S变换介绍(附代码)
1、S变换
作为小波变换和短时傅里叶变换的继承和发展, S 变换采用高斯窗函数且窗宽与频率的倒数成正比,免去了窗函数的选择和改善了窗宽固定的缺陷,并且时频表示中各频率分量的相位谱与原始信号保持直接的联系,使其在 PQD 分析中可以采用更多的特征量,同时, S 变换提取的特征量对噪声不敏感。因此,在电能电能质量扰动、轴承故障诊断领域运用广泛。适用于非平稳信号的时频分析方法,其定义为:
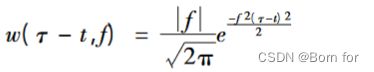
2、S变换matlab代码
unction [st,t,f] = st(timeseries,minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate)
% Returns the Stockwell Transform of the timeseries.
% Code by Robert Glenn Stockwell.
% DO NOT DISTRIBUTE
% BETA TEST ONLY
% Reference is "Localization of the Complex Spectrum: The S Transform"
% from IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 44., number 4, April 1996, pages 998-1001.
%
%-------Inputs Needed------------------------------------------------
%
% *****All frequencies in (cycles/(time unit))!******
% "timeseries" - vector of data to be transformed
%-------Optional Inputs ------------------------------------------------
%
%"minfreq" is the minimum frequency in the ST result(Default=0)
%"maxfreq" is the maximum frequency in the ST result (Default=Nyquist)
%"samplingrate" is the time interval between samples (Default=1)
%"freqsamplingrate" is the frequency-sampling interval you desire in the ST result (Default=1)
%Passing a negative number will give the default ex. [s,t,f] = st(data,-1,-1,2,2)
%-------Outputs Returned------------------------------------------------
%
% st -a complex matrix containing the Stockwell transform.
% The rows of STOutput are the frequencies and the
% columns are the time values ie each column is
% the "local spectrum" for that point in time
% t - a vector containing the sampled times
% f - a vector containing the sampled frequencies
%--------Additional details-----------------------
% % There are several parameters immediately below that
% the user may change. They are:
%[verbose] if true prints out informational messages throughout the function.
%[removeedge] if true, removes a least squares fit parabola
% and puts a 5% hanning taper on the edges of the time series.
% This is usually a good idea.
%[analytic_signal] if the timeseries is real-valued
% this takes the analytic signal and STs it.
% This is almost always a good idea.
%[factor] the width factor of the localizing gaussian
% ie, a sinusoid of period 10 seconds has a
% gaussian window of width factor*10 seconds.
% I usually use factor=1, but sometimes factor = 3
% to get better frequency resolution.
% Copyright (c) by Bob Stockwell
% $Revision: 1.2 $ $Date: 1997/07/08 $
% This is the S transform wrapper that holds default values for the function.
TRUE = 1;
FALSE = 0;
%%% DEFAULT PARAMETERS [change these for your particular application]
verbose = TRUE;
removeedge= FALSE;
analytic_signal = FALSE;
factor = 1;
%%% END of DEFAULT PARAMETERS
%%%START OF INPUT VARIABLE CHECK
% First: make sure it is a valid time_series
% If not, return the help message
if verbose disp(' '),end % i like a line left blank
if nargin == 0
if verbose disp('No parameters inputted.'),end
st_help
t=0;,st=-1;,f=0;
return
end
% Change to column vector
if size(timeseries,2) > size(timeseries,1)
timeseries=timeseries';
end
% Make sure it is a 1-dimensional array
if size(timeseries,2) > 1
error('Please enter a *vector* of data, not matrix')
return
elseif (size(timeseries)==[1 1]) == 1
error('Please enter a *vector* of data, not a scalar')
return
end
% use defaults for input variables
if nargin == 1
minfreq = 0;
maxfreq = fix(length(timeseries)/2);
samplingrate=1;
freqsamplingrate=1;
elseif nargin==2
maxfreq = fix(length(timeseries)/2);
samplingrate=1;
freqsamplingrate=1;
[ minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate] = check_input(minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,timeseries);
elseif nargin==3
samplingrate=1;
freqsamplingrate=1;
[ minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate] = check_input(minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,timeseries);
elseif nargin==4
freqsamplingrate=1;
[ minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate] = check_input(minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,timeseries);
elseif nargin == 5
[ minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate] = check_input(minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,timeseries);
else
if verbose disp('Error in input arguments: using defaults'),end
minfreq = 0;
maxfreq = fix(length(timeseries)/2);
samplingrate=1;
freqsamplingrate=1;
end
if verbose
disp(sprintf('Minfreq = %d',minfreq))
disp(sprintf('Maxfreq = %d',maxfreq))
disp(sprintf('Sampling Rate (time domain) = %d',samplingrate))
disp(sprintf('Sampling Rate (freq. domain) = %d',freqsamplingrate))
disp(sprintf('The length of the timeseries is %d points',length(timeseries)))
disp(' ')
end
%END OF INPUT VARIABLE CHECK
% If you want to "hardwire" minfreq & maxfreq & samplingrate & freqsamplingrate do it here
% calculate the sampled time and frequency values from the two sampling rates
t = (0:length(timeseries)-1)*samplingrate;
spe_nelements =ceil((maxfreq - minfreq+1)/freqsamplingrate) ;
f = (minfreq + [0:spe_nelements-1]*freqsamplingrate)/(samplingrate*length(timeseries));
if verbose disp(sprintf('The number of frequency voices is %d',spe_nelements)),end
% The actual S Transform function is here:
st = strans(timeseries,minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,removeedge,analytic_signal,factor);
% this function is below, thus nicely encapsulated
%WRITE switch statement on nargout
% if 0 then plot amplitude spectrum
if nargout==0
if verbose disp('Plotting pseudocolor image'),end
pcolor(t,f,abs(st))
end
return
%^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
%^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
%^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
%^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
%^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
function st = strans(timeseries,minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,removeedge,analytic_signal,factor);
% Returns the Stockwell Transform, STOutput, of the time-series
% Code by R.G. Stockwell.
% Reference is "Localization of the Complex Spectrum: The S Transform"
% from IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 44., number 4,
% April 1996, pages 998-1001.
%
%-------Inputs Returned------------------------------------------------
% - are all taken care of in the wrapper function above
%
%-------Outputs Returned------------------------------------------------
%
% ST -a complex matrix containing the Stockwell transform.
% The rows of STOutput are the frequencies and the
% columns are the time values
%
%
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------
% Compute the length of the data.
n=length(timeseries);
original = timeseries;
if removeedge
if verbose disp('Removing trend with polynomial fit'),end
ind = [0:n-1]';
r = polyfit(ind,timeseries,2);
fit = polyval(r,ind) ;
timeseries = timeseries - fit;
if verbose disp('Removing edges with 5% hanning taper'),end
sh_len = floor(length(timeseries)/10);
wn = hanning(sh_len);
if(sh_len==0)
sh_len=length(timeseries);
wn = 1&[1:sh_len];
end
% make sure wn is a column vector, because timeseries is
if size(wn,2) > size(wn,1)
wn=wn';
end
timeseries(1:floor(sh_len/2),1) = timeseries(1:floor(sh_len/2),1).*wn(1:floor(sh_len/2),1);
timeseries(length(timeseries)-floor(sh_len/2):n,1) = timeseries(length(timeseries)-floor(sh_len/2):n,1).*wn(sh_len-floor(sh_len/2):sh_len,1);
end
% If vector is real, do the analytic signal
if analytic_signal
if verbose disp('Calculating analytic signal (using Hilbert transform)'),end
% this version of the hilbert transform is different than hilbert.m
% This is correct!
ts_spe = fft(real(timeseries));
h = [1; 2*ones(fix((n-1)/2),1); ones(1-rem(n,2),1); zeros(fix((n-1)/2),1)];
ts_spe(:) = ts_spe.*h(:);
timeseries = ifft(ts_spe);
end
% Compute FFT's
tic;vector_fft=fft(timeseries);tim_est=toc;
vector_fft=[vector_fft,vector_fft];
tim_est = tim_est*ceil((maxfreq - minfreq+1)/freqsamplingrate) ;
if verbose disp(sprintf('Estimated time is %f',tim_est)),end
% Preallocate the STOutput matrix
st=zeros(ceil((maxfreq - minfreq+1)/freqsamplingrate),n);
% Compute the mean
% Compute S-transform value for 1 ... ceil(n/2+1)-1 frequency points
if verbose disp('Calculating S transform...'),end
if minfreq == 0
st(1,:) = mean(timeseries)*(1&[1:1:n]);
else
st(1,:)=ifft(vector_fft(minfreq+1:minfreq+n).*g_window(n,minfreq,factor));
end
%the actual calculation of the ST
% Start loop to increment the frequency point
for banana=freqsamplingrate:freqsamplingrate:(maxfreq-minfreq)
st(banana/freqsamplingrate+1,:)=ifft(vector_fft(minfreq+banana+1:minfreq+banana+n).*g_window(n,minfreq+banana,factor));
end % a fruit loop! aaaaa ha ha ha ha ha ha ha ha ha ha
% End loop to increment the frequency point
if verbose disp('Finished Calculation'),end
%%% end strans function
%------------------------------------------------------------------------
function gauss=g_window(length,freq,factor)
% Function to compute the Gaussion window for
% function Stransform. g_window is used by function
% Stransform. Programmed by Eric Tittley
%
%-----Inputs Needed--------------------------
%
% length-the length of the Gaussian window
%
% freq-the frequency at which to evaluate
% the window.
% factor- the window-width factor
%
%-----Outputs Returned--------------------------
%
% gauss-The Gaussian window
%
vector(1,:)=[0:length-1];
vector(2,:)=[-length:-1];
vector=vector.^2;
vector=vector*(-factor*2*pi^2/freq^2);
% Compute the Gaussion window
gauss=sum(exp(vector));
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------
%^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^%
function [ minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate] = check_input(minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,timeseries)
% this checks numbers, and replaces them with defaults if invalid
% if the parameters are passed as an array, put them into the appropriate variables
s = size(minfreq);
l = max(s);
if l > 1
if verbose disp('Array of inputs accepted.'),end
temp=minfreq;
minfreq = temp(1);;
if l > 1 maxfreq = temp(2);,end;
if l > 2 samplingrate = temp(3);,end;
if l > 3 freqsamplingrate = temp(4);,end;
if l > 4
if verbose disp('Ignoring extra input parameters.'),end
end;
end
if minfreq < 0 | minfreq > fix(length(timeseries)/2);
minfreq = 0;
if verbose disp('Minfreq < 0 or > Nyquist. Setting minfreq = 0.'),end
end
if maxfreq > length(timeseries)/2 | maxfreq < 0
maxfreq = fix(length(timeseries)/2);
if verbose disp(sprintf('Maxfreq < 0 or > Nyquist. Setting maxfreq = %d',maxfreq)),end
end
if minfreq > maxfreq
temporary = minfreq;
minfreq = maxfreq;
maxfreq = temporary;
clear temporary;
if verbose disp('Swapping maxfreq <=> minfreq.'),end
end
if samplingrate <0
samplingrate = abs(samplingrate);
if verbose disp('Samplingrate <0. Setting samplingrate to its absolute value.'),end
end
if freqsamplingrate < 0 % check 'what if freqsamplingrate > maxfreq - minfreq' case
freqsamplingrate = abs(freqsamplingrate);
if verbose disp('Frequency Samplingrate negative, taking absolute value'),end
end
% bloody odd how you don't end a function
%^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^%
function st_help
disp(' ')
disp('st() HELP COMMAND')
disp('st() returns - 1 or an error message if it fails')
disp('USAGE:: [localspectra,timevector,freqvector] = st(timeseries)')
disp('NOTE:: The function st() sets default parameters then calls the function strans()')
disp(' ')
disp('You can call strans() directly and pass the following parameters')
disp(' **** Warning! These inputs are not checked if strans() is called directly!! ****')
disp('USAGE:: localspectra = strans(timeseries,minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,removeedge,analytic_signal,factor) ')
disp(' ')
disp('Default parameters (available in st.m)')
disp('VERBOSE - prints out informational messages throughout the function.')
disp('REMOVEEDGE - removes the edge with a 5% taper, and takes')
disp('FACTOR - the width factor of the localizing gaussian')
disp(' ie, a sinusoid of period 10 seconds has a ')
disp(' gaussian window of width factor*10 seconds.')
disp(' I usually use factor=1, but sometimes factor = 3')
disp(' to get better frequency resolution.')
disp(' ')
disp('Default input variables')
disp('MINFREQ - the lowest frequency in the ST result(Default=0)')
disp('MAXFREQ - the highest frequency in the ST result (Default=nyquist')
disp('SAMPLINGRATE - the time interval between successive data points (Default = 1)')
disp('FREQSAMPLINGRATE - the number of frequencies between samples in the ST results')
% end of st_help procedure
代码引用来源IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 44., number 4, April 1996, pages 998-1001.

