线上 K8s 集群性能评估、基础服务部署调优
对于非结构化的数据存储系统来说,LIST 操作通常都是非常重量级的,不仅占用大量的 磁盘 IO、网络带宽和 CPU,而且会影响同时间段的其他请求(尤其是响应延迟要求极高的 选主请求),是集群稳定性的一大杀手。
例如,对于 Ceph 对象存储来说,每个 LIST bucket 请求都需要去多个磁盘中捞出这个 bucket 的全部数据;不仅自身很慢,还影响了同一时间段内的其他普通读写请求,因为 IO 是共享的,导致响应延迟上升乃至超时。如果 bucket 内的对象非常多(例如用作 harbor/docker-registry 的存储后端),LIST 操作甚至都无法在常规时间内完成( 因而依赖 LIST bucket 操作的 registry GC 也就跑不起来)。
又如 KV 存储 etcd。相比于 Ceph,一个实际 etcd 集群存储的数据量可能很小(几个 ~ 几十个 GB),甚至足够缓存到内存中。但与 Ceph 不同的是,它的并发请求数量可能会高 几个量级,比如它是一个 ~4000 nodes 的 k8s 集群的 etcd。单个 LIST 请求可能只需要 返回几十 MB 到上 GB 的流量,但并发请求一多,etcd 显然也扛不住,所以最好在前面有 一层缓存,这就是 apiserver 的功能(之一)。K8s 的 LIST 请求大部分都应该被 apiserver 挡住,从它的本地缓存提供服务,但如果使用不当,就会跳过缓存直接到达 etcd,有很大的稳定性风险。
本文深入研究 k8s apiserver/etcd 的 LIST 操作处理逻辑和性能瓶颈,并提供一些基础服务的 LIST 压力测试、 部署和调优建议,提升大规模 K8s 集群的稳定性。
kube-apiserver LIST 请求处理逻辑:
代码基于 v1.24.0,不过 1.19~1.24 的基本逻辑和代码路径是一样的,有需要可对照参考。
引 言
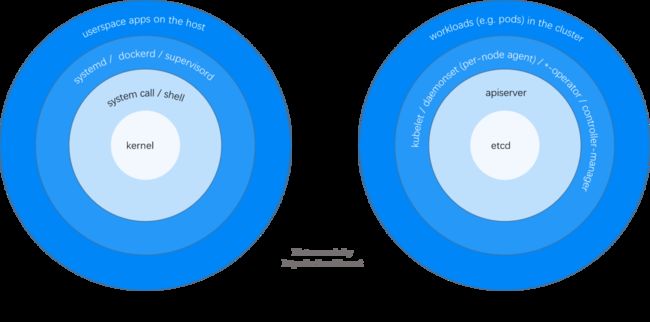
1.1 K8s 架构:环形层次视图
从架构层次和组件依赖角度,可以将一个 K8s 集群和一台 Linux 主机做如下类比:
Fig 1. Anology: a Linux host and a Kubernetes cluster
对于 K8s 集群,从内到外的几个组件和功能:
- etcd:持久化 KV 存储,集群资源(pods/services/networkpolicies/…)的唯一的权威数据(状态)源;
- apiserver:从 etcd 读取(ListWatch)全量数据,并缓存在内存中;无状态服务,可水平扩展;
- 各种基础服务(e.g. kubelet、*-agent、*-operator):连接 apiserver,获取(List/ListWatch)各自需要的数据;
- 集群内的 workloads:在 1 和 2 正常的情况下由 3 来创建、管理和 reconcile,例如 kubelet 创建 pod、cilium 配置网络和安全策略。
1.2 apiserver/etcd 角色
以上可以看到,系统路径中存在两级 List/ListWatch(但数据是同一份):
- apiserver List/ListWatch etcd
- 基础服务 List/ListWatch apiserver
因此,从最简形式上来说,apiserver 就是挡在 etcd 前面的一个代理(proxy):
+--------+ +---------------+ +------------+
| Client | -----------> | Proxy (cache) | --------------> | Data store |
+--------+ +---------------+ +------------+
infra services apiserver etcd- 绝大部分情况下,apiserver 直接从本地缓存提供服务(因为它缓存了集群全量数据);
- 某些特殊情况,例如:
- 客户端明确要求从 etcd 读数据(追求最高的数据准确性),
- apiserver 本地缓存还没建好
apiserver 就只能将请求转发给 etcd —— 这里就要特别注意了 —— 客户端 LIST 参数设置不当也可能会走到这个逻辑。
1.3 apiserver/etcd List 开销
1.3.1 请求举例
考虑下面几个 LIST 操作:
LIST apis/cilium.io/v2/ciliumendpoints?limit=500&resourceVersion=0
这里同时传了两个参数,但 resourceVersion=0 会导致 apiserver 忽略 limit=500, 所以客户端拿到的是全量 ciliumendpoints 数据。
一种资源的全量数据可能是比较大的,需要考虑清楚是否真的需要全量数据。后文会介绍定量测量与分析方法。
LIST api/v1/pods?filedSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1
这个请求是获取 node1 上的所有 pods(%3D 是 = 的转义)。
根据 nodename 做过滤,给人的感觉可能是数据量不太大,但其实背后要比看上去复杂:
这种行为是要避免的,除非对数据准确性有极高要求,特意要绕过 apiserver 缓存。
- 首先,这里没有指定 resourceVersion=0,导致 apiserver 跳过缓存,直接去 etcd 读数据;
- 其次,etcd 只是 KV 存储,没有按 label/field 过滤功能(只处理 limit/continue),
- 所以,apiserver 是从 etcd 拉全量数据,然后在内存做过滤,开销也是很大的,后文有代码分析。
LIST api/v1/pods?filedSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1&resourceVersion=0
跟 2 的区别是加上了 resourceVersion=0,因此 apiserver 会从缓存读数据,性能会有量级的提升。
但要注意,虽然实际上返回给客户端的可能只有几百 KB 到上百 MB(取决于 node 上 pod 的数量、pod 上 label 的多少等因素), 但 apiserver 需要处理的数据量可能是几个 GB。后面会有定量分析。
以上可以看到,不同的 LIST 操作产生的影响是不一样的,而客户端看到数据还有可能只 是 apiserver/etcd 处理数据的很小一部分。如果基础服务大规模启动或重启, 就极有可能把控制平面打爆。
1.3.2 处理开销
List 请求可以分为两种:
- List 全量数据:开销主要花在数据传输;
- 指定用 label 或字段(field)过滤,只需要匹配的数据。
这里需要特别说明的是第二种情况,也就是 list 请求带了过滤条件。
- 大部分情况下,apiserver 会用自己的缓存做过滤,这个很快,因此耗时主要花在数据传输;
- 需要将请求转给 etcd 的情况, 前面已经提到,etcd 只是 KV 存储,并不理解 label/field 信息,因此它无法处理过滤请求。实际的过程是:apiserver 从 etcd 拉全量数据,然后在内存做过滤,再返回给客户端。因此除了数据传输开销(网络带宽),这种情况下还会占用大量 apiserver CPU 和内存。
1.4 大规模部署时潜在的问题
再来看个例子,下面这行代码用 k8s client-go 根据 nodename 过滤 pod,
podList, err := Client().CoreV1().Pods("").List(ctx(), ListOptions{FieldSelector: "spec.nodeName=node1"})看起来非常简单的操作,我们来实际看一下它背后的数据量。以一个 4000 node,10w pod 的集群为例,全量 pod 数据量:
- etcd 中:紧凑的非结构化 KV 存储,在 1GB 量级;
- apiserver 缓存中:已经是结构化的 golang objects,在 2GB 量级( TODO:需进一步确认);
- apiserver 返回:client 一般选择默认的 json 格式接收, 也已经是结构化数据。全量 pod 的 json 也在 2GB 量级。
可以看到,某些请求看起来很简单,只是客户端一行代码的事情,但背后的数据量是惊人的。指定按 nodeName 过滤 pod 可能只返回了 500KB 数据,但 apiserver 却需要过滤 2GB 数据 —— 最坏的情况,etcd 也要跟着处理 1GB 数据 (以上参数配置确实命中了最坏情况,见下文代码分析)。
集群规模比较小的时候,这个问题可能看不出来(etcd 在 LIST 响应延迟超过某个阈值 后才开始打印 warning 日志);规模大了之后,如果这样的请求比较多,apiserver/etcd 肯定是扛不住的。
1.5 本文目的
通过深入代码查看 k8s 的 List/ListWatch 实现,加深对性能问题的理解,对大规模 K8s 集群的稳定性优化提供一些参考。
apiserver List( ) 操作源码分析
有了以上理论预热,接下来可以看代码实现了。
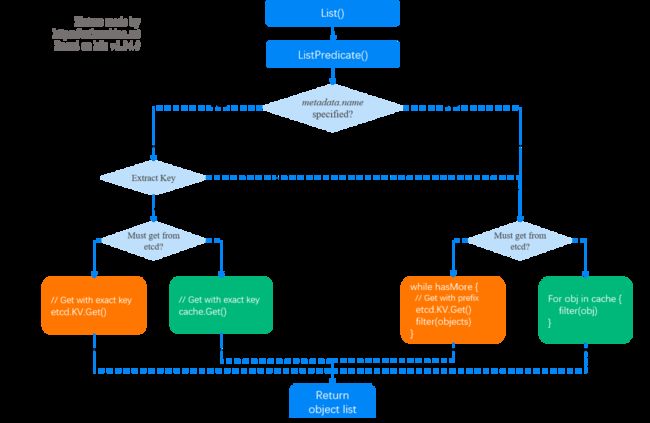
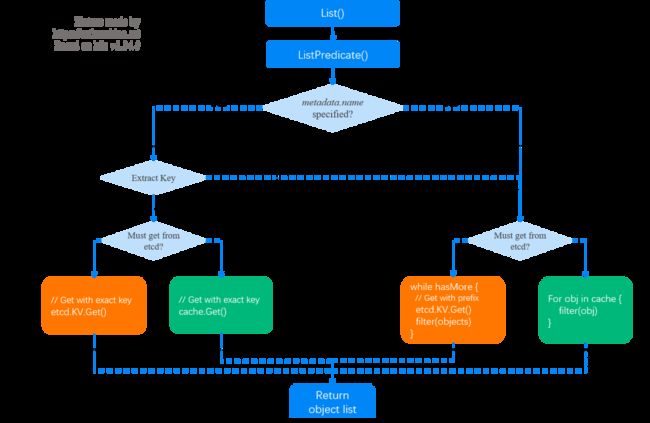
2.1 调用栈和流程图
store.List
|-store.ListPredicate
|-if opt == nil
| opt = ListOptions{ResourceVersion: ""}
|-Init SelectionPredicate.Limit/Continue fileld
|-list := e.NewListFunc() // objects will be stored in this list
|-storageOpts := storage.ListOptions{opt.ResourceVersion, opt.ResourceVersionMatch, Predicate: p}
|
|-if MatchesSingle ok // 1. when "metadata.name" is specified, get single obj
| // Get single obj from cache or etcd
|
|-return e.Storage.List(KeyRootFunc(ctx), storageOpts) // 2. get all objs and perform filtering
|-cacher.List()
| // case 1: list all from etcd and filter in apiserver
|-if shouldDelegateList(opts) // true if resourceVersion == ""
| return c.storage.List // list from etcd
| |- fromRV *int64 = nil
| |- if len(storageOpts.ResourceVersion) > 0
| | rv = ParseResourceVersion
| | fromRV = &rv
| |
| |- for hasMore {
| | objs := etcdclient.KV.Get()
| | filter(objs) // filter by labels or filelds
| | }
|
| // case 2: list & filter from apiserver local cache (memory)
|-if cache.notready()
| return c.storage.List // get from etcd
|
| // case 3: list & filter from apiserver local cache (memory)
|-obj := watchCache.WaitUntilFreshAndGet
|-for elem in obj.(*storeElement)
| listVal.Set() // append results to listOjb
|-return // results stored in listObj对应的流程图:
Fig 2-1. List operation processing in apiserver
2.2 请求处理入口:List( )
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.24.0/staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/registry/generic/registry/store.go#L361
// 根据 PredicateFunc 中指定的 LabelSelector 和 FieldSelector 过滤,返回一个对象列表
func (e *Store) List(ctx, options *metainternalversion.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
label := labels.Everything()
if options != nil && options.LabelSelector != nil
label = options.LabelSelector // Label 过滤器,例如 app=nginx
field := fields.Everything()
if options != nil && options.FieldSelector != nil
field = options.FieldSelector // 字段过滤器,例如 spec.nodeName=node1
out := e.ListPredicate(ctx, e.PredicateFunc(label, field), options) // 拉取(List)数据并过滤(Predicate)
if e.Decorator != nil
e.Decorator(out)
return out, nil
}2.3 ListPredicate( )
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.24.0/staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/registry/generic/registry/store.go#L411
func (e *Store) ListPredicate(ctx , p storage.SelectionPredicate, options *metainternalversion.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
// Step 1: 初始化
if options == nil
options = &metainternalversion.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: ""}
p.Limit = options.Limit
p.Continue = options.Continue
list := e.NewListFunc() // 返回结果将存储在这里面
storageOpts := storage.ListOptions{ // 将 API 侧的 ListOption 转成底层存储侧的 ListOption,字段区别见下文
ResourceVersion: options.ResourceVersion,
ResourceVersionMatch: options.ResourceVersionMatch,
Predicate: p,
Recursive: true,
}
// Step 2:如果请求指定了 metadata.name,则应获取单个 object,无需对全量数据做过滤
if name, ok := p.MatchesSingle(); ok { // 检查是否设置了 metadata.name 字段
if key := e.KeyFunc(ctx, name); err == nil { // 获取这个 object 在 etcd 中的 key(唯一或不存在)
storageOpts.Recursive = false
e.Storage.GetList(ctx, key, storageOpts, list)
return list
}
// else 逻辑:如果执行到这里,说明没有从 context 中拿到过滤用的 key,则 fallback 到下面拿全量数据再过滤
}
// Step 3: 对全量数据做过滤
e.Storage.GetList(ctx, e.KeyRootFunc(), storageOpts, list) // KeyRootFunc() 用来获取这种资源在 etcd 里面的 root key(即 prefix,不带最后的 /)
return list
}1.24.0 中 case 1 & 2 都是 调用 e.Storage.GetList(),之前的版本有点不同:
Case 1 中的 e.Storage.GetToList
Case 1 中的 e.Storage.List
不过基本流程是一样的。
- 如果客户端没传 ListOption,则初始化一个默认值,其中的 ResourceVersion 设置为空字符串, 这将使 apiserver 从 etcd 拉取数据来返回给客户端,而不使用本地缓存(除非本地缓存还没有建好);
- 举例,客户端设置 ListOption{Limit: 5000, ResourceVersion: 0} list ciliumendpoints 时,发送的请求将为 /apis/cilium.io/v2/ciliumendpoints?limit=500&resourceVersion=0。ResourceVersion 为空字符串的行为,后面会看到对它的解析。
- 用 listoptions 中的字段分别初始化过滤器(SelectionPredicate)的 limit/continue 字段;
- 初始化返回结果,list := e.NewListFunc();
- 将 API 侧的 ListOption 转成底层存储的 ListOption,字段区别见下文
metainternalversion.ListOptions 是 API 侧的结构体,包含了
// staging/src/k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/internalversion/types.go
// ListOptions is the query options to a standard REST list call.
type ListOptions struct {
metav1.TypeMeta
LabelSelector labels.Selector // 标签过滤器,例如 app=nginx
FieldSelector fields.Selector // 字段过滤器,例如 spec.nodeName=node1
Watch bool
AllowWatchBookmarks bool
ResourceVersion string
ResourceVersionMatch metav1.ResourceVersionMatch
TimeoutSeconds *int64 // Timeout for the list/watch call.
Limit int64
Continue string // a token returned by the server. return a 410 error if the token has expired.
}storage.ListOptions 是传给底层存储的结构体,字段有一些区别:
// staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/interfaces.go
// ListOptions provides the options that may be provided for storage list operations.
type ListOptions struct {
ResourceVersion string
ResourceVersionMatch metav1.ResourceVersionMatch
Predicate SelectionPredicate // Predicate provides the selection rules for the list operation.
Recursive bool // true: 根据 key 获取单个对象;false:根据 key prefix 获取全量数据
ProgressNotify bool // storage-originated bookmark, ignored for non-watch requests.
}2.4 请求指定了资源名(resource name):获取单个对象
接下来根据请求中是否指定了 meta.Name 分为两种情况:
- 如果指定了,说明是查询单个对象,因为 Name 是唯一的,接下来转入查询单个 object 的逻辑;
- 如果未指定,则需要获取全量数据,然后在 apiserver 内存中根据 SelectionPredicate 中的过滤条件进行过滤,将最终结果返回给客户端;
代码如下:
// case 1:根据 metadata.name 获取单个 object,无需对全量数据做过滤
if name, ok := p.MatchesSingle(); ok { // 检查是否设置了 metadata.name 字段
if key := e.KeyFunc(ctx, name); err == nil {
e.Storage.GetList(ctx, key, storageOpts, list)
return list
}
// else 逻辑:如果执行到这里,说明没有从 context 中拿到过滤用的 key,则 fallback 到下面拿全量数据再过滤
}e.Storage 是一个 Interface,
// staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/interfaces.go
// Interface offers a common interface for object marshaling/unmarshaling operations and
// hides all the storage-related operations behind it.
type Interface interface {
Create(ctx , key string, obj, out runtime.Object, ttl uint64) error
Delete(ctx , key string, out runtime.Object, preconditions *Preconditions,...)
Watch(ctx , key string, opts ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error)
Get(ctx , key string, opts GetOptions, objPtr runtime.Object) error
// unmarshall objects found at key into a *List api object (an object that satisfies runtime.IsList definition).
// If 'opts.Recursive' is false, 'key' is used as an exact match; if is true, 'key' is used as a prefix.
// The returned contents may be delayed, but it is guaranteed that they will
// match 'opts.ResourceVersion' according 'opts.ResourceVersionMatch'.
GetList(ctx , key string, opts ListOptions, listObj runtime.Object) errore.Storage.GetList() 会执行到 cacher 代码。
不管是获取单个 object,还是获取全量数据,都经历类似的过程:
- 优先从 apiserver 本地缓存获取(决定因素包括 ResourceVersion 等),
- 不得已才到 etcd 去获取;
获取单个对象的逻辑相对比较简单,这里就不看了。接下来看 List 全量数据再做过滤的逻辑。
2.5 请求未指定资源名,获取全量数据做过滤
2.5.1 apiserver 缓存层:GetList() 处理逻辑
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.24.0/staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/cacher/cacher.go#L622
// GetList implements storage.Interface
func (c *Cacher) GetList(ctx , key string, opts storage.ListOptions, listObj runtime.Object) error {
recursive := opts.Recursive
resourceVersion := opts.ResourceVersion
pred := opts.Predicate
// 情况一:ListOption 要求必须从 etcd 读
if shouldDelegateList(opts)
return c.storage.GetList(ctx, key, opts, listObj) // c.storage 指向 etcd
// If resourceVersion is specified, serve it from cache.
listRV := c.versioner.ParseResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
// 情况二:apiserver 缓存未建好,只能从 etcd 读
if listRV == 0 && !c.ready.check()
return c.storage.GetList(ctx, key, opts, listObj)
// 情况三:apiserver 缓存正常,从缓存读:保证返回的 objects 版本不低于 `listRV`
listPtr := meta.GetItemsPtr(listObj)
listVal := conversion.EnforcePtr(listPtr)
filter := filterWithAttrsFunction(key, pred) // 最终的过滤器
objs, readResourceVersion, indexUsed := c.listItems(listRV, key, pred, ...) // 根据 index 预筛,性能优化
for _, obj := range objs {
elem := obj.(*storeElement)
if filter(elem.Key, elem.Labels, elem.Fields) // 真正的过滤
listVal.Set(reflect.Append(listVal, reflect.ValueOf(elem))
}
// 更新最后一次读到的 ResourceVersion
if c.versioner != nil
c.versioner.UpdateList(listObj, readResourceVersion, "", nil)
return nil
}2.5.2 判断是否必须从 etcd 读数据:shouldDelegateList( )
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.24.0/staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/cacher/cacher.go#L591
func shouldDelegateList(opts storage.ListOptions) bool {
resourceVersion := opts.ResourceVersion
pred := opts.Predicate
pagingEnabled := DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.APIListChunking) // 默认是启用的
hasContinuation := pagingEnabled && len(pred.Continue) > 0 // Continue 是个 token
hasLimit := pagingEnabled && pred.Limit > 0 && resourceVersion != "0" // 只有在 resourceVersion != "0" 的情况下,hasLimit 才有可能为 true
// 1. 如果未指定 resourceVersion,从底层存储(etcd)拉去数据;
// 2. 如果有 continuation,也从底层存储拉数据;
// 3. 只有 resourceVersion != "0" 时,才会将 limit 传给底层存储(etcd),因为 watch cache 不支持 continuation
return resourceVersion == "" || hasContinuation || hasLimit || opts.ResourceVersionMatch == metav1.ResourceVersionMatchExact
}这里非常重要:
- 问:客户端未设置 ListOption{} 中的 ResourceVersion 字段,是否对应到这里的 resourceVersion == ""?答:是的,所以第一节的 例子 会导致从 etcd 拉全量数据。
- 问:客户端设置了 limit=500&resourceVersion=0 是否会导致下次 hasContinuation==true?答:不会,resourceVersion=0 将导致 limit 被忽略(hasLimit 那一行代码),也就是说, 虽然指定了 limit=500,但这个请求会返回全量数据。
- 问:ResourceVersionMatch 是什么用途?答:用来告诉 apiserver,该如何解读 ResourceVersion。官方有个很复杂的 表格 ,有兴趣可以看看。
接下来再返回到 cacher 的 GetList() 逻辑,来看下具体有哪几种处理情况。
2.5.3 情况一:ListOption 要求从 etcd 读数据
这种情况下,apiserver 会直接从 etcd 读取所有 objects 并过滤,然后返回给客户端, 适用于数据一致性要求极其高的场景。当然,也容易误入这种场景造成 etcd 压力过大,例如 第一节的例子。
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.24.0/staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/etcd3/store.go#L563
// GetList implements storage.Interface.
func (s *store) GetList(ctx , key string, opts storage.ListOptions, listObj runtime.Object) error {
listPtr := meta.GetItemsPtr(listObj)
v := conversion.EnforcePtr(listPtr)
key = path.Join(s.pathPrefix, key)
keyPrefix := key // append '/' if needed
newItemFunc := getNewItemFunc(listObj, v)
var fromRV *uint64
if len(resourceVersion) > 0 { // 如果 RV 非空(客户端不传时,默认是空字符串)
parsedRV := s.versioner.ParseResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
fromRV = &parsedRV
}
// ResourceVersion, ResourceVersionMatch 等处理逻辑
switch {
case recursive && s.pagingEnabled && len(pred.Continue) > 0: ...
case recursive && s.pagingEnabled && pred.Limit > 0 : ...
default : ...
}
// loop until we have filled the requested limit from etcd or there are no more results
for {
getResp = s.client.KV.Get(ctx, key, options...) // 从 etcd 拉数据
numFetched += len(getResp.Kvs)
hasMore = getResp.More
for i, kv := range getResp.Kvs {
if limitOption != nil && int64(v.Len()) >= pred.Limit {
hasMore = true
break
}
lastKey = kv.Key
data := s.transformer.TransformFromStorage(ctx, kv.Value, kv.Key)
appendListItem(v, data, kv.ModRevision, pred, s.codec, s.versioner, newItemFunc) // 这里面会做过滤
numEvald++
}
key = string(lastKey) + "\x00"
}
// instruct the client to begin querying from immediately after the last key we returned
if hasMore {
// we want to start immediately after the last key
next := encodeContinue(string(lastKey)+"\x00", keyPrefix, returnedRV)
return s.versioner.UpdateList(listObj, uint64(returnedRV), next, remainingItemCount)
}
// no continuation
return s.versioner.UpdateList(listObj, uint64(returnedRV), "", nil)
}- client.KV.Get() 就进入 etcd client 库了,感兴趣可以继续往下挖。
- appendListItem() 会对拿到的数据进行过滤,这就是我们第一节提到的 apiserver 内存过滤操作。
2.5.4 情况二:本地缓存还没建好,只能从 etcd 读数据
具体执行过程与情况一相同。
2.5.5 情况三:使用本地缓存
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.24.0/staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/cacher/cacher.go#L622
// GetList implements storage.Interface
func (c *Cacher) GetList(ctx , key string, opts storage.ListOptions, listObj runtime.Object) error {
// 情况一:ListOption 要求必须从 etcd 读
...
// 情况二:apiserver 缓存未建好,只能从 etcd 读
...
// 情况三:apiserver 缓存正常,从缓存读:保证返回的 objects 版本不低于 `listRV`
listPtr := meta.GetItemsPtr(listObj) // List elements with at least 'listRV' from cache.
listVal := conversion.EnforcePtr(listPtr)
filter := filterWithAttrsFunction(key, pred) // 最终的过滤器
objs, readResourceVersion, indexUsed := c.listItems(listRV, key, pred, ...) // 根据 index 预筛,性能优化
for _, obj := range objs {
elem := obj.(*storeElement)
if filter(elem.Key, elem.Labels, elem.Fields) // 真正的过滤
listVal.Set(reflect.Append(listVal, reflect.ValueOf(elem))
}
if c.versioner != nil
c.versioner.UpdateList(listObj, readResourceVersion, "", nil)
return nil
}LIST 测试
为了避免客户端库(例如 client-go)自动帮我们设置一些参数,我们直接用 curl 来测试,指定证书就行了:
$ cat curl-k8s-apiserver.sh
curl -s --cert /etc/kubernetes/pki/admin.crt --key /etc/kubernetes/pki/admin.key --cacert /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt $@使用方式:
$ ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "https://localhost:6443/api/v1/pods?limit=2"
{
"kind": "PodList",
"metadata": {
"resourceVersion": "2127852936",
"continue": "eyJ2IjoibWV0YS5rOHMuaW8vdjEiLCJ...",
},
"items": [ {pod1 data }, {pod2 data}]
}3.1 指定 limit=2:response 将返回分页信息(continue)
3.1.1 curl 测试
$ ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "https://localhost:6443/api/v1/pods?limit=2"
{
"kind": "PodList",
"metadata": {
"resourceVersion": "2127852936",
"continue": "eyJ2IjoibWV0YS5rOHMuaW8vdjEiLCJ...",
},
"items": [ {pod1 data }, {pod2 data}]
}可以看到,
- 确实返回了两个 pod 信息,在 items[] 字段中;
- 另外在 metadata 中返回了一个 continue 字段,客户端下次带上这个参数,apiserver 将继续返回剩下的内容,直到 apiserver 不再返回 continue。
3.1.2 kubectl 测试
调大 kubectl 的日志级别,也可以看到它背后用了 continue 来获取全量 pods:
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces --v=10
# 以下都是 log 输出,做了适当调整
# curl -k -v -XGET -H "User-Agent: kubectl/v1.xx" -H "Accept: application/json;as=Table;v=v1;g=meta.k8s.io,application/json;as=Table;v=v1beta1;g=meta.k8s.io,application/json"
# 'http://localhost:8080/api/v1/pods?limit=500'
# GET http://localhost:8080/api/v1/pods?limit=500 200 OK in 202 milliseconds
# Response Body: {"kind":"Table","metadata":{"continue":"eyJ2Ijoib...","remainingItemCount":54},"columnDefinitions":[...],"rows":[...]}
#
# curl -k -v -XGET -H "Accept: application/json;as=Table;v=v1;g=meta.k8s.io,application/json;as=Table;v=v1beta1;g=meta.k8s.io,application/json" -H "User-Agent: kubectl/v1.xx"
# 'http://localhost:8080/api/v1/pods?continue=eyJ2Ijoib&limit=500'
# GET http://localhost:8080/api/v1/pods?continue=eyJ2Ijoib&limit=500 200 OK in 44 milliseconds
# Response Body: {"kind":"Table","metadata":{"resourceVersion":"2122644698"},"columnDefinitions":[],"rows":[...]}第一次请求拿到了 500 个 pods,第二次请求把返回的 continue 带上了:GET
http://localhost:8080/api/v1/pods?continue=eyJ2Ijoib&limit=500,continue 是个 token, 有点长,为了更好的展示这里把它截断了。
3.2 指定 limit=2&resourceVersion=0:limit=2 将被忽略,返回全量数据
$ ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "https://localhost:6443/api/v1/pods?limit=2&resourceVersion=0"
{
"kind": "PodList",
"metadata": {
"resourceVersion": "2127852936",
"continue": "eyJ2IjoibWV0YS5rOHMuaW8vdjEiLCJ...",
},
"items": [ {pod1 data }, {pod2 data}, ...]
}items[] 里面是全量 pod 信息。
3.3 指定 spec.nodeName=node1&resourceVersion=0 vs. spec.nodeName=node1"
结果相同
$ ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "https://localhost:6443/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods?fieldSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1" | jq '.items[].spec.nodeName'
"node1"
"node1"
"node1"
...
$ ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "https://localhost:6443/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods?fieldSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1&resourceVersion=0" | jq '.items[].spec.nodeName'
"node1"
"node1"
"node1"
...结果是一样的,除非是 apiserver 缓存和 etcd 数据出现不一致,这个概率极小,我们这里不讨论。
速度差异很大:
用 time 测量以上两种情况下的耗时,会发现对于大一些的集群,这两种请求的响应时间就会有明显差异。
$ time ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh > result 对于 4K nodes, 100K pods 规模的集群,以下数据供参考:
- 不带 resourceVersion=0(读 etcd 并在 apiserver 过滤): 耗时 10s
- 带 resourceVersion=0(读 apiserver 缓存): 耗时 0.05s
差了 200 倍。
全量 pod 的总大小按 2GB 计算,平均每个 20KB。
LIST 请求对控制平面压力:量化分析
本节以 cilium-agent 为例,介绍定量测量它启动时对控制平面压力。
4.1 收集 LIST 请求
首先获取 agent 启动时,都 LIST k8s 哪些资源。有几种收集方式:
- 在 k8s access log,按 ServiceAccount、verb、request_uri 等过滤;
- 通过 agent 日志;
- 通过进一步代码分析等等。
假设我们收集到如下 LIST 请求:
1. api/v1/namespaces?resourceVersion=0
2. api/v1/pods?filedSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1&resourceVersion=0
3. api/v1/nodes?fieldSelector=metadata.name%3Dnode1&resourceVersion=0
4. api/v1/services?labelSelector=%21service.kubernetes.io%2Fheadless%2C%21service.kubernetes.io%2Fservice-proxy-name
5. apis/discovery.k8s.io/v1beta1/endpointslices?resourceVersion=0
6. apis/networking.k8s.io/networkpolicies?resourceVersion=0
7. apis/cilium.io/v2/ciliumnodes?resourceVersion=0
8. apis/cilium.io/v2/ciliumnetworkpolicies?resourceVersion=0
9. apis/cilium.io/v2/ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicies?resourceVersion=04.2 测试 LIST 请求数据量和耗时
有了 LIST 请求列表,接下来就可以手动执行这些请求,拿到如下数据:
- 请求耗时
- 请求处理的数据量,这里分为两种:
- apiserver 处理的数据量(全量数据),评估对 apiserver/etcd 的性能影响应该以这个为主
- agent 最终拿到的数据量(按 selector 做了过滤)
用下面这个脚本(放到真实环境 k8s master 上)来就可以执行一遍测试,
$ cat benchmark-list-overheads.sh
apiserver_url="https://localhost:6443"
# List k8s core resources (e.g. pods, services)
# API: GET/LIST /api/v1/?&resourceVersion=0
function benchmark_list_core_resource() {
resource=$1
selectors=$2
echo "----------------------------------------------------"
echo "Benchmarking list $2"
listed_file="listed-$resource"
url="$apiserver_url/api/v1/$resource?resourceVersion=0"
# first perform a request without selectors, this is the size apiserver really handles
echo "curl $url"
time ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "$url" > $listed_file
# perform another request if selectors are provided, this is the size client receives
listed_file2="$listed_file-filtered"
if [ ! -z "$selectors" ]; then
url="$url&$selectors"
echo "curl $url"
time ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "$url" > $listed_file2
fi
ls -ahl $listed_file $listed_file2 2>/dev/null
echo "----------------------------------------------------"
echo ""
}
# List k8s apiextension resources (e.g. pods, services)
# API: GET/LIST /apis//?&resourceVersion=0
function benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource() {
api_group=$1
resource=$2
selectors=$3
echo "----------------------------------------------------"
echo "Benchmarking list $api_group/$resource"
api_group_flatten_name=$(echo $api_group | sed 's/\//-/g')
listed_file="listed-$api_group_flatten_name-$resource"
url="$apiserver_url/apis/$api_group/$resource?resourceVersion=0"
if [ ! -z "$selectors" ]; then
url="$url&$selectors"
fi
echo "curl $url"
time ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "$url" > $listed_file
ls -ahl $listed_file
echo "----------------------------------------------------"
echo ""
}
benchmark_list_core_resource "namespaces" ""
benchmark_list_core_resource "pods" "filedSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1"
benchmark_list_core_resource "nodes" "fieldSelector=metadata.name%3Dnode1"
benchmark_list_core_resource "services" "labelSelector=%21service.kubernetes.io%2Fheadless%2C%21service.kubernetes.io%2Fservice-proxy-name"
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "discovery.k8s.io/v1beta1" "endpointslices" ""
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "apiextensions.k8s.io/v1" "customresourcedefinitions" ""
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "networking.k8s.io" "networkpolicies" ""
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "cilium.io/v2" "ciliumnodes" ""
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "cilium.io/v2" "ciliumendpoints" ""
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "cilium.io/v2" "ciliumnetworkpolicies" ""
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "cilium.io/v2" "ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicies" "" 执行效果如下:
$ benchmark-list-overheads.sh
----------------------------------------------------
Benchmarking list
curl https://localhost:6443/api/v1/namespaces?resourceVersion=0
real 0m0.090s
user 0m0.038s
sys 0m0.044s
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 69K listed-namespaces
----------------------------------------------------
Benchmarking list fieldSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1
curl https://localhost:6443/api/v1/pods?resourceVersion=0
real 0m18.332s
user 0m1.355s
sys 0m1.822s
curl https://localhost:6443/api/v1/pods?resourceVersion=0&fieldSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1
real 0m0.242s
user 0m0.044s
sys 0m0.188s
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2.0G listed-pods
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 526K listed-pods-filtered
----------------------------------------------------
...说明:凡是带了 selector 的 LIST,例如 LIST pods?spec.nodeName=node1,这个脚本会先执行一遍不带 selector 的请求,目的是测量 apiserver 需要处理的数据量,例如上面的 list pods:
- agent 真正执行的是 pods?resourceVersion=0&fieldSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1,所以请求耗时应该以这个为准
- 额外执行了 pods?resourceVersion=0,这样是为了测试 1 的请求到底需要 apiserver 处理多少数据量
注意:list all pods 这样的操作会产生 2GB 的文件,因此谨慎使用这个 benchmark 工具,首先理解你写的脚本在测什么,尤其不要自动化或并发跑,可能会把 apiserver/etcd 打爆。
4.3 测试结果分析
以上输出有如下关键信息:
- LIST 的资源类型,例如 pods/endpoints/services
- LIST 操作耗时
- LIST 操作涉及的数据量
- apiserver 需要处理的数据量(json 格式):以上面 list pods 为例,对应的是 listed-pods 文件,共 2GB;
- agent 收到的数据量(因为 agent 可能指定了 label/field 过滤器):以上面 list pods 为例,对应 listed-pods-filtered 文件,共计 526K
按以上方式将所有 LIST 请求都收集起来并排序,就知道了 agent 一次启动操作,对 apiserver/etcd 的压力。
$ ls -ahl listed-*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 222 listed-apiextensions.k8s.io-v1-customeresourcedefinitions
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5.8M listed-apiextensions.k8s.io-v1-customresourcedefinitions
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2.0M listed-cilium.io-v2-ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicies
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 193M listed-cilium.io-v2-ciliumendpoints
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 185 listed-cilium.io-v2-ciliumnetworkpolicies
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6.6M listed-cilium.io-v2-ciliumnodes
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 42M listed-discovery.k8s.io-v1beta1-endpointslices
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 69K listed-namespaces
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 222 listed-networking.k8s.io-networkpolicies
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 70M listed-nodes # 仅用于评估 apiserver 需要处理的数据量
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 25K listed-nodes-filtered
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2.0G listed-pods # 仅用于评估 apiserver 需要处理的数据量
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 526K listed-pods-filtered
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 23M listed-services # 仅用于评估 apiserver 需要处理的数据量
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 23M listed-services-filtered大规模基础服务:部署和调优建议
5.1 List 请求默认设置 ResourceVersion=0
前面已经介绍,不设置这个参数将导致 apiserver 从 etcd 拉全量数据再过滤,导致
- 很慢
- 规模大了 etcd 扛不住
因此,除非对数据准确性要求极高,必须从 etcd 拉数据,否则应该在 LIST 请求时设置 ResourceVersion=0 参数, 让 apiserver 用缓存提供服务。
如果你使用的是 client-go 的 ListWatch/informer 接口, 那它默认已经设置了 ResourceVersion=0。
5.2 优先使用 namespaced API
如果要 LIST 的资源在单个或少数几个 namespace,考虑使用 namespaced API:
- Namespaced API: /api/v1/namespaces/
/pods?query=xxx - Un-namespaced API: /api/v1/pods?query=xxx
5.3 Restart backoff
对于 per-node 部署的基础服务,例如 kubelet、cilium-agent、daemonsets,需要 通过有效的 restart backoff 降低大面积重启时对控制平面的压力。
例如,同时挂掉后,每分钟重启的 agent 数量不超过集群规模的 10%(可配置,或可自动计算)。
5.4 优先通过 label/field selector 在服务端做过滤
如果需要缓存某些资源并监听变动,那需要使用 ListWatch 机制,将数据拉到本地,业务逻辑根据需要自己从 local cache 过滤。这是 client-go 的 ListWatch/informer 机制。
但如果只是一次性的 LIST 操作,并且有筛选条件,例如前面提到的根据 nodename 过滤 pod 的例子, 那显然应该通过设置 label 或字段过滤器,让 apiserver 帮我们把数据过滤出来。LIST 10w pods 需要几十秒(大部分时间花在数据传输上,同时也占用 apiserver 大量 CPU/BW/IO), 而如果只需要本机上的 pod,那设置 nodeName=node1 之后,LIST 可能只需要 0.05s 就能返回结果。另外非常重要的一点时,不要忘记在请求中同时带上 resourceVersion=0。
5.4.1 Label selector
在 apiserver 内存过滤。
5.4.2 Field selector
在 apiserver 内存过滤。
5.4.3 Namespace selector
etcd 中 namespace 是前缀的一部分,因此能指定 namespace 过滤资源,速度比不是前缀的 selector 快很多。
5.5 配套基础设施(监控、告警等)
以上分析可以看成,client 的单个请求可能只返回几百 KB 的数据,但 apiserver(更糟糕的情况,etcd)需要处理上 GB 的数据。因此,应该极力避免基础服务的大规模重启,为此需要在监控、告警上做的尽量完善。
5.5.1 使用独立 ServiceAccount
每个基础服务(例如 kubelet、cilium-agent 等),以及对 apiserver 有大量 LIST 操作的各种 operator, 都使用各自独立的 SA, 这样便于 apiserver 区分请求来源,对监控、排障和服务端限流都非常有用。
5.5.2 Liveness 监控告警
基础服务必须覆盖到 liveness 监控。
必须有 P1 级别的 liveness 告警,能第一时间发现大规模挂掉的场景。然后通过 restart backoff 降低对控制平面的压力。
5.5.3 监控和调优 etcd
需要针对性能相关的关键指标做好监控和告警:
- 内存
- 带宽
- 大 LIST 请求数量及响应耗时
比如下面这个 LIST all pods 日志:
{
"level":"warn",
"msg":"apply request took too long",
"took":"5357.87304ms",
"expected-duration":"100ms",
"prefix":"read-only range ",
"request":"key:\"/registry/pods/\" range_end:\"/registry/pods0\" ",
"response":"range_response_count:60077 size:602251227"
}部署和配置调优:
- K8s events 拆到单独的 etcd 集群
- 其他。
其 他
6.1 Get 请求:GetOptions{ }
基本原理与 ListOption{ } 一样,不设置 ResourceVersion=0 会导致 apiserver 去 etcd 拿数据,应该尽量避免。