JavaDay6
学习来源:日撸 Java 三百行(21-30天,树与二叉树)_闵帆的博客——CSDN博客
一、汉诺塔问题
汉诺塔问题是典型的递归使用的案例,其中最关键的就是递归过程中参数的变化规律。通过手动推演层数较少的汉诺塔迭代过程可以很好地理解递归参数变化。
package JavaDay6;
/**
* @author Kexiong Wang
*
* @date 2022年4月21日
*/
public class Hanoi {
/**
***********
* 移动汉诺塔
*
* @param paraSource 源地址
* @param paraIntermediary 中介
* @param paraDestination 目的地
* @param paraNumber 汉诺塔层数
***********
*/
public static void hanoi(char paraSource, char paraIntermediary, char paraDestination,int paraNumber) {
if (paraNumber == 1) {
System.out.println(paraSource + "->" + paraDestination + " ");
return;
}//Of if
hanoi(paraSource, paraDestination, paraIntermediary, paraNumber - 1);
System.out.println(paraSource + "->" + paraDestination + " ");
hanoi(paraIntermediary, paraSource, paraDestination, paraNumber - 1);
}//Of hanoi
/**
*********************
* 程序入口
*
* @param args 暂未使用
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
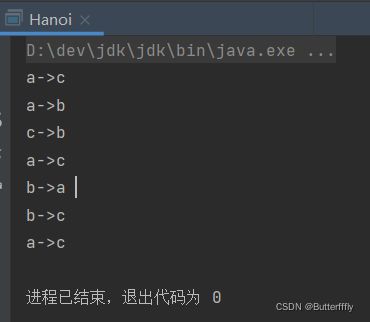
hanoi('a', 'b', 'c', 3);
}//Of main
}//Of class Hanoi运行结果
二、哈夫曼树和哈夫曼编码
1. 哈夫曼树的定义
在含有n个带权叶节点的二叉树中,带权路径长度最小的数称为哈夫曼树。
2. 哈夫曼树的构造
哈夫曼树的构造是自底向上的过程,每次选择权值最小的两个节点作为一个新节点的左右孩子,将新节点作为可选择的对象加入下一次选取的集合中,重复上述过程就得到一棵哈夫曼树。
package JavaDay6;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Huffman {
//哈夫曼树节点
class HuffmanNode {
//叶节点的字符
char character;
//字符的权重(出现次数)
int weight;
//左孩子
HuffmanNode leftChild;
//右孩子
HuffmanNode rightChild;
//父节点
HuffmanNode parent;
/**
***********
* 哈夫曼数节点的构造函数
*
* @param paraCharacter 节点的字符(仅叶节点有)
* @param paraWeight 字符的权重
* @param paraLeftChild 左孩子
* @param paraRightChild 右孩子
* @param paraParent 父节点
***********
*/
public HuffmanNode(char paraCharacter, int paraWeight, HuffmanNode paraLeftChild, HuffmanNode paraRightChild, HuffmanNode paraParent) {
character = paraCharacter;
weight = paraWeight;
leftChild = paraLeftChild;
rightChild = paraRightChild;
parent = paraParent;
}//Of HuffmanNode
/**
***********
* toString方法
***********
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "(" + character + ", " + weight + ")";
return resultString;
}//Of toString
}//Of class HuffmanNode
//所有字符数
public static final int NUM_CHARS = 256;
//输入的字符串
String inputText;
//字符个数,叶节点个数
int alphabetLength;
//叶节点字符集
char[] alphabet;
//字符出现的次数
int[] charCounts;
//字符在alphabet表中的下标映射
int[] charMapping;
//叶节点字符的哈夫曼码
String[] huffmanCodes;
//所有哈夫曼树节点,最后一个节点是根节点
HuffmanNode[] nodes;
/**
***********
* 构造函数
*
* @param paraFilename 文本文件名称
***********
*/
public Huffman(String paraFilename) {
charMapping = new int[NUM_CHARS];
readText(paraFilename);
}//Of Huffman
/**
***********
* 读文本
*
* @param paraFilename 文本文件名
***********
*/
public void readText(String paraFilename) {
try {
inputText = Files.newBufferedReader(Paths.get(paraFilename), StandardCharsets.UTF_8).lines().collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
System.exit(0);
}//Of try
System.out.println("The text is:\r\n" + inputText);
}//Of readText
/**
***********
* 构造字符表
***********
*/
public void constructAlphabet() {
//初始化
Arrays.fill(charMapping, -1);
//每个字符出现的次数
int[] tempCharCounts = new int[NUM_CHARS];
//字符在ASCII码表的序号
int tempCharIndex;
//统计字符出现的次数
char tempChar;
for (int i = 0; i < inputText.length(); i++) {
tempChar = inputText.charAt(i);
tempCharIndex = (int) tempChar;
System.out.print("" + tempCharIndex + " ");
tempCharCounts[tempCharIndex]++;
}//Of for i
//统计有多少个不同的字符
alphabetLength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 255; i++) {
if (tempCharCounts[i] > 0) {
alphabetLength++;
}//Of if
}//Of for i
//存入字符表
alphabet = new char[alphabetLength];
charCounts = new int[2 * alphabetLength - 1];
int tempCounter = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_CHARS; i++) {
if (tempCharCounts[i] > 0) {
alphabet[tempCounter] = (char) i;
charCounts[tempCounter] = tempCharCounts[i];
charMapping[i] = tempCounter;
tempCounter++;
}//Of if
}//Of for i
System.out.println("The alphabet is: " + Arrays.toString(alphabet));
System.out.println("Their counts are: " + Arrays.toString(charCounts));
System.out.println("The char mappings are: " + Arrays.toString(charMapping));
}//Of constructAlphabet
/**
***********
* 构造哈夫曼树
***********
*/
public void constructTree() {
//分配空间
nodes = new HuffmanNode[alphabetLength * 2 - 1];
//用来标记节点是否已被选择过
boolean[] tempProcessed = new boolean[alphabetLength * 2 - 1];
//初始化叶节点
for (int i = 0; i < alphabetLength; i++) {
nodes[i] = new HuffmanNode(alphabet[i], charCounts[i], null, null, null);
}//Of for i
//构建哈夫曼树
int tempLeft, tempRight, tempMinimal;
for (int i = alphabetLength; i < 2 * alphabetLength - 1; i++) {
//选择权重最小的作为左孩子
tempLeft = -1;
tempMinimal = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (tempProcessed[j]) {
continue;
}//Of if
if (tempMinimal > charCounts[j]) {
tempMinimal = charCounts[j];
tempLeft = j;
}//Of if
}//Of for j
tempProcessed[tempLeft] = true;
//选择权重第二小的节点作为右孩子
tempRight = -1;
tempMinimal = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (tempProcessed[j]) {
continue;
}//Of if
if (tempMinimal > charCounts[j]) {
tempMinimal = charCounts[j];
tempRight = j;
}//Of if
}//Of for j
tempProcessed[tempRight] = true;
System.out.println("Selecting " + tempLeft + " and " + tempRight);
//将两个节点合成一个新节点
charCounts[i] = charCounts[tempLeft] + charCounts[tempRight];
nodes[i] = new HuffmanNode('*', charCounts[i], nodes[tempLeft], nodes[tempRight], null);
//链接左右孩子
nodes[tempLeft].parent = nodes[i];
nodes[tempRight].parent = nodes[i];
System.out.println("The children of " + i + " are " + tempLeft + " and " + tempRight);
}//Of for i
}//Of constructTree
/**
***********
* 查询根节点
*
* @return 根节点
***********
*/
public HuffmanNode getRoot() {
return nodes[nodes.length - 1];
}//Of getRoot
/**
***********
* 先序遍历
***********
*/
public void preOrderVisit(HuffmanNode paraNode) {
System.out.print("(" + paraNode.character + ", " + paraNode.weight + ") ");
if (paraNode.leftChild != null) {
preOrderVisit(paraNode.leftChild);
}//Of if
if (paraNode.rightChild != null) {
preOrderVisit(paraNode.rightChild);
}//Of if
}//Of preOrderVisit
/**
***********
* 程序入口
*
* @param args 暂未使用
***********
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
Huffman tempHuffman = new Huffman("E:/test.txt");
tempHuffman.constructAlphabet();
tempHuffman.constructTree();
HuffmanNode tempRoot = tempHuffman.getRoot();
System.out.println("The root is: " + tempRoot);
System.out.println("Preorder visit:");
tempHuffman.preOrderVisit(tempHuffman.getRoot());
System.out.println();
tempHuffman.generateCodes();
System.out.println();
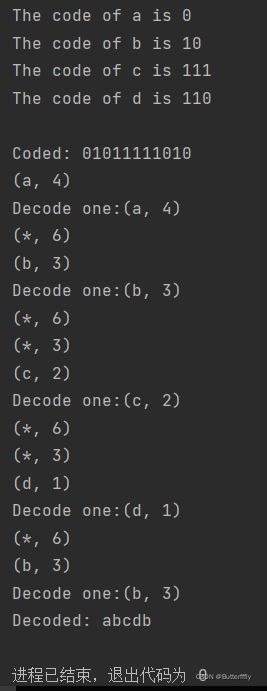
String tempCoded = tempHuffman.coding("abcdb");
System.out.println("Coded: " + tempCoded);
String tempDecoded = tempHuffman.decoding(tempCoded);
System.out.println("Decoded: " + tempDecoded);
}// Of main
}//Of class Huffman运行结果
3. 哈夫曼编码和解码
哈夫曼编码为文件中的每个字符分配一个前缀编码(没有一个编码是另一个编码的前缀)。其特点是出现频率高的字符编码较短,出现频率低的字符编码较长,从而使得字符的平均编码长度减小,起到压缩数据的效果。
由于每个字符对应一个前缀编码,因此可以将一个码串唯一还原为一个字符串,这就是解码的过程。
/**
***********
* 为字符生成哈夫曼码
***********
*/
public void generateCodes() {
huffmanCodes = new String[alphabetLength];
HuffmanNode tempNode;
for (int i = 0; i < alphabetLength; i++) {
tempNode = nodes[i];
String tempCharCode = "";
while (tempNode.parent != null) {
if (tempNode == tempNode.parent.leftChild) {
tempCharCode = "0" + tempCharCode;
} else {
tempCharCode = "1" + tempCharCode;
}//Of if
tempNode = tempNode.parent;
}//Of while
huffmanCodes[i] = tempCharCode;
System.out.println("The code of " + alphabet[i] + " is " + tempCharCode);
}//Of for i
}//Of generateCodes
/**
***********
* 对字符串进行编码
*
* @param paraString 给定字符串
***********
*/
public String coding(String paraString) {
String resultCodeString = "";
int tempIndex;
for (int i = 0; i < paraString.length(); i++) {
//定位字符在alphabet表的位置
tempIndex = charMapping[(int) paraString.charAt(i)];
resultCodeString += huffmanCodes[tempIndex];
}//Of for i
return resultCodeString;
}//Of coding
/**
***********
* 解码
*
* @param paraString 哈夫曼码
***********
*/
public String decoding(String paraString) {
String resultCodeString = "";
HuffmanNode tempNode = getRoot();
for (int i = 0; i < paraString.length(); i++) {
if (paraString.charAt(i) == '0') {
tempNode = tempNode.leftChild;
System.out.println(tempNode);
} else {
tempNode = tempNode.rightChild;
System.out.println(tempNode);
}//Of if
if (tempNode.leftChild == null) {
System.out.println("Decode one:" + tempNode);
resultCodeString += tempNode.character;
tempNode = getRoot();
}//Of if
}//Of for i
return resultCodeString;
}//Of decoding运行结果(检测的字符串为"abcdb")