PINN(Python通过递归神经网络直接实现常微分方程积分)
Python构建PINN:(1)加载工具包;(2)搭建基于物理定律的模型结构;(3)将数据驱动内核与基于物理的内核耦合(PINN);(4)搭建神经网络;(5)使用训练好的神经网络预测
(1)、加载工具包
import pandas as pd #用于数据导入和操作的pandas
import numpy as np #用于数据导入和操作的numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#专门化模型
from tensorflow.keras.layers import RNN, Dense, Layer
from tensorflow.keras import Sequential #使用models.Sequential()来搭建神经网络
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import RMSprop #超参数优化
from tensorflow.python.framework import tensor_shape
from tensorflow import float32, concat, convert_to_tensor #数据类型(浮点型32位)、拼接两个矩阵、 将python的数据类型(列表和矩阵)转换成 TensorFlow可用的tensor数据类型
(2)、搭建数据驱动的欧拉公式结构
#欧拉积分单元
class EulerIntegratorCell(Layer):
def __init__(self, C, m, dKlayer, a0=None, units=1, **kwargs):
def call(self, inputs, states): #构造公式
inputs = convert_to_tensor(inputs) #将python的数据类型(列表和矩阵)转换成TensorFlow可用的 tensor数据类型
a_tm1 = convert_to_tensor(states)
x_d_tm1 = concat((inputs, a_tm1[0, :]), axis=1) #按列拼接两个矩阵:aixs=d 这项参数,表示沿着第d+1(d=- 1表示倒数第一维)维的方向操作。
dk_t = self.dKlayer(x_d_tm1)
da_t = self.C * (dk_t ** self.m)
a = da_t + a_tm1[0, :]
return a, [a]
def get_initial_state(self, inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None) #令初始状态为零#batch_size:样 本数量,即维度
return self.a0
(3)、使用来自EulerIntegratorCell的对象,并将其与RNN耦合,创建一个可供训练的模型
#使用model.compile()方法来配置训练方法
def create_model(C, m, a0, dKlayer, batch_input_shape, return_sequences=False, return_state=False):
euler = EulerIntegratorCell(C=C, m=m, dKlayer=dKlayer, a0=a0, batch_input_shape=batch_input_shape)
#batch_input_shape来增强输入的形状
PINN = RNN(cell=euler, batch_input_shape=batch_input_shape, return_sequences=return_sequences, return_state=return_state)
model = Sequential()
model.add(PINN)
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=RMSprop(1e-2)) #使用model.compile()方法来配置训练方法:使用 RMSprop优化器(起到的效果是在参数空间更为平缓 的方向,会取得更大的进步),学习率为1e-2
return model
(4)、使用models.Sequential()来搭建神经网络
dKlayer = Sequential() #初始化dKlayer,准备按顺序接收不同的层
dKlayer.add(Normalization(np.min(Strain), np.max(Strain), np.min(atrain), np.max(atrain)))
dKlayer.add(Dense(5, activation='tanh’)) #model.add,添加层,增加了第一层5个神经元 (tanh作为激活函数)输出,全连接层 Dense定义 神经网络的一层
dKlayer.add(Dense(1)) #添加第二层1个神经元输入
5)、使用训练好的模型预测
# fitting physics-informed neural network #使用model.fit()方法来执行训练过程
model = create_model(C=C, m=m, a0=convert_to_tensor(a0, dtype=float32), dKlayer=dKlayer, batch_input_shape=Strain.shape) #创建混合物理信息神经网络模型
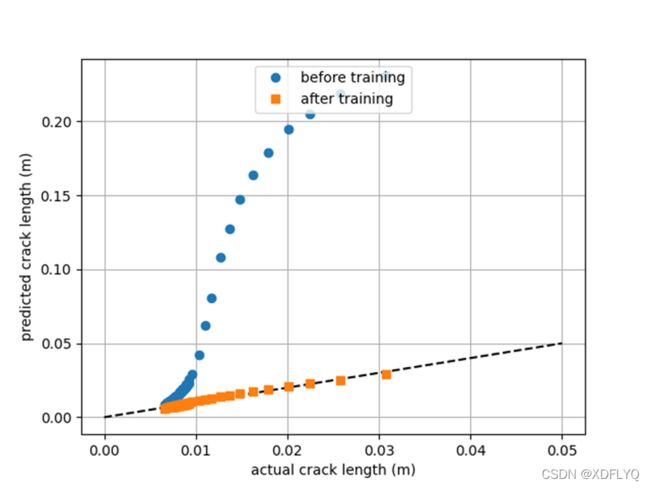
aPred_before = model.predict_on_batch(Strain)[:,:] #训练前后检查训练集的预测
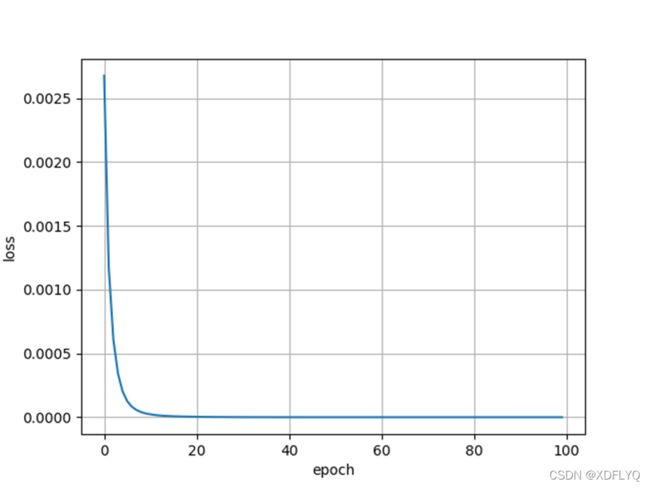
model.fit(Strain, atrain, epochs=100, steps_per_epoch=1, verbose=1) #模型已经准备好接受培训,使 用model.fit()方法来执行训练过程
aPred = model.predict_on_batch(Strain)[:,:] #训练前后检查训练集的预测
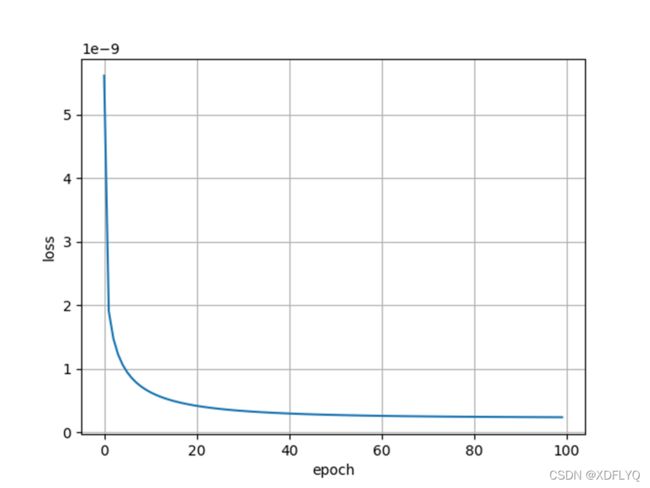
损失在20个时期内迅速收敛,40个时期后仅略有改善
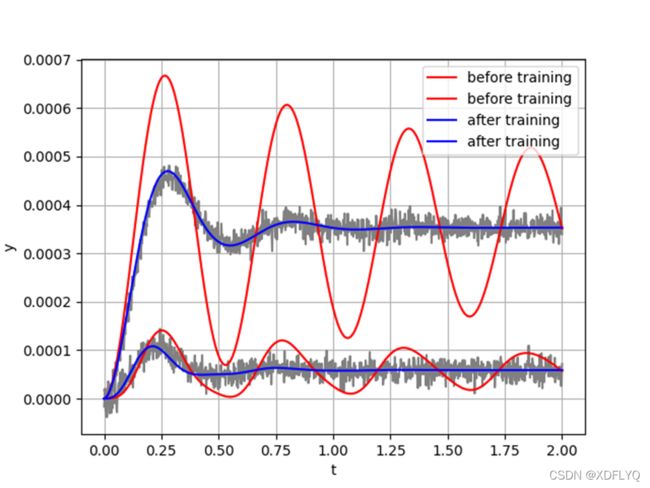
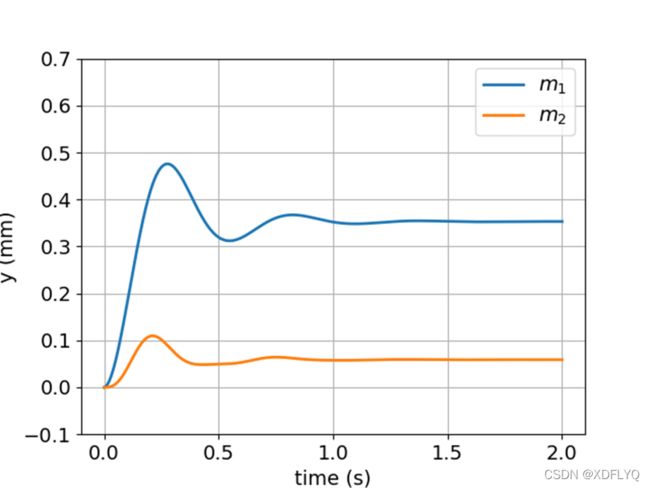
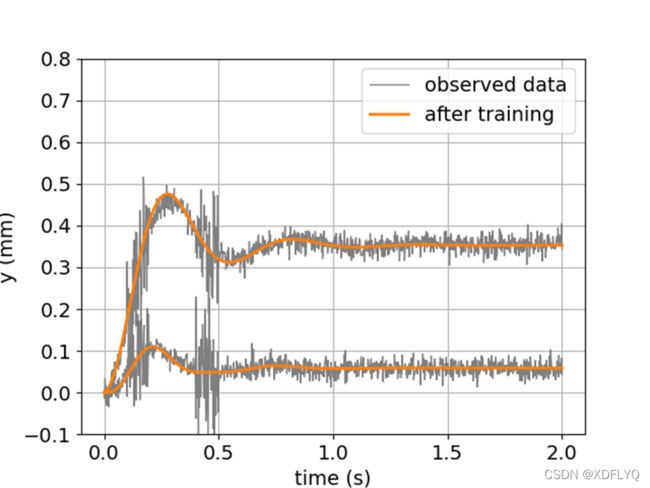
对实际位移的预测
数据损坏发生在两个不同的时间段(0.1s到0.2s)和(0.4s到0.5s)