Linux从入门到入土②(系统管理)
文章目录
- 系统管理
-
- Linux 中的进程和服务
- Service服务管理(CentOS 6 版本-了解)
-
- 基本语法
- 使用
- systemctl服务管理(CentOS 7 版本-重点掌握)
-
- 基本语法
- 使用
- chkconfig 设置后台服务的自启配置(CentOS 6 版本)
-
- 基本语法
- 使用
- systemctl 设置后台服务的自启配置
-
- 基本语法
- 使用
- 附:Linux系统中文件颜色分别代表什么?
- Linux 系统启动级别
系统管理
Linux 中的进程和服务
计算机中,一个正在执行的程序或命令,被叫做“进程”(process)。
启动之后一只存在、常驻内存的进程,一般被称作“服务”(service)。
这里有几个注意点:
- 在linux中,每一个程序都有自己的一个进程,每一个进程有一个id号(PID)
- 每一个进程,都有一个父进程!
- 进程可以有两种存在方式:前台、后台
- 一般的服务都是后台运行的,基本的程序都是前台运行的
我们整个系统运行的时候可能需要很多后台的服务来支撑,这些服务往往都是在系统一启动的时候就开始了,直到系统关闭的时候才会被终止,所有的这些服务,我们称作系统服务,而具体执行这些服务的进程,我们往往把他们叫做守护进程(deamon).
我们可以发现Linux中的很多服务是以d结尾的,说明当成的进程是守护进程。
在Linux里面系统服务和守护进程可以当成一个东西
Service服务管理(CentOS 6 版本-了解)
基本语法
service 服务名 start | stop |· restart | status
使用
首先我们查看一下服务:
ls /etc/init.d/服务名
(1)查看网络服务的状态
[root@hadoop100 桌面]#service network status
(2)停止网络服务
[root@hadoop100 桌面]#service network stop
(3)启动网络服务
[root@hadoop100 桌面]#service network start
(4)重启网络服务
[root@hadoop100 桌面]#service network restart
systemctl服务管理(CentOS 7 版本-重点掌握)
基本语法
systemctl start | stop | restart | status 服务名
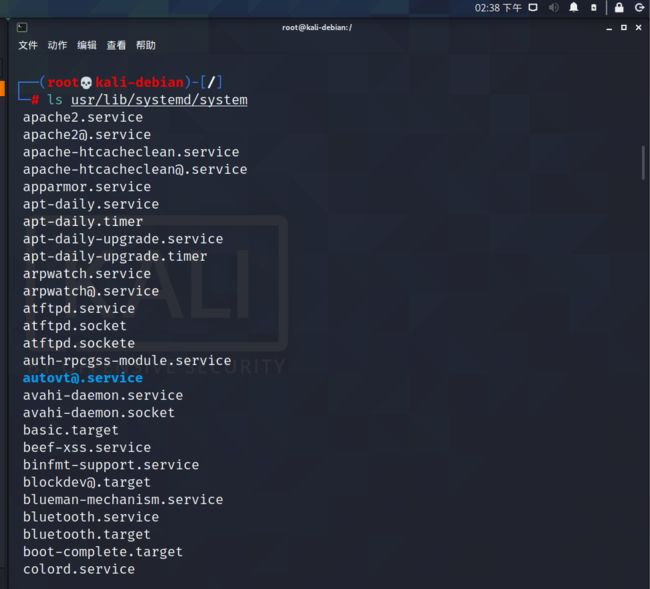
我们还是来查看一下服务:
这回的位置不一样
ls /usr/lib/systemd/system
我们可以明显的感觉到服务的数量变多了
使用
(1)查看防火墙服务的状态
[root@hadoop100 桌面]# systemctl status firewalld
(2)停止防火墙服务
[root@hadoop100 桌面]# systemctl stop firewalld
(3)启动防火墙服务
[root@hadoop100 桌面]# systemctl start firewalld
(4)重启防火墙服务
[root@hadoop100 桌面]# systemctl restart firewalled
chkconfig 设置后台服务的自启配置(CentOS 6 版本)
基本语法
chkconfig (功能描述:查看所有服务器自启配置)
chkconfig 服务名 off (功能描述:关掉指定服务的自动启动)
chkconfig 服务名 on (功能描述:开启指定服务的自动启动)
chkconfig 服务名 --list (功能描述:查看服务开机启动状态)
使用
(1)开启/关闭 network(网络)服务的自动启动
[root@hadoop100 桌面]#chkconfig network on
[root@hadoop100 桌面]#chkconfig network off
(2)开启/关闭 network 服务指定级别的自动启动
[root@hadoop100 桌面]#chkconfig --level 指定级别 network on
[root@hadoop100 桌面]#chkconfig --level 指定级别 network of
systemctl 设置后台服务的自启配置
基本语法
systemctl list-unit-files (功能描述:查看服务开机启动状态)
systemctl disable service_name (功能描述:关掉指定服务的自动启动)
systemctl enable service_name (功能描述:开启指定服务的自动启动)
static代表我现在不能确定这个服务是否启动还是不启动,因为当前服务可能与其他服务相关联,他可能依赖于其他服务。
使用
(1)开启/关闭 iptables(防火墙)服务的自动启动
[root@hadoop100 桌面]# systemctl enable firewalld.service
[root@hadoop100 桌面]# systemctl disable firewalld.service
附:Linux系统中文件颜色分别代表什么?
1、蓝色代表目录
2、白色代表一般性文件,如文本文件、配置文件、源码文件等
3、绿色代表可执行文件
4、黄色代表设备文件
5、红色代表压缩文件
6、红色代表闪烁代表连接文件有问题
7、灰色代表其他文件
8、浅蓝色代表链接文件
Linux 系统启动级别
Linux的启动分为五个阶段:
- 内核的引导
- 运行init
- 系统初始化
- 建立终端
- 用户登陆系统
init程序的类型:
SysV: init, CentOS 5之前, 配置文件: /etc/inittab。Upstart: init,CentOS 6, 配置文件: /etc/inittab, /etc/init/*.conf。Systemd: systemd, CentOS 7,配置文件: /usr/lib/systemd/system、 /etc/systemd/system。
启动步骤:开机之后首先进入到BIOS的自检和启动过程,然后去引导分区里面去获取引导文件和linux内核中的一些内容进行整个系统的初始化,初始化完成之后进入init进程,它是用户级别主动启动的第一个进程,接下来他就会判断当前系统的运行级别,根据运行级别启动对应的系统服务。
我们可以看到Linux系统有七种运行级别,级别越高支持的功能就会越丰富。
级别6是一个重启的级别,与前面无关
NFS指网络文件系统
CentOS7 的运行级别简化为:
multi-user.target 等价于原运行级别 3(多用户有网,无图形界面)
graphical.target 等价于原运行级别 5(多用户有网,有图形界面)
查看当前运行级别:
systemctl get-default
修改当前运行级别
systemctl set-default TARGET.target
(这里 TARGET 取 multi-user 或者 graphical)
我们也可以在命令行使用:
- init 3进入非图形化模式
- init 5进入图形化模式