JavaDay3
学习来源:日撸 Java 三百行(11-20天,线性数据结构)_闵帆的博客-CSDN博客
一、线性表
线性表是具有相同数据类型的n个数据元素的有限序列,当n=0时,线性表是一个空表。表中第一个数据元素称为表头元素,最后一个数据元素称表尾元素。除第一个元素外,每个元素有且仅有一个直接前驱;除最后一个元素外,每个元素有且仅有一个直接后继。
线性表是一种逻辑结构,表示元素之间一对一的相邻关系。根据存储结构的不同,可将线性表分为顺序表和链表。
1. 线性表的顺序存储——顺序表
顺序表是用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表中的数据元素,从而使得逻辑上相邻的元素在物理位置上也相邻。由于顺序表中的数据元素的逻辑顺序与物理顺序相同,因此顺序表的存储结构是一种随机存取的物理结构。
以下是对顺序表的定义以及简单操作。
package JavaDay3;
/**
* @author Kexiong Wang
*
* @date 2022年4月15日
*
* 顺序表
*/
public class SequenceList {
//最大表长
public static final int MAX_LENGTH = 10;
//用数组存储元素
int data[];
//表长
int length;
/**
***********
* 默认无参构造函数
* 创建一个空的顺序表
***********
*/
public SequenceList() {
length = 0;
data = new int[MAX_LENGTH];
}//Of SequenceList
/**
***********
* 带参数的构造函数
* 根据数组初始化一个顺序表
*
* @param paraArray 构造顺序表所用的元素所在的数组
***********
*/
public SequenceList(int[] paraArray) {
length = paraArray.length;
data = new int[MAX_LENGTH];
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
data[i] = paraArray[i];
}//Of for i
}//Of SequenceList
/**
***********
* 重写Object类的toString方法
***********
*/
public String toString() {
//返回的字符串
String resultString = "";
if(length == 0) {
return "empty";
}//Of if
for(int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
resultString += data[i] + ",";
}//Of for i
resultString += data[length - 1];
return resultString;
}//Of toString
/**
***********
* 将顺序表清空
***********
*/
public void init() {
length = 0;
}//Of init
/**
***********
* 程序入口
* 将顺序表输出
*
* @param args 暂未使用
***********
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] tempArray = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
SequenceList sequenceList = new SequenceList(tempArray);
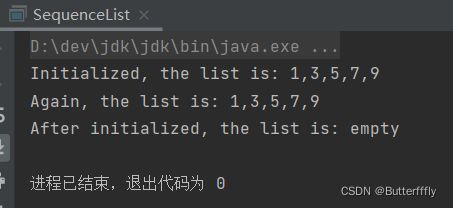
System.out.println("Initialized, the list is: " + sequenceList.toString());
System.out.println("Again, the list is: " + sequenceList);
sequenceList.init();
System.out.println("After initialized, the list is: " + sequenceList);
}//Of main
}//Of class SequenceList运行结果
2. 顺序表的查找、插入、删除操作
顺序表的插入操作首先检查插入的位置是否合法,若合法,则将其后的所有元素依次往后移动一个位置,然后插入新元素,顺序表的长度增加1。其删除操作与插入操作对应,检查删除位置是否合法,然后将元素删除,并将其后的所有元素依次往前移动一个位置,顺序表的长度减1。
package JavaDay3;
/**
* @author Kexiong Wang
*
* @date 2022年4月15日
*
* 顺序表的查找、插入、删除操作
*/
public class SequenceList2 {
//最大表长
public static final int MAX_LENGTH = 10;
//用数组存储元素
int data[];
//表长
int length;
/**
***********
* 默认无参构造函数
* 创建一个空的顺序表
***********
*/
public SequenceList2() {
length = 0;
data = new int[MAX_LENGTH];
}//Of SequenceList
/**
***********
* 带参数的构造函数
* 根据数组初始化一个顺序表
*
* @param paraArray 构造顺序表所用的元素所在的数组
***********
*/
public SequenceList2(int[] paraArray) {
length = paraArray.length;
data = new int[MAX_LENGTH];
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
data[i] = paraArray[i];
}//Of for i
}//Of SequenceList
/**
***********
* 重写Object类的toString方法
***********
*/
public String toString() {
//返回的字符串
String resultString = "";
if(length == 0) {
return "empty";
}//Of if
for(int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
resultString += data[i] + ",";
}//Of for i
resultString += data[length - 1];
return resultString;
}//Of toString
/**
***********
* 将顺序表清空
***********
*/
public void init() {
length = 0;
}//Of init
/**
***********
* 查找
*
* @param paraValue 要查找的值
***********
*/
public int locate(int paraValue) {
//元素的位置
int tempPosition = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if(data[i] == paraValue) {
tempPosition = i + 1;
break;
}//Of if
}//Of for i
return tempPosition;
}//Of locate
/**
***********
* 插入元素
*
* @param paraPosition 插入的位置
* @param paraValue 插入的元素
* @return 插入是否成功
***********
*/
public boolean insert(int paraPosition, int paraValue) {
//表满插入失败
if(length == MAX_LENGTH) {
System.out.println("List is full!");
return false;
}//Of if
//插入的位置不合法
if((paraPosition < 0) || (paraPosition > length)) {
System.out.println("The position is invalid!");
return false;
}//Of if
for(int i = length; i > paraPosition - 1; i--) {
data[i] = data[i - 1];
}//Of for i
data[paraPosition - 1] = paraValue;
length ++;
return true;
}//Of insert
/**
***********
* 删除元素
*
* @param paraPosition 要删除的元素的位置
* @return 删除是否成功
***********
*/
public boolean delete(int paraPosition) {
if(length == 0) {
System.out.println("The list is empty!");
return false;
}//Of if
if((paraPosition < 0) || (paraPosition > length - 1)) {
System.out.println("The position is invalid!");
return false;
}//Of if
for(int i = paraPosition - 1; i < length - 1; i++) {
data[i] = data[i + 1];
}//Of for i
length --;
return true;
}//Of delete
/**
***********
* 程序入口
*
* @param args 暂未使用
***********
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] tempArray = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 };
SequenceList2 sequenceList2 = new SequenceList2(tempArray);
System.out.println("After initialization, the list is " + sequenceList2.toString());
int tempValue1 = 5;
int tempPosition = sequenceList2.locate(tempValue1);
System.out.println("The position of " + tempValue1 + " is " + tempPosition);
int tempPosition2 = 3;
int tempValue2 = 4;
sequenceList2.insert(tempPosition2,tempValue2);
System.out.println("After insert " + tempValue2 + " in position " + tempPosition2 + ", the list is " + sequenceList2.toString());
int tempPosition3 = 5;
sequenceList2.delete(tempPosition3);
System.out.println("After delete the value of position " + tempPosition3 + ", the list is " + sequenceList2.toString());
}//Of main
}//Of class SequenceList2运行结果
3. 线性表的链式存储——链表
链表是指通过一组任意的存储单元来存储线性表中的数据元素。对每个链表节点,除了存放元素本身,还有一个存放指向其后继的指针。链表具有与顺序表一样的查找、插入、删除操作。
package JavaDay3;
import java.nio.file.NotDirectoryException;
/**
* @author Kexiong Wang
*
* @date 2022年4月15日
*
* 链表的操作
*/
public class LinkedList {
//节点类
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
/**
***********
* 链表节点的构造函数
*
* @param paraValue 节点的数据
***********
*/
public Node(int paraValue) {
data = paraValue;
next = null;
}//Of Node
}//Of class Node
//头结点
Node head;
/**
***********
* 创建空链表
***********
*/
public LinkedList() {
head = new Node(0);
}//Of LinkedList
/**
***********
* 重写Object类的toString方法输出链表
***********
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "";
if(head.next == null) {
return "Empty";
}//Of if
Node p = head.next;
while(p.next != null) {
resultString += p.data + ", ";
p = p.next;
}//Of while
resultString += p.data;
return resultString;
}//Of toString
/**
***********
* 将链表置空
***********
*/
public void init() {
head.next = null;
}//Of init
/**
***********
* 查找元素的位置
*
* @param paraValue1 要查找的元素
* @return 元素的位置
***********
*/
public int locate(int paraValue1) {
int tempPosition = 0;
int position = 1;
Node p = head.next;
while(p != null) {
if(p.data == paraValue1) {
tempPosition = position;
break;
}//Of if
position ++;
p = p.next;
}//Of while
return tempPosition;
}//Of locate
/**
***********
* 插入元素
*
* @param paraPosition2 插入元素的位置
* @param paraValue2 插入元素的值
* @return 插入是否成功
***********
*/
public boolean insert(int paraPosition2, int paraValue2) {
Node tempNode = head;
Node newNode;
for(int i = 1; i < paraPosition2; i++) {
if(tempNode == null) {
System.out.println("The position is invalid!");
return false;
}//Of if
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}//Of for i
newNode = new Node(paraValue2);
newNode.next = tempNode.next;
tempNode.next = newNode;
return true;
}//Of insert
/**
***********
* 删除指定位置的元素
*
* @param paraPosition3 删除元素的位置
* @return 删除是否成功
***********
*/
public boolean delete(int paraPosition3) {
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("The linkedList id empty!");
return false;
}//Of if
Node tempNode = head;
for(int i = 1; i < paraPosition3; i++) {
if(tempNode.next.next ==null) {
System.out.println("The position is invalid!");
return false;
}//Of if
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}//Of for i
tempNode.next = tempNode.next.next;
return true;
}//Of delete
/**
***********
* 程序入口
*
* @param args 暂未使用
***********
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
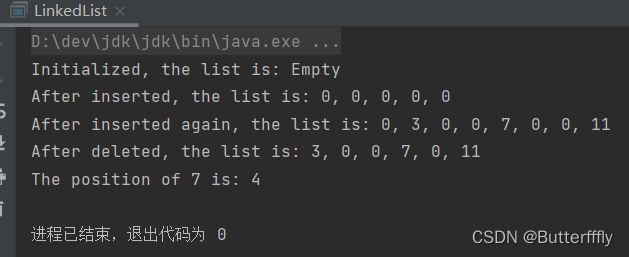
System.out.println("Initialized, the list is: " + linkedList.toString());
for(int i =1; i < 6; i++) {
linkedList.insert(i, 0);
}//Of for i
System.out.println("After inserted, the list is: " + linkedList.toString());
linkedList.insert(6, 11);
linkedList.insert(4, 7);
linkedList.insert(2, 3);
System.out.println("After inserted again, the list is: " + linkedList.toString());
linkedList.delete(1);
linkedList.delete(5);
System.out.println("After deleted, the list is: " + linkedList.toString());
System.out.println("The position of 7 is: " + linkedList.locate(7));
}//Of main
}//Of class LinkedList运行结果
二、总结
今天主要学习了线性表的概念及由顺序存储和链式存储对应的顺序表和链表。实现了两种线性表基本的查找、插入和删除操作。并且通过重写父类Object类的toString方法实现将线性表中的元素以字符串输出。