程序逻辑控制
程序逻辑控制
- 1. 顺序结构
- 2.分支结构
-
- 2.1 if 语句
- 2.2 switch 语句
- 3.循环结构
-
- 3.1 while 循环
- 3.2 break
- 3.3 continue
- 3.4 for 循环
- 3.5 do while 循环(选学)
- 4.输入输出
-
- 4.1 输出到控制台
- 4.2 从键盘输入
- 5.猜数字游戏
- 6补充知识点:
-
- 6.1Java输入整形:
- 6.2Java输入字符串:
- 6.3关于调试
-
- 6.3.1键位的分布
- 6.3.2调试操作步骤
大家好,我是晓星航。今天为大家带来的是程序逻辑控制相关知识点的讲解!
1. 顺序结构
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("aaa");
System.out.println("bbb");
System.out.println("ccc");
}
}
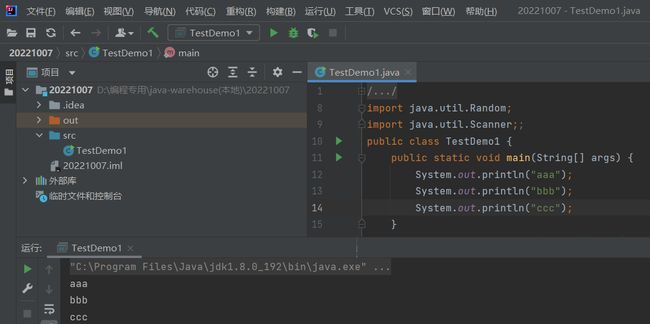
即程序的执行和代码的书写顺序有关。
2.分支结构
2.1 if 语句
基本格式:
if(布尔表达式){
//条件满足时执行代码
}else if(布尔表达式){
//条件满足时执行代码
}else{
//条件都不满足时执行代码
}
代码示例1: 判定一个数字是奇数还是偶数
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 10;
if (num % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("num 是偶数");
} else {
System.out.println("num 是奇数");
}
}
}

代码示例2: 判定一个数字是正数还是负数
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 10;
if (num > 0) {
System.out.println("num 是正数");
} else if (num < 0) {
System.out.println("num 是负数");
} else {
System.out.println("num 是 0");
}
}
}

代码示例3: 判定某一年份是否是闰年
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int year = 2000;
if (year % 100 == 0) {
// 判定世纪闰年
if (year % 400 == 0) {
System.out.println("是闰年");
} else {
System.out.println("不是闰年");
}
} else {
// 普通闰年
if (year % 4 == 0) {
System.out.println
("是闰年");
} else {
System.out.println("不是闰年");
}
}
}
}

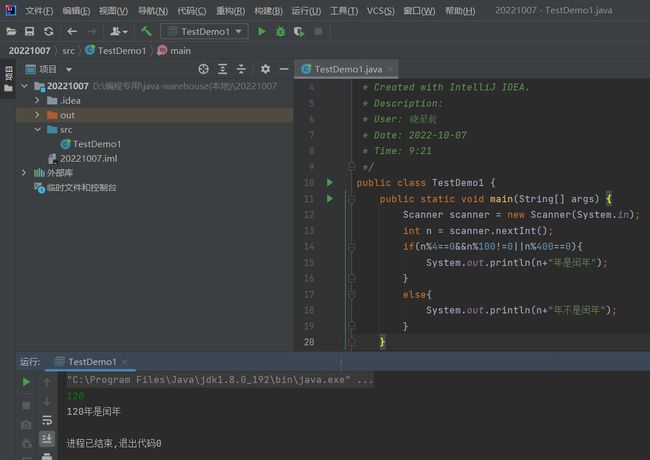
升级版本:
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
if(n%4==0&&n%100!=0||n%400==0){
System.out.println(n+"年是闰年");
}
else{
System.out.println(n+"年不是闰年");
}
}
}
2.2 switch 语句
基本语法:
switch(整数|枚举|字符|字符串){
case 内容1 : {
内容满足时执行语句;
[break;]
}
case 内容2 : {
内容满足时执行语句;
[break;]
}
...
default:{
内容都不满足时执行语句;
[break;]
}
}
代码示例: 根据 day 的值输出星期几:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
switch(n){
case 1:
System.out.println("星期一");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("星期二");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("星期三");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("星期四");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("星期五");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("星期六");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("星期天");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误");
break;
}
}
}

注意事项
1 break 不要遗漏, 否则会失去 “多分支选择” 的效果 我们发现, 不写 break 的时候, case 语句会依次向下执行, 从而失去了多分支的效果.
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int day = 1;
switch(day) {
case 1:
System.out.println("星期一");
// break;
case 2:
System.out.println("星期二");
break;
}
}
}
// 运行结果
//星期一
//星期二
2 switch 中的值只能是 整数|枚举|字符|字符串 long float double boolean 这四种不可作为switch参数
3 switch 不能表达复杂的条件

4 switch 虽然支持嵌套, 但是很丑~

3.循环结构
3.1 while 循环
基本语法格式:
while(循环条件){
循环语句;
}
循环条件为 true, 则执行循环语句; 否则结束循环
代码示例1: 计算 1 - 100 的和
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 1;
int num = 0;
while (n<=100) {
num += n;
n++;
}
System.out.println(num);
}
}

代码示例2: 计算 n 的阶乘 以及1到n的阶乘的和 换行分别打印:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);//给scanner赋值输入量
int n = scanner.nextInt();//对n进行输入
int i = 1;
int num = 1;
int sum = 0;
while(i<=n){
num *= i;
i++;
sum += num;
}
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}

注意事项
-
和 if 类似, while 下面的语句可以不写 { } , 但是不写的时候只能支持一条语句. 建议还是加上 { }
-
和 if 类似, while 后面的 { 建议和 while 写在同一行.
-
和 if 类似, while 后面不要多写 分号, 否则可能导致循环不能正确执行.
3.2 break
break 的功能是让循环提前结束.
执行到 break 就会让循环结束.
代码示例: 找到 100 - 200 中第一个 3的倍数
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 100;
while (num <= 200) {
if (num % 3 == 0) {
System.out.println("找到了 3 的倍数, 为:" + num);
break;
}
num++;
}
}
}

3.3 continue
continue 的功能是跳过这次循环, 立即进入下次循环.
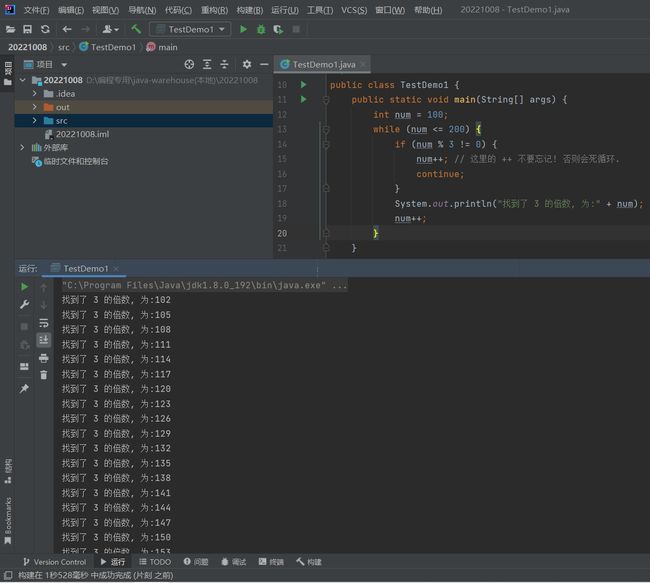
代码示例: 找到 100 - 200 中所有 3 的倍数
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 100;
while (num <= 200) {
if (num % 3 != 0) {
num++; // 这里的 ++ 不要忘记! 否则会死循环.
continue;
}
System.out.println("找到了 3 的倍数, 为:" + num);
num++;
}
}
}
注意:
1 break 和 continue 必须在循环中(特例break可以再switch中)
3.4 for 循环
基本语法:
for(表达式1;表达式2;表达式3){
循环体;
}

代码示例1: 计算 1 - 100 的和
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}

代码示例2: 计算 n 的阶乘 以及1到n的阶乘的和 换行分别打印:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int i = 0;
int num = 1;//作为计算阶乘的第一个数 乘数等于本身 所以为1
int sum = 0;//作为计算阶乘的和的第一个数 所以为0
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++){
num *= i;
sum += num;
}
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}

3.5 do while 循环(选学)
基本语法:
do{
循环语句;
}while(循环条件);
注意事项:
4.输入输出
4.1 输出到控制台
基本语法:
System.out.println(msg); // 输出一个字符串, 带换行
System.out.print(msg); // 输出一个字符串, 不带换行
System.out.printf(format, msg); // 格式化输出
注意:
println 输出的内容自带 \n, print 不带 \n
printf 的格式化输出方式和 C 语言的 printf 是基本一致的.
4.2 从键盘输入
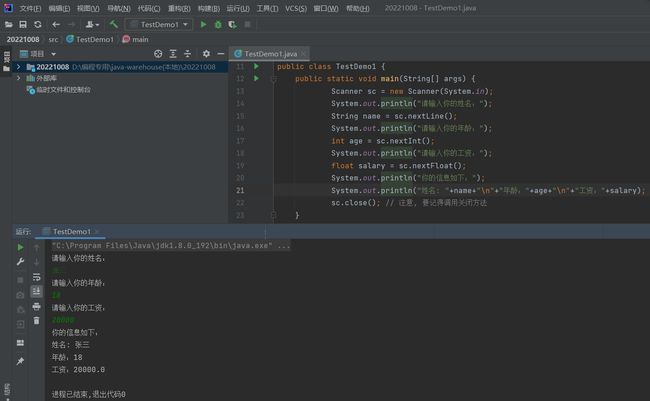
使用 Scanner 读取字符串/整数/浮点数:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入你的年龄:");
int age = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入你的工资:");
float salary = sc.nextFloat();
System.out.println("你的信息如下:");
System.out.println("姓名: "+name+"\n"+"年龄:"+age+"\n"+"工资:"+salary);
sc.close(); // 注意, 要记得调用关闭方法
}
}

5.猜数字游戏
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
int rand = random.nextInt(100);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
System.out.println("请输入你要猜的数字:");
int n = scanner.nextInt();
if(n < rand) {
System.out.println("猜小了");
}else if(n == rand) {
System.out.println("猜对了");
break;
}else {
System.out.println("猜大了");
}
}
}
}

6补充知识点:
6.1Java输入整形:
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
这里还要包含一个头文件:
import java.util.Scanner;
这里我们输入sca直接回车,idea会自动帮我们加上这个头文件。如果忘记了可以鼠标点一下Scanner,然后alt+回车也可以帮助我们自动加上这个头文件
6.2Java输入字符串:
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scanner.nextLine();
这里还要包含一个头文件:
import java.util.Scanner;
这里我们输入sca直接回车,idea会自动帮我们加上这个头文件。如果忘记了可以鼠标点一下Scanner,然后alt+回车也可以帮助我们自动加上这个头文件
这里我们也可以用String str = scanner.next();来读字符串 但它遇到空格会读取结束
而String str = scanner.nextLine();遇到空格不会结束 所以我们读取字符串一般用String str = scanner.nextLine();
6.3关于调试
6.3.1键位的分布

6.3.2调试操作步骤
先设置断点(鼠标右键点击即可) 还可设置条件断点 鼠标右键设置一个断点再右键点击一下设置条件 例如我们想把n直接变为99开始调试 则为:

再点击小瓢虫(Shift+F9)进行调试
直接一行一行调试:F8
跳入函数一行一行调试:F7
步出:Shift+F8
中止:Ctrl+F2
7. 作业
-
根据年龄, 来打印出当前年龄的人是少年(低于18), 青年(19-28), 中年(29-55), 老年(56以上) (用if else if else 输出结果)
-
判定一个数字是否是素数(n % i == 0为判断是否为素数的条件 除了1和本身其余数都不是自己的公因数 这里采用根号n可以减少计算机的计算量)
-
打印 1 - 100 之间所有的素数(n % i == 0为判断是否为素数的条件 除了1和本身其余数都不是自己的公因数 这里采用根号n可以减少计算机的计算量)
-
输出 1000 - 2000 之间所有的闰年 (能被4整除&&能被400整除||不能被100整除)
-
输出乘法口诀表(两次for循环)
-
求两个正整数的最大公约数(最小公倍数=(a*b)/最大公约数)
-
计算1/1-1/2+1/3-1/4+1/5 …… + 1/99 - 1/100 的值。(sum = sum + 1/i * flg; flg = -flg;前者为计算所有的分数 后者为变化符号为加一次减一次)
-
编写程序数一下 1到 100 的所有整数中出现多少个数字9。(i % 10 == 9 判断个位上是否出现9 i / 10 == 9 判断十位上是否出现9 然后用count来计数即可)
-
求出0~999之间的所有“水仙花数”并输出。(“水仙花数”是指一个三位数,其各位数字的立方和确好等于该数本身,如;153=1+5+3?,则153是一个“水仙花数”。)
-
编写代码模拟三次密码输入的场景。 最多能输入三次密码,密码正确,提示“登录成功”,密码错误, 可以重新输入,最多输入三次。三次均错,则提示退出程序(用equals来比较字符串是否相等)
-
写一个函数返回参数二进制中 1 的个数 比如: 15 0000 1111 4 个 1
-
获取一个数二进制序列中所有的偶数位和奇数位, 分别输出二进制序列。
-
输出一个整数的每一位.(用%10 %100以及/10 /100来取出每一位 %取小位 /取大位)
-
完成猜数字游戏(详细解答见目录5. 猜数字游戏)

感谢各位读者的阅读,本文章有任何错误都可以在评论区发表你们的意见,我会对文章进行改正的。如果本文章对你有帮助请动一动你们敏捷的小手三连一波,你的每一次鼓励都是作者创作的动力哦!