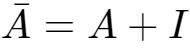深入浅出带你读懂图卷积神经网络原理和pytorch代码实现
01
大话图神经网络
看了挺久的图神经网络,从一窍不通到略懂一二,今天想表达一些在GCN,GraghSAGE,GAT等图神经网络的特征集成(聚合)思想,一方面,让更多人学习到图神经网络的本质,另一方面,加深自己对知识的记忆。
02
什么是图,有什么特点?
图作为一种特殊的数据结构,为非欧式空间:1)局部输入维度可变,表现为每个节点的邻居节点数量不同;2)排列无序,表现为节点之间只存在连接关系不存在先后顺序。而图结构即使邻居节点数量相同的情况下,也需要根据一定规律,比如度的大小,将节点进行排序使得用一阶邻居节点表示的每个节点是唯一的。不像排列规则的图像和自然语言可以通过CNN或者RNN进行处理并得到较好的效果,而CNN或者RNN在图结构数据上的效果一般较差或者不能使用
03
图如何表示?
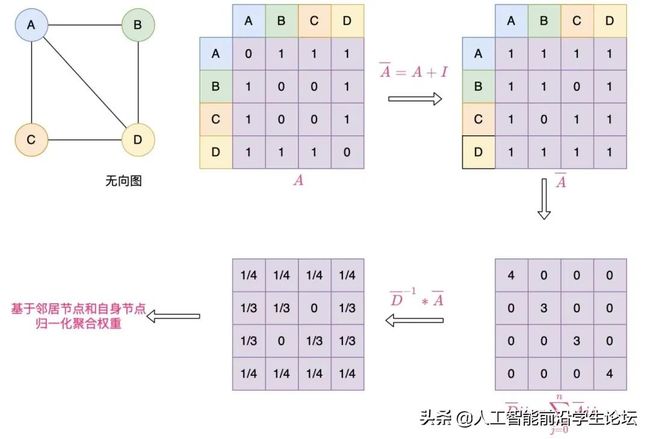
对于图,我们习惯上用
表示。这里V是图中节点的集合,而E为边的集合,这里记图的节点数为N。其中有3个比较重要的矩阵:
- 邻接矩阵A:adjacency matrix,用来表示节点间的连接关系,这里我们假定是0-1矩阵;
- 度矩阵D:degree matrix,每个节点的度指的是其连接的节点数,这是一个对角矩阵,其中对角线元素
- 特征矩阵X:用于表示节点的特征,这里F是特征的维度;使用连续,低维度,实数向量进行分布式表示,特征矩阵通常通过FM矩阵分解,DeepWalk随机游走,基于图神经网络的监督和半监督学习等方式获得图嵌入表征
数学表示是比较抽象的,下面是邻接矩阵实例:数学表示是比较抽象的,下面是邻接矩阵实例:
04
图节点如何表征?
其实我们可以将上述学习分成三个部分:
- 变换(transform):对当前的节点特征进行变换学习,这里就是乘法规则(XW),其中X为节点表征,W为模型权重
- 聚合(aggregate):通过邻接矩阵聚合领域节点的特征,得到该节点的新特征,根据聚合节点的权重是否可学习可以分为GCN和GAT,GCN直接采用邻接矩阵作为权重聚合邻居节点和自身节点作为当前节点的表征,GAT通过学习邻居节点对当前节点的重要程度的权重,通过加权得到节点的表征;根据聚合节点是否通过采样获得全局图卷积和局部图卷积
- 激活(activate):采用激活函数,增加非线性
下面我们分别介绍GCN,GraghSAGE,GAT的图神经网络的特征聚合思路和实现
全图卷积神经网络-GCN
我们不用太过纠结GCN为什么叫GCN,只需要知道它是一种将当前节点特征和一阶节点特征进行聚合来表征当前节点的新特征,通过这种方式有利于引入图节点的上下文信息,使得每个节点预测结果受邻居节点的影响,那么具体怎么集成呢?由于邻接矩阵可以表示节点之间的连接关系,我们可以在邻接矩阵上稍作调整,添加单位矩阵来结合节点自身的连接,并进行归一化,每一行表示一个节点与其他节点的连接权重大小,并作为当前节点的特征集成权重。
我们也可以将调整后的邻接矩阵看成是一种掩码(MASK),每一行权重为0的位置表示其对当前节点的聚合特征没有影响,由于这种权重本身由图的连接情况决定,是【固定的】和【不可学习的】,这种基于【整个图】结构的特征聚合网络就是GCN,属于转导学习。
下面介绍两种不同的聚合方式:
聚合方法1:
通过将当前节点的特征向量与其一阶节点的特征向量【加和平均】的方式进行聚合来表征当前节点的上下文表征向量,这种方法只考虑了当前节点的连接情况,没有考虑其一阶节点的连接情况,容易造成节点的度越大,参与的节点特征聚合次数越多,而这种度越大的节点本身特殊性应该越弱,影响应该进行削弱。具体实现:
![]()
这个公式中:
聚合方法2:
我们通过将当前节点的特征向量与其一阶节点的特征向量【加权求和】的方式进行聚合来表征当前节点的上下文表征向量,但考虑到方法1的不足,这种方法每个节点的聚合权重除了和自身的连接数相关,也和一阶节点的连接数【度】相关,度越大的节点,说明普遍性越强,重要度反而越低--简单解释,就和一篇文章中,如果一个词出现次数越多,那么它的重要程度越低,比如最容易出现的【的,得,地】等,节点也是类似,有点反直觉吧,具体实现:
这个公式中:
主要特点
1)需要基于全图获得邻接矩阵和训练,在计算资源有限的情况下,无法拓展到大规模图结构的模型训练与预测
2)属于转导学习,无法应用于未见过的节点预测或者应用于新的图结构
3)图卷积的层数反映了节点的感受野大小,n阶
Pytorch实现GCN
参考论文:Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks
https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.02907
class GraphConvolution(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim, use_bias=True):
"""图卷积:L*X*\theta
Args:
----------
input_dim: int
节点输入特征的维度
output_dim: int
输出特征维度
use_bias : bool, optional
是否使用偏置
"""
super(GraphConvolution, self).__init__()
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.output_dim = output_dim
self.use_bias = use_bias
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(input_dim, output_dim))
if self.use_bias:
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(output_dim))
else:
self.register_parameter('bias', None)
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight)
if self.use_bias:
init.zeros_(self.bias)
def forward(self, adjacency, input_feature):
"""邻接矩阵是稀疏矩阵,因此在计算时使用稀疏矩阵乘法
Args:
-------
adjacency: torch.sparse.FloatTensor
邻接矩阵
input_feature: torch.Tensor
输入特征
"""
support = torch.mm(input_feature, self.weight)
output = torch.sparse.mm(adjacency, support)
if self.use_bias:
output += self.bias
return output
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' + str(self.input_dim) + ' -> ' + str(self.output_dim) + ')'
# 模型定义
# 读者可以自己对GCN模型结构进行修改和实验
class GcnNet(nn.Module):
"""
定义一个包含两层GraphConvolution的模型
"""
def __init__(self, input_dim=1433):
super(GcnNet, self).__init__()
self.gcn1 = GraphConvolution(input_dim, 16)
self.gcn2 = GraphConvolution(16, 7)
def forward(self, adjacency, feature):
h = F.relu(self.gcn1(adjacency, feature))
logits = self.gcn2(adjacency, h)
return logits局部图卷积神经网络-GraghSAGE
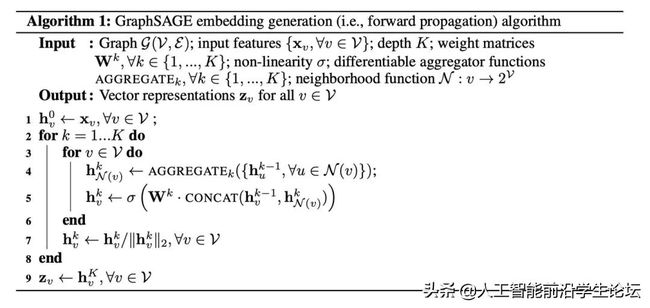
考虑到GCN的缺点,GraghSAGE通过局部采样的方法,为每个节点采样固定的n阶邻接节点个数,每一层神经网络通过聚合中心节点和邻居节点的特征作为此中心节点的新的上下文表征,且同一层不同节点共享聚合参数。
主要特点
1)使用这种方式,神经网络可以进行小批量的模型训练,而不需要输入整个图结构,可以用于大规模图结构的训练
2)训练过程未使用测试过程的数据,可以用于未见节点的预测,属于归纳学习
Pytorch实现GraghSAGE
class NeighborAggregator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim,
use_bias=False, aggr_method="mean"):
"""聚合节点邻居
Args:
input_dim: 输入特征的维度
output_dim: 输出特征的维度
use_bias: 是否使用偏置 (default: {False})
aggr_method: 邻居聚合方式 (default: {mean})
"""
super(NeighborAggregator, self).__init__()
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.output_dim = output_dim
self.use_bias = use_bias
self.aggr_method = aggr_method
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(input_dim, output_dim))
if self.use_bias:
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(self.output_dim))
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight)
if self.use_bias:
init.zeros_(self.bias)
def forward(self, neighbor_feature):
if self.aggr_method == "mean":
aggr_neighbor = neighbor_feature.mean(dim=1)
elif self.aggr_method == "sum":
aggr_neighbor = neighbor_feature.sum(dim=1)
elif self.aggr_method == "max":
aggr_neighbor = neighbor_feature.max(dim=1)
else:
raise ValueError("Unknown aggr type, expected sum, max, or mean, but got {}"
.format(self.aggr_method))
neighbor_hidden = torch.matmul(aggr_neighbor, self.weight)
if self.use_bias:
neighbor_hidden += self.bias
return neighbor_hidden
def extra_repr(self):
return 'in_features={}, out_features={}, aggr_method={}'.format(
self.input_dim, self.output_dim, self.aggr_method)
class SageGCN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim,
activation=F.relu,
aggr_neighbor_method="mean",
aggr_hidden_method="sum"):
"""SageGCN层定义
Args:
input_dim: 输入特征的维度
hidden_dim: 隐层特征的维度,
当aggr_hidden_method=sum, 输出维度为hidden_dim
当aggr_hidden_method=concat, 输出维度为hidden_dim*2
activation: 激活函数
aggr_neighbor_method: 邻居特征聚合方法,["mean", "sum", "max"]
aggr_hidden_method: 节点特征的更新方法,["sum", "concat"]
"""
super(SageGCN, self).__init__()
assert aggr_neighbor_method in ["mean", "sum", "max"]
assert aggr_hidden_method in ["sum", "concat"]
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.aggr_neighbor_method = aggr_neighbor_method
self.aggr_hidden_method = aggr_hidden_method
self.activation = activation
self.aggregator = NeighborAggregator(input_dim, hidden_dim,
aggr_method=aggr_neighbor_method)
self.dropout=nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(input_dim, hidden_dim))
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight)
def forward(self, src_node_features, neighbor_node_features):
neighbor_hidden = self.aggregator(neighbor_node_features)
self_hidden = torch.matmul(src_node_features, self.weight)
# self_hidden=self.dropout(self_hidden)
if self.aggr_hidden_method == "sum":
hidden = self_hidden + neighbor_hidden
elif self.aggr_hidden_method == "concat":
hidden = torch.cat([self_hidden, neighbor_hidden], dim=1)
else:
raise ValueError("Expected sum or concat, got {}"
.format(self.aggr_hidden))
if self.activation:
return self.activation(hidden)
else:
return hidden
def extra_repr(self):
output_dim = self.hidden_dim if self.aggr_hidden_method == "sum" else self.hidden_dim * 2
return 'in_features={}, out_features={}, aggr_hidden_method={}'.format(
self.input_dim, output_dim, self.aggr_hidden_method)
class GraphSage(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim,
num_neighbors_list):
super(GraphSage, self).__init__()
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.num_neighbors_list = num_neighbors_list
self.num_layers = len(num_neighbors_list)
self.gcn = nn.ModuleList()
self.gcn.append(SageGCN(input_dim, hidden_dim[0]))
for index in range(0, len(hidden_dim) - 2):
self.gcn.append(SageGCN(hidden_dim[index], hidden_dim[index+1]))
self.gcn.append(SageGCN(hidden_dim[-2], hidden_dim[-1], activation=None))
def forward(self, node_features_list):
hidden = node_features_list
for l in range(self.num_layers):
next_hidden = []
gcn = self.gcn[l]
for hop in range(self.num_layers - l):
src_node_features = hidden[hop]
src_node_num = len(src_node_features)
neighbor_node_features = hidden[hop + 1] \
.view((src_node_num, self.num_neighbors_list[hop], -1))
h = gcn(src_node_features, neighbor_node_features)
next_hidden.append(h)
hidden = next_hidden
return hidden[0]图注意力神经网络-GAT
上述两种方式的聚合权重是不可学习的,那么不同的邻居节点对中心节点的关联程度应该是不一样的,我们希望通过神经网络学习到节点之间隐含关联程度,并作为权重进行特征聚合。由于节点的度是不固定的,我们很容易联想到使用attention机制进行对齐,并使用邻接矩阵作为掩码(MASK)屏蔽非邻居节点对聚合权重的影响。
Pytorch实现GAT
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GraphAttentionLayer(nn.Module):
"""
Simple GAT layer, similar to https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10903
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, dropout, alpha, concat=True):
super(GraphAttentionLayer, self).__init__()
self.dropout = dropout
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.alpha = alpha
self.concat = concat
self.W = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(size=(in_features, out_features)))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.W.data, gain=1.414)
self.Q = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(size=(in_features, out_features)))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.Q.data, gain=1.414)
self.V = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(size=(in_features, out_features)))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.V.data, gain=1.414)
self.a = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(size=(2*out_features, 1)))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.a.data, gain=1.414)
self.leakyrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(self.alpha)
def forward(self, input, adj):
h = torch.mm(input, self.W)
q = torch.mm(input, self.Q)
v = torch.mm(input, self.V)
N = h.size()[0]
a_input = torch.cat([h.repeat(1, N).view(N * N, -1), q.repeat(N, 1)], dim=1).view(N, -1, 2 * self.out_features)
e = self.leakyrelu(torch.matmul(a_input, self.a).squeeze(2))
zero_vec = -9e15*torch.ones_like(e)
attention = torch.where(adj > 0, e, zero_vec)
attention = F.softmax(attention, dim=1)
attention = F.dropout(attention, self.dropout, training=self.training)
h_prime = torch.matmul(attention, v)
if self.concat:
return F.elu(h_prime)
else:
return h_prime
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' + str(self.in_features) + ' -> ' + str(self.out_features) + ')'
class GAT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nfeat, nhid, nclass, dropout, alpha, nheads):
"""Dense version of GAT."""
super(GAT, self).__init__()
self.dropout = dropout
self.attentions = [GraphAttentionLayer(nfeat, nhid, dropout=dropout, alpha=alpha, concat=True) for _ in range(nheads)]
for i, attention in enumerate(self.attentions):
self.add_module('attention_{}'.format(i), attention)
self.out_att = GraphAttentionLayer(nhid * nheads, nclass, dropout=dropout, alpha=alpha, concat=False)
def forward(self, x, adj):
x = F.dropout(x, self.dropout, training=self.training)
x = torch.cat([att(x, adj) for att in self.attentions], dim=1)
x = F.dropout(x, self.dropout, training=self.training)
x = F.elu(self.out_att(x, adj))
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)推荐下我自己建的Python学习群:[856833272],群里都是学Python的,如果你想学或者正在学习Python ,欢迎你加入,大家都是软件开发党,不定期分享干货,还有免费直播课程领取。包括我自己整理的一份2021最新的Python进阶资料和零基础教学,欢迎进阶中和对Python感兴趣的小伙伴加入!还可以扫码加VX领取资料哦!
![]()