Open3D点云处理
Open3D点云处理
一、Open3D
Open3D is an open-source library that supports rapid development of software that deals with 3D data. The Open3D frontend exposes a set of carefully selected data structures and algorithms in both C++ and Python. The backend is highly optimized and is set up for parallelization.
Open3D是一个支持3D数据处理软件快速开发的开源库,在前端提供了一组精挑细选的C++和Python数据结构与算法。并且在后端高度优化且支持并行化。
其核心要素包括:
- 3D数据结构
- 3D数据处理算法
- 场景重建
- 3D可视化
- 3D机器学习等
Python版快速安装
需要的环境为:
- OS:Ubuntu 18.04+、macOS 10.15+、Windows 10(64-bit)
- Python: 3.6-3.9
- Pre-packages:
pipandconda
# Install
pip install open3d
# Verify installation
python -c "import open3d as o3d; print(o3d.__version__)"
# Python API
python -c "import open3d as o3d; \
mesh = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_sphere(); \
mesh.compute_vertex_normals(); \
o3d.visualization.draw(mesh, raw_mode=True)"
# Open3D CLI
open3d example visualization/draw
二、Open3D点云加载与显示
2.1 点云读取
Open3D提供了直接从文件中读取点云数据的API:
open3d.io.read_point_cloud(filename, format='auto', remove_nan_points=False, \
remove_infinite_points=False, print_progress=False)
Parameters
- filename (str) – 文件路径
- format (str,optional,default=‘auto’) – 文件的格式,默认是
auto,将影响如何读取文件 - remove_nan_points (bool*,* optional*,* default=False) – 是否移除值为
nan的点 - remove_infinite_points (bool*,* optional*,* default=False) – 是否移除值为
inf的点 - print_progress (bool*,* optional*,* default=False) – 当该值为True时,将会在可视化时出现一个过程条
Return
- open3d.geometry.PointCloud对象
其中,format参数的可选参数为:
| 格式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| xyz | 每一行包含[x,y,z] |
| xyzn | 每一行包含[x,y,z,nx,ny,nz] |
| xyzrgb | 每一行包括[x,y,z,r,g,b] rgb为[0,1]之间的float类型 |
| pts | 第一行表示点数,之后每行包括[x,y,z,i,r,g,b] rgb为unit8类型 |
| ply | ply文件 |
| pcd | pcd文件 |
我们来尝试读取一下数据
import open3d as o3d
pcd=o3d.io.read_point_cloud(r"Cloud.pcd")
print(pcd)
'''
PointCloud with 2001009 points.
'''
# 此时点云数据已经被读入了
当然,对于某些格式稀奇古怪的,我们也可以通过转成ndarray然后再进行读取:
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
# 读取到ndarray
data=np.genfromtxt(r'modelnet40_normal_resampled\airplane\airplane_0001.txt',delimiter=",")
# 创建PointCloud类
pcd=o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
pcd.points=o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(data[:,:3])
print(pcd)
'''
PointCloud with 10000 points.
'''
关于PointCloud的属性,主要有以下四类:
- colors: 颜色信息,在可视化时能为几何体赋予视觉信息
- covariances: 协方差
- normal: 法向量
- points: 位置信息
2.2 点云可视化
在Open3D中,点云可视化其中之一的API为:
draw_geometries(geometry_list, window_name=’Open3D’, width=1920,\
height=1080, left=50, top=50, point_show_normal=False,\
mesh_show_wireframe=False, mesh_show_back_face=False,\
lookat, up, front, zoom)
Parameters
- geometry_list (List[open3d.geometry.Geometry]) – 需要可视化的几何体列表.
- window_name (str, optional, default=‘Open3D’) – 窗口名称
- width (int, optional, default=1920) – 窗口宽度
- height (int, optional, default=1080) – 窗口高度
- left (int, optional, default=50) – 窗口左边界
- top (int, optional, default=50) – 窗口顶部边界
- point_show_normal (bool, optional, default=False) – 是否展示法向量
- mesh_show_wireframe (bool, optional, default=False) – 是否可视化网格线框
- mesh_show_back_face (bool, optional, default=False) – 同时可视化格网三角形背部
- **lookat ** (numpy.ndarray[float64[3,1]]) – 相机注视向量
- up (numpy.ndarray[float64[3,1]]) – 相机的上方向向量
- front (numpy.ndarray[float64[3,1]]) – 相机的前矢量
- zoom (float) – 相机缩放倍数
Returns
- None
我们来尝试一下:
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd])
显示法向量:
pcd.normals=o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(data[:,3:])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd],window_name="o3d",width=1920,height=1080,
left=50,top=50,point_show_normal=True)
看起来跟毛毛虫一样…
提供了一组用户交互指令:
-- Mouse view control --
Left button + drag : Rotate.
Ctrl + left button + drag : Translate.
Wheel button + drag : Translate.
Shift + left button + drag : Roll.
Wheel : Zoom in/out.
-- Keyboard view control --
[/] : Increase/decrease field of view.
R : Reset view point.
Ctrl/Cmd + C : Copy current view status into the clipboard.
Ctrl/Cmd + V : Paste view status from clipboard.
-- General control --
Q, Esc : Exit window.
H : Print help message.
P, PrtScn : Take a screen capture.
D : Take a depth capture.
O : Take a capture of current rendering settings.
也可以指定点云的颜色:
pcd.colors=o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(data[:,3:])
参数geometry_list支持多个空间集合对象:
def read_txt(path):
data=np.genfromtxt(path,delimiter=",")
pcd=o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(data[:, :3])
pcd.normals = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(data[:, 3:])
pcd.colors = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(data[:, 3:])
return pcd
path=r'\airplane'
pcd1=read_txt(path+r"\airplane_0001.txt")
pcd2=read_txt(path+r"\airplane_0012.txt")
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd1,pcd2],window_name="o3d",width=1920,height=1080,
left=50,top=50,mesh_show_back_face=True)
o3d提供了自动计算法向量的API:
radius=0.01 # 搜索半径
max_nn=30 # 邻域内用于估算法线的最大点数
# 执行KD树搜索
pcd1.estimate_normals(search_param=o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius,max_nn))
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd1],window_name="o3d",width=1920,height=1080,
left=50,top=50,point_show_normal=True)
# 同样能用KD树构建协方差表
2.3 点云保存
API如下:
open3d.io.write_point_cloud(filename, pointcloud, write_ascii=False, compressed=False, print_progress=False)
Parameters
- filename (str) – 文件路径
- pointcloud (open3d.geometry.PointCloud) – 点云对象
- write_ascii (bool,optional,default=False) – 该参数为True时,将会写入ASCII码,否则一般写入二进制文件
- compressed (bool,optional,default=False) – 是否以压缩格式进行输出
- print_progress (bool,optional,default=False) –是否在控制台打印一个进度条
Returns
- bool
o3d.io.write_point_cloud("02.pcd",pcd2,write_ascii=True)
此时可以看到已经将读取的点云写入到文件中了。
三、Open3D点云常见操作
3.1 体素下采样
体素下采样(Voxel downsampling)采用规则体素格网从输入点云中创建分布均匀的下采样点云,是许多点云处理任务的预处理步骤。该算法主要分为两步:
- 创建指定大小(分辨率)的体素网络
- 当点云中至少有一个点落在某个体素内,则认为该体素被占用,体素的颜色(属性)是该体素内所有点的平均值
print("Downsample the point cloud with a voxel of 0.05")
downpcd = pcd1.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size=0.05)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([downpcd])
print("The number of PC is : ",pcd1)
print("The number of downPC is : ",downpcd)
'''
Downsample the point cloud with a voxel of 0.05
The number of PC is : PointCloud with 10000 points.
The number of downPC is : PointCloud with 1389 points.
Downsample the point cloud with a voxel of 0.005
The number of PC is : PointCloud with 10000 points.
The number of downPC is : PointCloud with 9825 points.
'''
3.2 点云正态估计
在交互页面,可以通过N查看点法线,+,-控制法线长度。
作为点云的基本操作之一,点云正态估计通过指定算法参数估测每个点可能的法向量,estimate_normals查找指定搜索半径内的临近点,通过这些临近点的协方差计算其主轴,从而估计法向量。正常情况下会产生两个方向相反的法向量,在不知道几何体的全局结构下,两者都可以是正确的。Open3D会尝试调整法线的方向,使其与原始法线对齐。
print("Recompute the normal of the downsampled point cloud")
downpcd.estimate_normals(
search_param=o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=0.1, max_nn=30))
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([downpcd],
zoom=0.3412,
front=[0.4257, -0.2125, -0.8795],
lookat=[2.6172, 2.0475, 1.532],
up=[-0.0694, -0.9768, 0.2024],
point_show_normal=True)
如果想要访问顶点法线的话,可以直接通过索引获取:
print("Print a normal vector of the 0th point")
print(downpcd.normals[0])
'''
Print a normal vector of the 0th point
[ 0.99552379 -0.03798043 0.08654404]
'''
也可以将其转为numpy数组:
print("Print the normal vectors of the first 10 points")
print(np.asarray(downpcd.normals)[:10, :])
'''
Print the normal vectors of the first 10 points
[[ 0.99552379 -0.03798043 0.08654404]
[-0.00180642 -0.97317626 0.23005372]
[-0.03311035 0.95990356 -0.27836821]
[-0.18007638 -0.98233851 -0.05082867]
[ 0.03201738 -0.92865206 0.36956763]
[-0.09411325 0.9584897 -0.26914715]
[-0.00804695 0.97716482 -0.21233029]
[-0.95046739 -0.20590633 0.2328397 ]
[ 0.58566868 0.7923609 0.17075245]
[-0.19273423 -0.87191173 0.45013714]]
'''
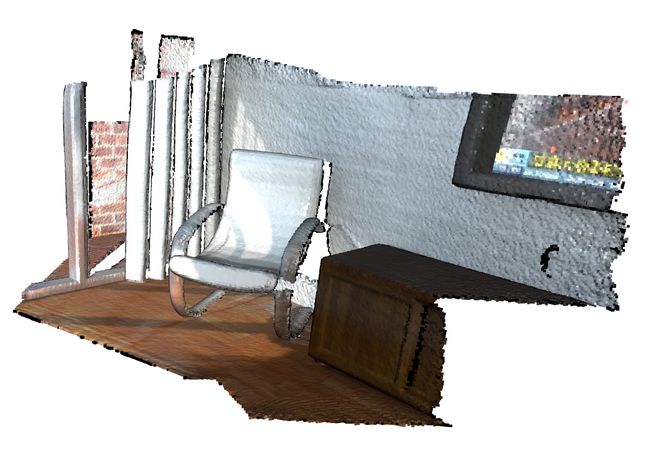
3.3 点云裁剪
Open3D的点云裁剪需要通过read_selection_polygon_volume读取多边形选择区域的json文件,接着通过.crop_point_cloud()方法过滤出点。
print("Load a polygon volume and use it to crop the original point cloud")
demo_crop_data = o3d.data.DemoCropPointCloud()
pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_crop_data.point_cloud_path)
vol = o3d.visualization.read_selection_polygon_volume(demo_crop_data.cropped_json_path)
chair = vol.crop_point_cloud(pcd)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([chair],
zoom=0.7,
front=[0.5439, -0.2333, -0.8060],
lookat=[2.4615, 2.1331, 1.338],
up=[-0.1781, -0.9708, 0.1608])
3.4 绘制点云
paint_uniform_color可以将点云颜色绘制成同一的色彩。注意颜色是在[0,1]之间的float类型。
print("Paint chair")
chair.paint_uniform_color([1, 0.706, 0])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([chair],
zoom=0.7,
front=[0.5439, -0.2333, -0.8060],
lookat=[2.4615, 2.1331, 1.338],
up=[-0.1781, -0.9708, 0.1608])
3.5 选择点云
在Open3D中,可以通过点云索引来进行筛选。select_by_index也可以通过修改invert方法进行反向选取。
inner=pcd1.select_by_index([i for i in range(len(pcd1.points)) if i%2==0])
outer=pcd1.select_by_index([i for i in range(10)],invert=True)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd1])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([inner])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([outer])
四、点云数据计算
4.1 点云距离
Open3D提供了compute_point_cloud_distance方法,能够计算源点云到目标点云的最近距离,该方法也能用于计算两点云之间的切角距离。
demo_crop_data = o3d.data.DemoCropPointCloud()
pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_crop_data.point_cloud_path)
vol = o3d.visualization.read_selection_polygon_volume(demo_crop_data.cropped_json_path)
chair = vol.crop_point_cloud(pcd)
# 从原始图像到裁剪图像中最近点的距离
dists=pcd.compute_point_cloud_distance(chair)
dists=np.asarray(dists)
ind=np.where(dists>0.1)[0]
pcd_without_chair = pcd.select_by_index(ind)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd_without_chair],
zoom=0.3412,
front=[0.4257, -0.2125, -0.8795],
lookat=[2.6172, 2.0475, 1.532],
up=[-0.0694, -0.9768, 0.2024])
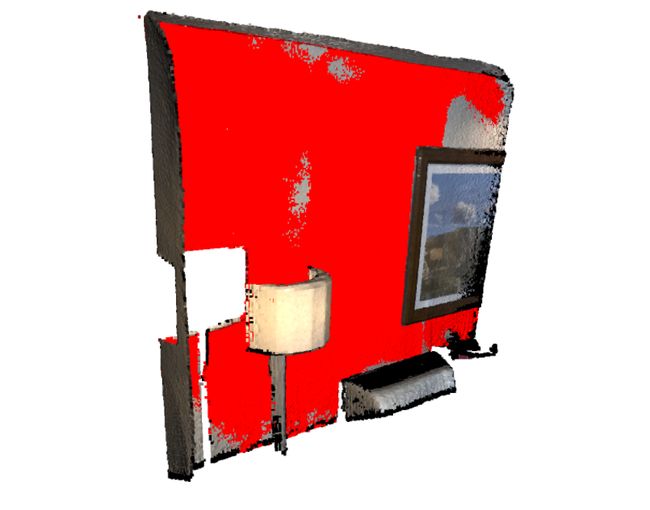
4.2 边界体积
与其几何类型相似,PointCloud也具有边界体积。
aabb = chair.get_axis_aligned_bounding_box()
aabb.color = (1, 0, 0)
obb = chair.get_oriented_bounding_box()
obb.color = (0, 1, 0)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([chair, aabb, obb],
zoom=0.7,
front=[0.5439, -0.2333, -0.8060],
lookat=[2.4615, 2.1331, 1.338],
up=[-0.1781, -0.9708, 0.1608])
4.3 凸包计算
点云凸包是包含所有点的最小凸集,在Open3D中,可采用compute_convex_hull计算。
bunny = o3d.data.BunnyMesh()
mesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(bunny.path)
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
pcl = mesh.sample_points_poisson_disk(number_of_points=2000)
hull, _ = pcl.compute_convex_hull()
hull_ls = o3d.geometry.LineSet.create_from_triangle_mesh(hull)
hull_ls.paint_uniform_color((1, 0, 0))
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcl, hull_ls])
4.4 DBSCAN聚类
DBSCAN是Ester在1996年提出的一种聚类算法,Open3D中也提供了该算法的APIpc.cluster_dbscan(eps,min_points,print_progress),eps定义了簇的半径距离,而min_points定义形成簇的最小点数量。返回是一个标签对象,若值为-1则表示噪声。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ply_point_cloud = o3d.data.PLYPointCloud()
pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(ply_point_cloud.path)
with o3d.utility.VerbosityContextManager(
o3d.utility.VerbosityLevel.Debug) as cm:
labels = np.array(
pcd.cluster_dbscan(eps=0.02, min_points=10, print_progress=True))
max_label = labels.max()
print(f"point cloud has {max_label + 1} clusters")
colors = plt.get_cmap("tab20")(labels / (max_label if max_label > 0 else 1))
colors[labels < 0] = 0
pcd.colors = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(colors[:, :3])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd],
zoom=0.455,
front=[-0.4999, -0.1659, -0.8499],
lookat=[2.1813, 2.0619, 2.0999],
up=[0.1204, -0.9852, 0.1
4.5 平面分割
Open3D支持使用RANSAC方法从点云中分割几何基元(geometric primitives)。通过segment_plane方法,可以找到点云中的最大支持平面(the plane with the largest support)。该方法提供了三个参数:
distance_threshold:定义了一个点可被视为内嵌点的估计平面的最大距离ransac_n:定义用来估计平面的随机抽样点数量num_iterations:定义了随机平面抽样和验证的频率
4.6 消隐点
当我们从给定视角渲染点云时,由于前方没有遮挡,可能会有背面的点渗入到前景中。Katz提出了一种消隐算法(Hidden point removal),可以从给定的视图中近似地获得点云的可见性,而无需表面重建或正常的估计。
print("Convert mesh to a point cloud and estimate dimensions")
armadillo = o3d.data.ArmadilloMesh()
mesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(armadillo.path)
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
pcd = mesh.sample_points_poisson_disk(5000)
diameter = np.linalg.norm(
np.asarray(pcd.get_max_bound()) - np.asarray(pcd.get_min_bound()))
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd])
print("Define parameters used for hidden_point_removal")
camera = [0, 0, diameter]
radius = diameter * 100
print("Get all points that are visible from given view point")
_, pt_map = pcd.hidden_point_removal(camera, radius)
print("Visualize result")
pcd = pcd.select_by_index(pt_map)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd])