SpringSecurity详解
一、Spring Security简介
Spring Security是一个功能强大且高度可定制的身份验证和访问控制框架。Spring Security致力于为Java应用程序提供身份验证和授权的能力。像所有Spring项目一样,Spring Security的真正强大之处在于它可以轻松扩展以满足定制需求的能力。
Spring Security两大重要核心功能:用户认证(Authentication)和用户授权(Authorization)。
用户认证:验证某个用户是否为系统中的合法主体,也就是说用户能否访问该系统。用户认证一般要求用户提供用户名和密码。系统通过校验用户名和密码来完成认证过程。
用户授权:验证某个用户是否有权限执行某个操作。在一个系统中,不同用户所有的权限是不同的。比如对一个文件来说,有的用户只能进行读取,有的用户既能读取,又能修改。一般来说,系统会为不同的用户分配不同的角色,而每个角色则对应一系列的权限。
二、快速开始
使用Springboot工程搭建Spring Security项目。
1.引入依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-security
org.springframework.security
spring-security-core
5.2.6.RELEASE
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.4.2
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-generator
3.3.2
org.apache.velocity
velocity
1.7
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-configuration-processor
true
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-extension
3.4.2
org.springframework.security
spring-security-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
runtime
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-configuration-processor
true
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.18.20
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
在pom中新增了Spring Security的依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-security
2.创建测试访问接口
用于访问接口时触发Spring Security登陆页面
@RestController
public class SecurityController {
@RequestMapping("/add")
public String add(){
return "hello security!";
}
}3.访问接口,自动跳转至Security登陆页面
通过浏览器输入框输入localhost:8080/add,将自动跳转至Security的登陆页面
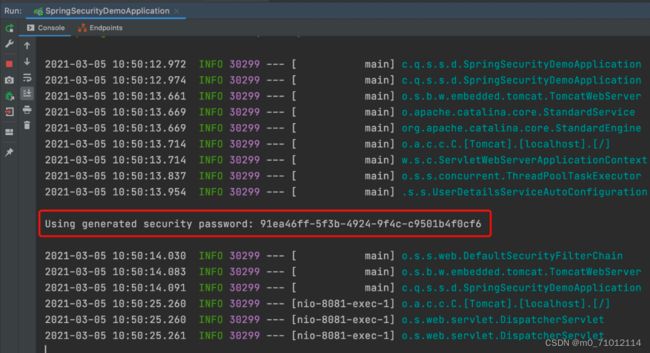
默认账号是: user
默认密码是:启动项目的控制台中输出的密码
三、原理剖析
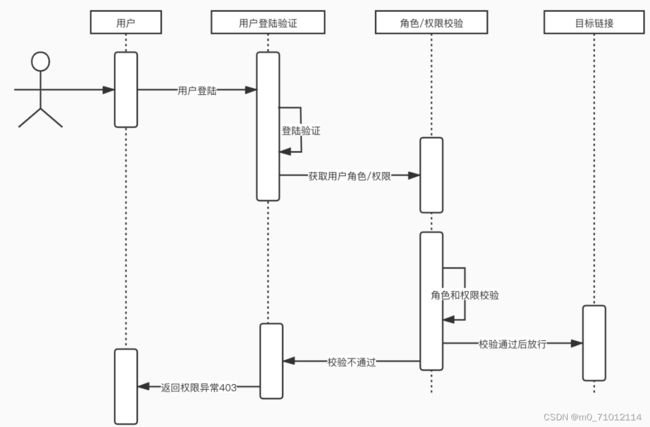
在上面中访问add接口,发现被Spring Security的登陆页面拦截,可以猜到这是触发了Security框架的过滤器。Spring Security本质上就是一个过滤器链。下面讲介绍Security框架的过滤器链。
1.过滤器链
FilterSecurityInterceptor:是一个方法级的权限过滤器,位于过滤器链的最底部。
ExceptionTranslationFilter: 异常过滤器,用来处理在认证授权过程中抛出异常。
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter: 用于对/login的POST请求做拦截,校验表单中的用户名和密码。
2.过滤器加载过程
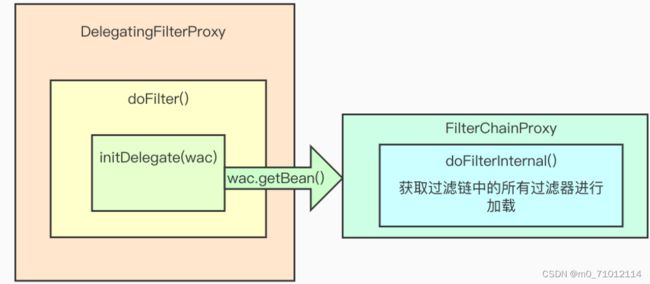
Springboot在整合Spring Security项目时会自动配置DelegatingFilterProxy过滤器,若非Springboot工程,则需要手动配置该过滤器。
过滤器如何进行加载的?
结合上图和源码,Security在DelegatingFilterProxy的doFilter()调用了initDelegat()方法,在该方法中调用了WebApplicationContext的getBean()方法,该方法出发FilterChainProxy的doFilterInternal方法,用于获取过滤链中的所有过滤器并进行加载。
3.Security的两个关键接口
在快速开始中发现Spring Security使用了默认的用户名和密码,实际用户名和密码需要自定义,因此会用到以下两个接口。下述两个接口的具体实现将在之后的例子中体现。
1) UserDetailsService接口
若需要从数据库中获取用户名和密码,则需要把查询数据库的过程写在这个接口里。
2)PasswordEncoder接口
在密码的处理上,需要进行编解码器,该接口实现对密码进行加密。
四、多种方式配置登陆的用户名和密码
1.通过配置文件设置用户名和密码
# 方式一:设置登陆的用户名和密码
spring:
security:
user:
name: qfadmin
password: 1234562.通过创建配置类实现设置
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//用于密码的密文处理
BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
//生成密文
String password = passwordEncoder.encode("123456");
//设置用户名和密码
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("qfAdmin").password(password).roles("admin");
}
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}3.编写自定义实现类(常用)
第一步:编写UserDetailsService实现类,可以从数据库中获取用户名和密码
@Service("userDetailsService")
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//设置角色,角色的概念在之后章节介绍
List auths = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("role");
//可以从数据库获取用户名和密码,这里返回的是数据库中的数据,然后再去和用户输入的密码比较
return new User("qfAdmin",new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456"),auths);
}
} 第二步:编写配置类
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfigByImpl extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html") //设置自定义登陆页面,注意如果不通过controller跳转这个页面需要放在static中
.loginProcessingUrl("/user/login") //登陆时访问的路径,也就是s这个路径表示表单提交,处理登录请求的controller不需要我们写,security帮我们做到了
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index").permitAll() //登陆成功后跳转的路径
.and().authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/","/add","/user/login").permitAll() //设置可以直接访问的路径,取消拦截
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护
}
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}为了测试顺利,这里临时关闭csrf防护。所谓csrf防护,全称为跨站请求伪造(Cross-site request forgery),是一种网络攻击方式,CSRF攻击利用网站对于用户网页浏览器的信任,挟持用户当前已登陆的Web应用程序,去执行并非用户本意的操作。简而言之,用户通过盗取目标网站保存的cookie中的用户信息,实现非法使用。
其中,login.html为自己提供的登陆页面,具体内容如下:
Title
注意:表单提交的地址为配置类中配置的登陆时访问路径:/usr/login
第三步:在controller中添加/index接口
@RestController
public class SecurityController {
@RequestMapping("/add")
public String add(){
return "hello security!";
}
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return "hello index";
}
}五、基于角色和权限进行访问控制
Spring Security提供了四个方法用于角色和权限的访问控制。通过这些方法,对用户是否具有某个或某些权限,进行过滤访问。对用户是否具备某个或某些角色,进行过滤访问。
1.hasAuthority方法
判断当前主题是否有指定的权限,有返回true,否则返回false
该方法适用于只拥有一个权限的用户。
1)在配置类中设置当前主体具有怎样的权限才能访问。
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//配置没有权限的跳转页面
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/error.html");
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html") //设置自定义登陆页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/usr/login") //登陆时访问的路径
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index").permitAll() //登陆成功后跳转的路径
.and().authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/","/add","/user/login").permitAll() //设置可以直接访问的路径,取消拦截
//1.hasAuthority方法:当前登陆用户,只有具有admin权限才可以访问这个路径
.antMatchers("/index").hasAuthority("admin")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护
}2)在userdetailsService,为返回的User对象设置权限
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//因目前还没引入角色的概念,先用工具类快速生成角色
List auths = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin");
//可以从数据库获取用户名和密码
return new User("qfAdmin",new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456"),auths);
} 2.hasAnyAuthority方法
适用于一个主体有多个权限的情况,多个权限用逗号隔开。
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//注销的配置
http.logout().logoutUrl("/logout") //注销时访问的路径
.logoutSuccessUrl("/logoutSuccess").permitAll(); //注销成功后访问的路径
//配置没有权限的跳转页面
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/error.html");
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html") //设置自定义登陆页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/usr/login") //登陆时访问的路径
// .defaultSuccessUrl("/index").permitAll() //登陆成功后跳转的路径
.defaultSuccessUrl("/success.html").permitAll() //登陆成功后跳转的路径
.and().authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/","/add","/user/login").permitAll() //设置可以直接访问的路径,取消拦截
//2.hasAnyAuthority方法:当前登陆用户,具有admin或manager权限可以访问这个路径
.antMatchers("/index").hasAnyAuthority("admin,manager")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护
}2)在userdetailsService,为返回的User对象设置权限
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//因目前还没引入角色的概念,先用工具类快速生成角色
List auths = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin");
//可以从数据库获取用户名和密码
return new User("Admin",new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456"),auths);
} 3.hasRole方法
如果用户具备给定角色就允许访问,否则报403错误。
1)修改配置类
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//注销的配置
http.logout().logoutUrl("/logout") //注销时访问的路径
.logoutSuccessUrl("/logoutSuccess").permitAll(); //注销成功后访问的路径
//配置没有权限的跳转页面
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/error.html");
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html") //设置自定义登陆页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/usr/login") //登陆时访问的路径
// .defaultSuccessUrl("/index").permitAll() //登陆成功后跳转的路径
.defaultSuccessUrl("/success.html").permitAll() //登陆成功后跳转的路径
.and().authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/","/add","/user/login").permitAll() //设置可以直接访问的路径,取消拦截
//3.hasRole方法:当前主体具有指定角色,则允许访问
.antMatchers("/index").hasRole("student")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护
}2)修改user对象
//权限设置
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//因目前还没引入角色的概念,先用工具类快速生成角色
//hasRole: 由于源码会把role加上"ROLE_",因此在这里设计角色时需加上前缀
List auths = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin,ROLE_student");
//可以从数据库获取用户名和密码
return new User("qfAdmin",new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456"),auths);
} 其中角色student需要在设置时加上“ROLE”前缀,因为通过源码hasRole方法给自定义的角色名前加上了“ROLE”前缀
private static String hasRole(String role) {
Assert.notNull(role, "role cannot be null");
Assert.isTrue(!role.startsWith("ROLE_"), () -> {
return "role should not start with 'ROLE_' since it is automatically inserted. Got '" + role + "'";
});
return "hasRole('ROLE_" + role + "')";
}4.hasAnyRole方法
设置多个角色,多个角色之间使用逗号隔开,只要用户具有某一个角色,就能访问。
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//注销的配置
http.logout().logoutUrl("/logout") //注销时访问的路径
.logoutSuccessUrl("/logoutSuccess").permitAll(); //注销成功后访问的路径
//配置没有权限的跳转页面
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/error.html");
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html") //设置自定义登陆页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/usr/login") //登陆时访问的路径
// .defaultSuccessUrl("/index").permitAll() //登陆成功后跳转的路径
.defaultSuccessUrl("/success.html").permitAll() //登陆成功后跳转的路径
.and().authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/","/add","/user/login").permitAll() //设置可以直接访问的路径,取消拦截
//4.hasAnyRole方法:当前主体只要具备其中某一个角色就能访问
.antMatchers("/index").hasAnyRole("student1,teacher")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护
}六、SpringSecurity的常用注解
1、@Secured注解
@Secured注解用于校验用户具有某个角色,才可以访问方法
1)启动类上开启注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
public class SecurityDemo1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SecurityDemo1Application.class, args);
}
}2)在方法上配置注解
@RequestMapping("/admin")
@Secured("ROLE_ls")
public String testAuthority(){
return "ls的角色";
}3)用户对象中设置角色
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
List auths = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin,ROLE_student");
//可以从数据库获取用户名和密码
return new User("qfAdmin",new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456"),auths);
} 2、@PreAuthorize
进入方法前的权限验证
步骤
在启动类上开启注解
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true, prePostEnabled = true)在方法上使用注解
@RequestMapping("/items")
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('admin')")
public String items(){
return "show itemds";
}注意:方法参数是之前介绍的四个方法。
3、@PostAuthorize
在方法访问之后进行校验,实际使用并不多
步骤
启动类上开启注解
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true, prePostEnabled = true)方法上使用注解
@RequestMapping("/postItems")
@PostAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('teacher')")
public String postItems(){
//先执行方法内容,再做权限校验
System.out.println("show detail here...");
return "show post items";
}4、@PostFilter
权限验证之后对数据进行过滤,只能获取满足条件的数据
步骤
在方法上使用注解
@RequestMapping("/postFilterItems")
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('admin')")
@PostFilter("filterObject.userName == 'xiaoming'")
public List getUsers(){
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new User(1L,"xiaowang"));
list.add(new User(2L,"xiaoming"));
return list;
} 访问接口,发现list集合中中获取了满足条件的xiaoming对象
5、@PreFilter
对传入方法的数据进行过滤
步骤
在方法上使用注解
@RequestMapping("/preFilterItems")
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('admin')")
@PreFilter(value="filterObject.userName == 'xiaoming'")
public List getUsersByPreFilter(@RequestBody List list){
//只有userName是'xiaoming'的数据才会被传入
list.forEach(t->{
System.out.println(t.getUserName());
});
return list;
} 访问方法,发现只有userName是'xiaoming'的数据才会被传入
七、案例
1.从数据库查询角色或权限案例
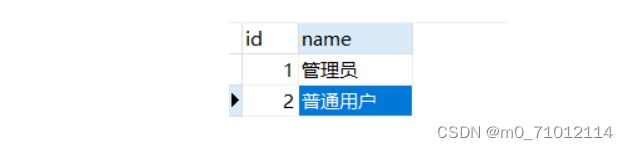
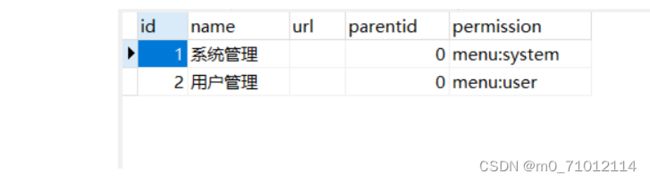
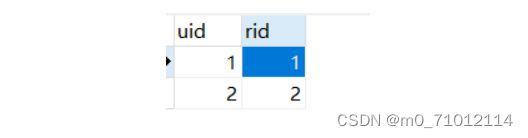
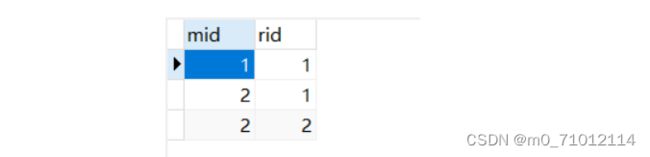
1.1准备数据库:
用户表users:
1.2创建配置类继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
用注解方式验证权限
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html") //设置自定义登陆页面,注意如果不通过controller跳转这个页面需要放在static中
.loginProcessingUrl("/user/login") //登陆时访问的路径,也就是s这个路径表示表单提交,处理登录请求的controller不需要我们写,security帮我们做到了
.defaultSuccessUrl("/main").permitAll() //登陆成功后跳转的路径
.and().authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/","/add","/user/login").permitAll() //设置可以直接访问的路径,取消拦截
.antMatchers("/main","/users/manage").hasAnyRole("普通用户")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护
}
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
1.3创建application.yml配置文件
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bank?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 123456
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl # 查看sql输出日志
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: auto # id自增
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml #设置
thymeleaf:
cache: false
type-aliases-package: com.ymk.securitydemo1.pojo #设置别名
logging:
level:
com.ymk.securitydemo1: debug
1.4创UsersMapper和UsersMapper.xml
@Repository
public interface UsersMapper extends BaseMapper {
//根据用户id查询用户角色
List selectRoleByUserId(Integer userId);
//根据用户id查询权限
List
1.5编写实现类UserDetailsService
在此类进行数据库查询
@Service("userDetailsService")
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private UsersMapper usersMapper;
// 接受传过来的用户名 根据传过来的用户名查询数据库的密码,返回数据库中的用户名、密码、权限信息
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//查询数据库
QueryWrapper queryWrapper1 = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper1.eq("username", username);
Users users = usersMapper.selectOne(queryWrapper1);
if (users == null) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户名不存在!");
}
System.out.println(users);
// 这个集合是 保存 用户的权限和角色的集合
// List auths =
// AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("manger,ROLE_admin");
//查询权限和角色,然后封装到User中
ArrayList auths = new ArrayList<>();
//查询用户角色的列表
List roles = usersMapper.selectRoleByUserId(users.getId().intValue());
//查询权限的列表
List 1.6创建UserController类
是对用户登录时进行的操作,此时不用谢UserService和UserServiceImpl
@RequestMapping("/users")
@RestController
public class UsersController {
@Autowired
private UsersService usersService;
@RequestMapping("/admin")
@Secured("ROLE_管理员") // 需要的角色
public String testAuthority(){
return "张三的角色";
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('menu:user')") //需要的权限
@RequestMapping("/manage")
public String testAuthority2(){
return "李四的角色";
}
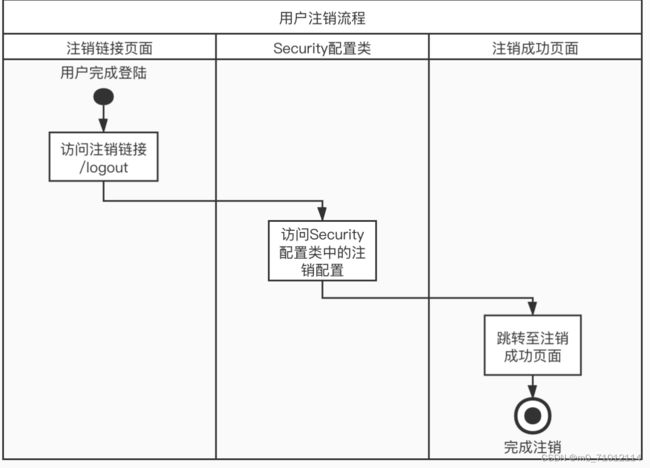
}八、用户注销
1.在配置类添加注销的配置
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//注销的配置
http.logout().logoutUrl("/logout") //注销时访问的路径
.logoutSuccessUrl("/logoutSuccess").permitAll(); //注销成功后访问的路径
//配置没有权限的跳转页面
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/error.html");
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html") //设置自定义登陆页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/usr/login") //登陆时访问的路径
// .defaultSuccessUrl("/index").permitAll() //登陆成功后跳转的路径
.defaultSuccessUrl("/success.html").permitAll() //登陆成功后跳转的路径
.and().authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/","/add","/user/login").permitAll() //设置可以直接访问的路径,取消拦截
//1.hasAuthority方法:当前登陆用户,只有具有admin权限才可以访问这个路径
//.antMatchers("/index").hasAuthority("admin")
//2.hasAnyAuthority方法:当前登陆用户,具有admin或manager权限可以访问这个路径
//.antMatchers("/index").hasAnyAuthority("admin,manager")
//3.hasRole方法:当前主体具有指定角色,则允许访问
//.antMatchers("/index").hasRole("student")
//4.hasAnyRole方法:当前主体只要具备其中某一个角色就能访问
.antMatchers("/index").hasAnyRole("student1,teacher")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护
}2.设置注销链接
添加success.html页面作为登陆成功后的跳转页面
Title
登陆成功 退出
登陆后访问退出按钮,实现注销功能。