bboxmax[j] = std::min(clamp[j], std::max(bboxmax[j], pts[i][j])); //右下边界
}
}
Vec3f P; //用P去遍历包围盒中的每一个点
for (P.x = bboxmin.x; P.x <= bboxmax.x; P.x++) {
for (P.y = bboxmin.y; P.y <= bboxmax.y; P.y++) {
Vec3f bc_screen = barycentric(pts[0], pts[1], pts[2], P);
//质心坐标有一个负值,说明点在三角形外
if (bc_screen.x < 0 || bc_screen.y < 0 || bc_screen.z < 0) continue;
P.z = 0;
//对该像素点进行深度插值
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
P.z += pts[i][2] * bc_screen[i]; //对三个顶点的深度进行插值
//更新zbuffer(这个zbuffer是个一维数组)
if (zbuffer[int(P.x + P.y * width)] < P.z) {
zbuffer[int(P.x + P.y * width)] = P.z;
image.set(P.x, P.y, color); //对该点着色
}
}
}
}
Vec3f world2screen(Vec3f v) {
return Vec3f(int((v.x + 1.) * width / 2.), int((v.y + 1.) * height / 2. ), v.z);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
//命令行控制方式和代码方式构造model
//构造模型(obj文件路径)
if (2 == argc) {
model = new Model(argv[1]);
}
else {
model = new Model("obj/african_head/african_head.obj");
}
//构造tga(宽,高,指定颜色空间)
TGAImage image(width, height, TGAImage::RGB);
//创建zbuffer,大小为画布大小
float* zbuffer = new float[width * height];
//初始化zbuffer,设定一个很小的值
for (int i = width * height; i--; zbuffer[i] = -std::numeric_limits::max());
//(添加的模型变换、光照模型部分并不严谨!)
//指定光照方向
Vec3f light_dir(0, 0, -1);
//模型面作为循环控制变量
for (int i = 0; i < model->nfaces(); i++) {
std::vectorface = model->face(i);
Vec3f screen_coords[3]; //屏幕坐标
Vec3f world_coords[3]; //世界坐标
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Vec3f v = model->vert(face[j]);
screen_coords[j] = world2screen(v);
world_coords[j] = v;
}
//用世界坐标计算这个面的法向量
Vec3f n = cross((world_coords[2] - world_coords[0]), (world_coords[1] - world_coords[0]));
n.normalize();
float intensity = n * light_dir;
if (intensity > 0)
//注意这里的颜色乘上了光照强度
triangle(screen_coords, zbuffer, image, TGAColor(intensity * 255, intensity * 255, intensity * 255, 255));
}
//输出到图片
image.flip_vertically(); //左下角做原点
image.write_tga_file("output.tga");
delete model;
} 五、添加透视投影和uv贴图
这里既没有用bbox和重心插值去算uv贴图,透视矩阵和101也完全不同,视角矩阵之类的都只是针对特定数据,存疑...
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "tgaimage.h"
#include "model.h"
#include "geometry.h"
#include
const TGAColor white = TGAColor(255, 255, 255, 255);
const TGAColor red = TGAColor(255, 0, 0, 255);
const TGAColor green = TGAColor(0, 255, 0, 255);
Model* model = NULL;
//定义宽度高度
const int width = 800;
const int height = 800;
const int depth = 255;
Vec3f light_dir(0.2, 0.15, -1);
Vec3f camera(0, 0, 3);
//4d-->3d
//除以最后一个分量。(当最后一个分量为0,表示向量)
//不为0,表示坐标
Vec3f m2v(Matrix m) {
return Vec3f(m[0][0] / m[3][0], m[1][0] / m[3][0], m[2][0] / m[3][0]);
}
//3d-->4d
//添加一个1表示坐标
Matrix v2m(Vec3f v) {
Matrix m(4, 1);
m[0][0] = v.x;
m[1][0] = v.y;
m[2][0] = v.z;
m[3][0] = 1.f;
return m;
}
//视角矩阵
Matrix viewport(int x, int y, int w, int h) {
Matrix m = Matrix::identity(4);
m[0][3] = x + w / 2.f;
m[1][3] = y + h / 2.f;
m[2][3] = depth / 2.f;
m[0][0] = w / 2.f;
m[1][1] = h / 2.f;
m[2][2] = depth / 2.f;
return m;
}
画线算法1.0
//void Line(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1, TGAImage& image, TGAColor color) {
// bool steep = false; //k>1?
// if (abs(x0 - x1) < abs(y0 - y1)) {
// std::swap(x0, y0);
// std::swap(x1, y1);
// steep = true;
// }
//
// if (x0 > x1) {
// std::swap(x0, x1);
// std::swap(y0, y1);
// }
//
// for (int x = x0; x <= x1; x++) {
// float t =(x - x0) / (float)(x1 - x0); //t是一个比例
// int y = y0 + t * (y1 - y0);
// if (steep)
// image.set(y, x, color); //若k>1画根据y=x对称的点
// else
// image.set(x, y, color); //画点
// }
//
//}
//画线算法2.0(事实上只是把原来四个参数xy换成了两个参数p,p有xy成员)
void Line(Vec2i p0, Vec2i p1, TGAImage& image, TGAColor color) {
bool steep=false;
if (abs(p0.x - p1.x) < abs(p0.y - p1.y)) {
std::swap(p0.x, p0.y);
std::swap(p1.x, p1.y);
steep = true;
}
if (p0.x > p1.x) {
std::swap(p0.x, p1.x);
std::swap(p0.y, p1.y);
}
for (int x = p0.x; x <= p1.x; x++) {
float t = (x - p0.x) / (float)(p1.x - p0.x);
int y = p0.y + t * (p1.y - p0.y);
if (steep)
image.set(y, x, color);
else
image.set(x, y, color);
}
}
//计算重心坐标
Vec3f barycentric(Vec3f v1, Vec3f v2, Vec3f v3, Vec3f p)
{
//别丢了分母等于0的情况
if ((-(v1.x - v2.x) * (v3.y - v2.y) + (v1.y - v2.y) * (v3.x - v2.x)) == 0)
return Vec3f(1, 0, 0);
if (-(v2.x - v3.x) * (v1.y - v3.y) + (v2.y - v3.y) * (v1.x - v3.x) == 0)
return Vec3f(1, 0, 0);
float alpha = (-(p.x - v2.x) * (v3.y - v2.y) + (p.y - v2.y) * (v3.x - v2.x)) / (-(v1.x - v2.x) * (v3.y - v2.y) + (v1.y - v2.y) * (v3.x - v2.x));
float beta = (-(p.x - v3.x) * (v1.y - v3.y) + (p.y - v3.y) * (v1.x - v3.x)) / (-(v2.x - v3.x) * (v1.y - v3.y) + (v2.y - v3.y) * (v1.x - v3.x));
float gamma = 1 - alpha - beta;
return Vec3f(alpha, beta, gamma);
}
//绘制三角形(顶点坐标,uv坐标,tga指针,亮度,zbuffer)
void triangle(Vec3i t0, Vec3i t1, Vec3i t2, Vec2i uv0, Vec2i uv1, Vec2i uv2, TGAImage& image, float intensity, int* zbuffer) {
if (t0.y == t1.y && t0.y == t2.y) return;
//分割成两个三角形
if (t0.y > t1.y) { std::swap(t0, t1); std::swap(uv0, uv1); }
if (t0.y > t2.y) { std::swap(t0, t2); std::swap(uv0, uv2); }
if (t1.y > t2.y) { std::swap(t1, t2); std::swap(uv1, uv2); }
//用高度做循环控制
int total_height = t2.y - t0.y;
for (int i = 0; i < total_height; i++) {
//判断属于哪一部分以确定高度
bool second_half = i > t1.y - t0.y || t1.y == t0.y;
int segment_height = second_half ? t2.y - t1.y : t1.y - t0.y;
//计算当前的比例
float alpha = (float)i / total_height;
float beta = (float)(i - (second_half ? t1.y - t0.y : 0)) / segment_height; // be careful: with above conditions no division by zero here
//A表示t0与t2之间的点
//B表示t0与t1之间的点
Vec3i A = t0 + Vec3f(t2 - t0) * alpha;
Vec3i B = second_half ? t1 + Vec3f(t2 - t1) * beta : t0 + Vec3f(t1 - t0) * beta;
//计算UV
Vec2i uvA = uv0 + (uv2 - uv0) * alpha;
Vec2i uvB = second_half ? uv1 + (uv2 - uv1) * beta : uv0 + (uv1 - uv0) * beta;
//保证B在A的右边
if (A.x > B.x) { std::swap(A, B); }// std::swap(uvA, uvB);}
//用横坐标作为循环控制,对这一行进行着色
for (int j = A.x; j <= B.x; j++) {
//计算当前点在AB之间的比例
float phi = B.x == A.x ? 1. : (float)(j - A.x) / (float)(B.x - A.x);
//计算出当前点的坐标和uv坐标,A,B保存了z轴信息
Vec3i P = Vec3f(A) + Vec3f(B - A) * phi;
Vec2i uvP = uvA + (uvB - uvA) * phi;
if (P.x < width && P.y < height)
{
//计算当前zbuffer下标=P.x+P.y*width
int idx = P.x + P.y * width;
//当前点的z大于zbuffer信息,覆盖掉,并更新zbuffer
if (zbuffer[idx] < P.z) {
zbuffer[idx] = P.z;
TGAColor color = model->diffuse(uvP);
image.set(P.x, P.y, TGAColor(color.r * intensity, color.g * intensity, color.b * intensity));
}
}
}
}
}
Vec3f world2screen(Vec3f v) {
return Vec3f(int((v.x + 1.) * width / 2.), int((v.y + 1.) * height / 2. ), v.z);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
//命令行控制方式和代码方式构造model
//构造模型(obj文件路径)
if (2 == argc) {
model = new Model(argv[1]);
}
else {
model = new Model("obj/african_head/african_head.obj");
}
//构造tga(宽,高,指定颜色空间)
TGAImage image(width, height, TGAImage::RGB);
int * zbuffer = NULL;
//初始化zbuffer,设定一个很小的值
zbuffer = new int[width * height];
for (int i = 0; i < width * height; i++) {
//初始化zbuffer
zbuffer[i] = std::numeric_limits::min();
}
//(添加的模型变换、光照模型部分并不严谨!)
//初始化投影矩阵
Matrix Projection = Matrix::identity(4);
//初始化视角矩阵
Matrix ViewPort = viewport(width / 8, height / 8, width * 3 / 4, height * 3 / 4);
//投影矩阵[3][2]=-1/c,c为相机z坐标
Projection[3][2] = -1.f / camera.z;
//模型面作为循环控制变量
for (int i = 0; i < model->nfaces(); i++) {
std::vectorface = model->face(i);
Vec3i screen_coords[3]; //屏幕坐标
Vec3f world_coords[3]; //世界坐标
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Vec3f v = model->vert(face[j]);
//视角矩阵*投影矩阵*坐标
screen_coords[j] = m2v(ViewPort * Projection * v2m(v));
world_coords[j] = v;
}
//用世界坐标计算这个面的法向量
Vec3f n = (world_coords[2] - world_coords[0]) ^ (world_coords[1] - world_coords[0]);
n.normalize();
float intensity = n * light_dir;
intensity = std::min(std::abs(intensity), 1.f);
if (intensity > 0) {
Vec2i uv[3];
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
uv[k] = model->uv(i, k);
}
//绘制三角形
triangle(screen_coords[0], screen_coords[1], screen_coords[2], uv[0], uv[1], uv[2], image, intensity, zbuffer);
}
}
//输出到图片
image.flip_vertically(); //左下角做原点
image.write_tga_file("output.tga");
delete model;
} 六、移动相机
此处的变换矩阵仍与game101不尽相同
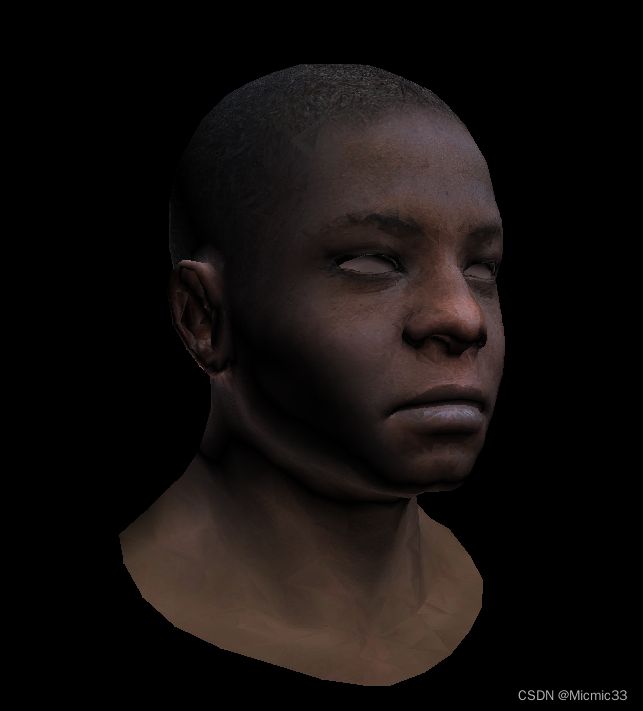
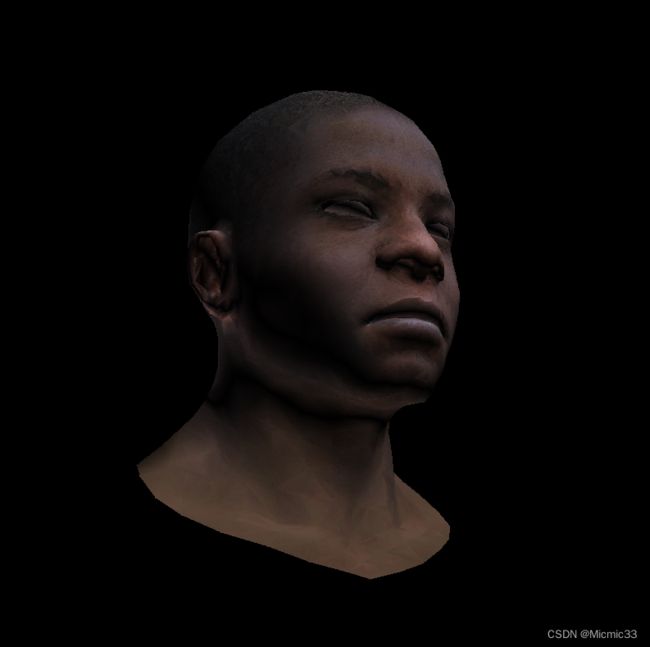
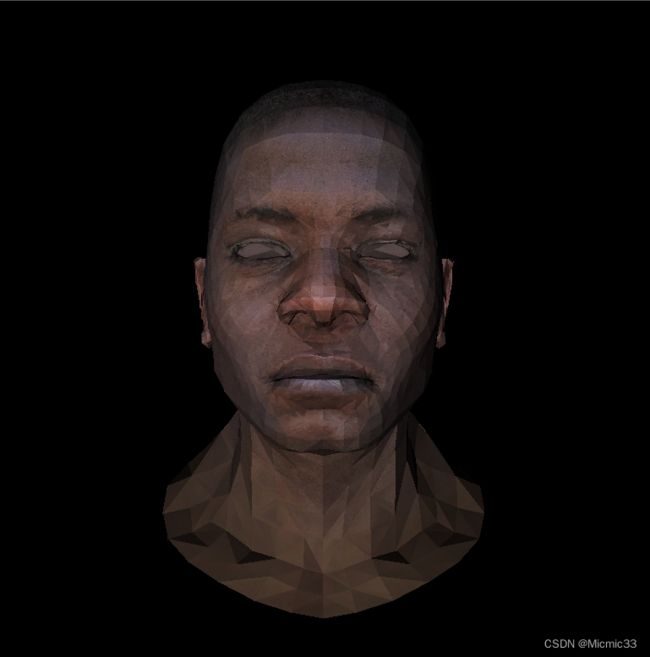
这一次的颜色过渡平滑了很多,注意观察光照处添加了光的falloff(这里还是和games101不一样,别扭.....)
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "tgaimage.h"
#include "model.h"
#include "geometry.h"
#include
const int width = 800;
const int height = 800;
const int depth = 255;
Model* model = NULL;
int* zbuffer = NULL;
Vec3f light_dir = Vec3f(0, -1, -1).normalize();
//摄像机位置
Vec3f eye(0, 0, 3);
//焦点位置
Vec3f center(0, 0, 0);
//视角矩阵,用于将(-1,1),(-1,1),(-1,1)映射到(1/8w,7/8w),(1/8h,7/8h),(0,255)
Matrix viewport(int x, int y, int w, int h) {
Matrix m = Matrix::identity(4);
m[0][3] = x + w / 2.f;
m[1][3] = y + h / 2.f;
m[2][3] = depth / 2.f;
m[0][0] = w / 2.f;
m[1][1] = h / 2.f;
m[2][2] = depth / 2.f;
return m;
}
//朝向矩阵,变换矩阵
//更改摄像机视角=更改物体位置和角度,操作为互逆矩阵
//摄像机变换是先旋转再平移,所以物体需要先平移后旋转,且都是逆矩阵
Matrix lookat(Vec3f eye, Vec3f center, Vec3f up) {
//计算出z,根据z和up算出x,再算出y
Vec3f z = (eye - center).normalize();
Vec3f x = (up ^ z).normalize();
Vec3f y = (z ^ x).normalize();
Matrix rotation = Matrix::identity(4);
Matrix translation = Matrix::identity(4);
//***矩阵的第四列是用于平移的。因为观察位置从原点变为了center,所以需要将物体平移-center***
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
translation[i][3] = -center[i];
}
//正交矩阵的逆 = 正交矩阵的转置
//矩阵的第一行即是现在的x
//矩阵的第二行即是现在的y
//矩阵的第三行即是现在的z
//***矩阵的三阶子矩阵是当前视线旋转矩阵的逆矩阵***
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
rotation[0][i] = x[i];
rotation[1][i] = y[i];
rotation[2][i] = z[i];
}
//这样乘法的效果是先平移物体,再旋转
Matrix res = rotation * translation;
return res;
}
//绘制三角形(坐标1,坐标2,坐标3,顶点光照强度1,顶点光照强度2,顶点光照强度3,tga指针,zbuffer)
void triangle(Vec3i t0, Vec3i t1, Vec3i t2, float ity0, float ity1, float ity2, Vec2i uv0, Vec2i uv1, Vec2i uv2, float dis0, float dis1, float dis2, TGAImage& image, int* zbuffer) {
//按照y分割为两个三角形
if (t0.y == t1.y && t0.y == t2.y) return;
if (t0.y > t1.y) { std::swap(t0, t1); std::swap(ity0, ity1); std::swap(uv0, uv1); }
if (t0.y > t2.y) { std::swap(t0, t2); std::swap(ity0, ity2); std::swap(uv0, uv2); }
if (t1.y > t2.y) { std::swap(t1, t2); std::swap(ity1, ity2); std::swap(uv1, uv2); }
int total_height = t2.y - t0.y;
for (int i = 0; i < total_height; i++) {
bool second_half = i > t1.y - t0.y || t1.y == t0.y;
int segment_height = second_half ? t2.y - t1.y : t1.y - t0.y;
float alpha = (float)i / total_height;
float beta = (float)(i - (second_half ? t1.y - t0.y : 0)) / segment_height;
//计算A,B两点的坐标
Vec3i A = t0 + Vec3f(t2 - t0) * alpha;
Vec3i B = second_half ? t1 + Vec3f(t2 - t1) * beta : t0 + Vec3f(t1 - t0) * beta;
//计算A,B两点的光照强度
float ityA = ity0 + (ity2 - ity0) * alpha;
float ityB = second_half ? ity1 + (ity2 - ity1) * beta : ity0 + (ity1 - ity0) * beta;
//计算UV
Vec2i uvA = uv0 + (uv2 - uv0) * alpha;
Vec2i uvB = second_half ? uv1 + (uv2 - uv1) * beta : uv0 + (uv1 - uv0) * beta;
//计算距离
float disA = dis0 + (dis2 - dis0) * alpha;
float disB = second_half ? dis1 + (dis2 - dis1) * beta : dis0 + (dis1 - dis0) * beta;
if (A.x > B.x) { std::swap(A, B); std::swap(ityA, ityB); }
//x坐标作为循环控制
for (int j = A.x; j <= B.x; j++) {
float phi = B.x == A.x ? 1. : (float)(j - A.x) / (B.x - A.x);
//计算当前需要绘制点P的坐标,光照强度
Vec3i P = Vec3f(A) + Vec3f(B - A) * phi;
float ityP = ityA + (ityB - ityA) * phi;
ityP = std::min(1.f, std::abs(ityP) + 0.01f);
Vec2i uvP = uvA + (uvB - uvA) * phi;
float disP = disA + (disB - disA) * phi;
int idx = P.x + P.y * width;
//边界限制
if (P.x >= width || P.y >= height || P.x < 0 || P.y < 0) continue;
if (zbuffer[idx] < P.z) {
zbuffer[idx] = P.z;
TGAColor color = model->diffuse(uvP);
image.set(P.x, P.y, TGAColor(color.bgra[2], color.bgra[1], color.bgra[0]) * ityP * (20.f / std::pow(disP, 2.f)));
//image.set(P.x, P.y, TGAColor(255,255,255)* ityP);
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
//读取模型
if (2 == argc) {
model = new Model(argv[1]);
}
else {
model = new Model("obj/african_head/african_head.obj");
}
//构造zbuffer并初始化
zbuffer = new int[width * height];
for (int i = 0; i < width * height; i++) {
zbuffer[i] = std::numeric_limits::min();
}
//绘制模型
{
//模型变换矩阵
Matrix ModelView = lookat(eye, center, Vec3f(0, 1, 0));
//透视矩阵
Matrix Projection = Matrix::identity(4);
Projection[3][2] = -1.f / (eye - center).norm();
//视角矩阵
Matrix ViewPort = viewport(width / 8, height / 8, width * 3 / 4, height * 3 / 4);
TGAImage image(width, height, TGAImage::RGB);
for (int i = 0; i < model->nfaces(); i++) {
std::vector face = model->face(i);
Vec3i screen_coords[3];
float intensity[3];
float distance[3];
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Vec3f v = model->vert(face[j]);
Matrix m_v = ModelView * Matrix(v);
screen_coords[j] = Vec3f(ViewPort * Projection * m_v);
intensity[j] = model->norm(i, j) * light_dir;
Vec3f new_v = Vec3f(m_v);
distance[j] = std::pow((std::pow(new_v.x - eye.x, 2.0f) + std::pow(new_v.y - eye.y, 2.0f) + std::pow(new_v.z - eye.z, 2.0f)), 0.5f);
}
Vec2i uv[3];
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
uv[k] = model->uv(i, k);
}
triangle(screen_coords[0], screen_coords[1], screen_coords[2], intensity[0], intensity[1], intensity[2], uv[0], uv[1], uv[2], distance[0], distance[1], distance[2], image, zbuffer);
}
image.flip_vertically();
image.write_tga_file("output.tga");
}
//输出zbuffer图像
{
TGAImage zbimage(width, height, TGAImage::GRAYSCALE);
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < height; j++) {
zbimage.set(i, j, TGAColor(zbuffer[i + j * width]));
}
}
zbimage.flip_vertically();
zbimage.write_tga_file("zbuffer.tga");
}
delete model;
delete[] zbuffer;
return 0;
}