Pytorch 基于ResNet-18的服饰识别(使用Fashion-MNIST数据集)
![]()
✅作者简介:人工智能专业本科在读,喜欢计算机与编程,写博客记录自己的学习历程。
个人主页:小嗷犬的博客
个人信条:为天地立心,为生民立命,为往圣继绝学,为万世开太平。
本文内容:Pytorch 基于ResNet-18的服饰识别(使用Fashion-MNIST数据集)
更多内容请见
- Pytorch 基于AlexNet的服饰识别(使用Fashion-MNIST数据集)
- Pytorch 基于VGG-16的服饰识别(使用Fashion-MNIST数据集)
- Pytorch 基于NiN的服饰识别(使用Fashion-MNIST数据集)
本文目录
- 介绍
- 1.导入相关库
- 2.定义 ResNet-18 网络结构
- 3.下载并配置数据集和加载器
- 4.定义训练函数
- 5.训练模型(或加载模型)
- 6.可视化展示
- 7.预测图
介绍
使用到的库:
- Pytorch
- matplotlib
- d2l
d2l 为斯坦福大学李沐教授打包的一个库,其中包含一些深度学习中常用的函数方法。
安装:
pip install matplotlib
pip install d2l
Pytorch 环境请自行配置。
数据集:
Fashion-MNIST 是一个替代 MNIST 手写数字集的图像数据集。 它是由 Zalando(一家德国的时尚科技公司)旗下的研究部门提供。其涵盖了来自 10 种类别的共 7 万个不同商品的正面图片。
Fashion-MNIST 的大小、格式和训练集/测试集划分与原始的 MNIST 完全一致。60000/10000的训练测试数据划分,28x28的灰度图片。你可以直接用它来测试你的机器学习和深度学习算法性能,且不需要改动任何的代码。
下载地址:
本文使用 Pytorch 自动下载。
残差神经网络(ResNet) 是由微软研究院的 何恺明、张祥雨、任少卿、孙剑 等人提出的。ResNet 在 2015 年的 ILSVRC(ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge)中取得了冠军。
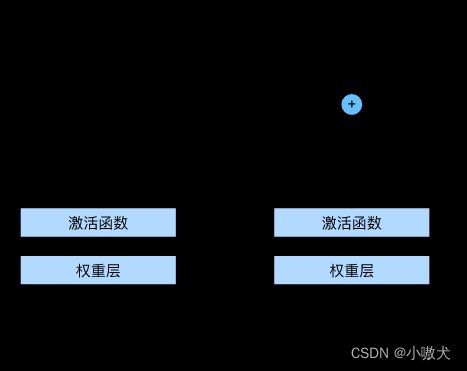
残差神经网络 的主要贡献是发现了“退化现象(Degradation)”,并针对退化现象发明了 “快捷连接(Shortcut connection)”,极大的消除了深度过大的神经网络训练困难问题。神经网络的“深度”首次突破了 100 层、最大的神经网络甚至超过了 1000 层。
1.导入相关库
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from d2l import torch as d2l
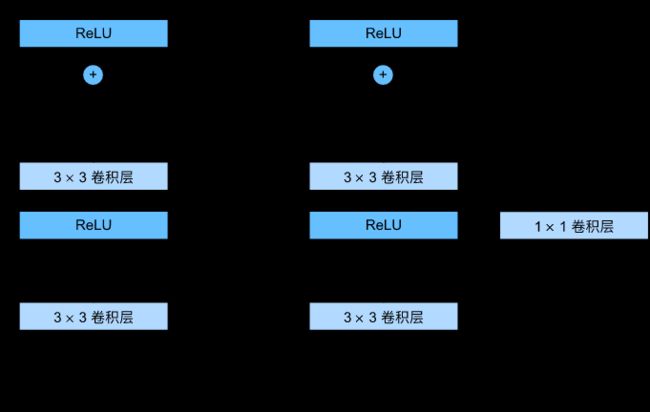
2.定义 ResNet-18 网络结构
class Residual(nn.Module):
# 残差块
def __init__(self, input_channels, num_channels,
use_1x1conv=False, strides=1):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, num_channels,
kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=strides)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels, num_channels,
kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if use_1x1conv:
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, num_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=strides)
else:
self.conv3 = None
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels)
def forward(self, X):
Y = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(X)))
Y = self.bn2(self.conv2(Y))
if self.conv3:
X = self.conv3(X)
Y += X
return F.relu(Y)
# ResNet-18
b1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
def resnet_block(input_channels, num_channels, num_residuals,
first_block=False):
blk = []
for i in range(num_residuals):
if i == 0 and not first_block:
blk.append(Residual(input_channels, num_channels,
use_1x1conv=True, strides=2))
else:
blk.append(Residual(num_channels, num_channels))
return blk
b2 = nn.Sequential(*resnet_block(64, 64, 2, first_block=True))
b3 = nn.Sequential(*resnet_block(64, 128, 2))
b4 = nn.Sequential(*resnet_block(128, 256, 2))
b5 = nn.Sequential(*resnet_block(256, 512, 2))
net = nn.Sequential(b1, b2, b3, b4, b5,
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)),
nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(512, 10))
3.下载并配置数据集和加载器
# 下载并配置数据集
trans = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize((96, 96)), transforms.ToTensor()])
train_dataset = datasets.FashionMNIST(root=r'E:\Deep Learning\dataset', train=True,
transform=trans, download=True)
test_dataset = datasets.FashionMNIST(root=r'E:\Deep Learning\dataset', train=False,
transform=trans, download=True)
# 配置数据加载器
batch_size = 64
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
4.定义训练函数
训练完成后会保存模型,可以修改模型的保存路径。
def train(net, train_iter, test_iter, epochs, lr, device):
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear or type(m) == nn.Conv2d:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
net.apply(init_weights)
print(f'Training on:[{device}]')
net.to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
timer, num_batches = d2l.Timer(), len(train_iter)
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 训练损失之和,训练准确率之和,样本数
metric = d2l.Accumulator(3)
net.train()
for i, (X, y) in enumerate(train_iter):
timer.start()
optimizer.zero_grad()
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
with torch.no_grad():
metric.add(l * X.shape[0], d2l.accuracy(y_hat, y), X.shape[0])
timer.stop()
train_l = metric[0] / metric[2]
train_acc = metric[1] / metric[2]
if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 30) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1:
print(f'Epoch: {epoch+1}, Step: {i+1}, Loss: {train_l:.4f}')
test_acc = d2l.evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter)
print(
f'Train Accuracy: {train_acc*100:.2f}%, Test Accuracy: {test_acc*100:.2f}%')
print(f'{metric[2] * epochs / timer.sum():.1f} examples/sec '
f'on: [{str(device)}]')
torch.save(net.state_dict(),
f"E:\\Deep Learning\\model\\ResNet-18_Fashion-MNIST_Epoch{epochs}_Accuracy{test_acc*100:.2f}%.pth")
5.训练模型(或加载模型)
如果环境正确配置了CUDA,则会由GPU进行训练。
加载模型需要根据自身情况修改路径。
epochs, lr = 10, 0.05
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
train(net, train_loader, test_loader, epochs, lr, device)
# 加载保存的模型
# net.load_state_dict(torch.load(r"E:\Deep Learning\model\ResNet-18_Fashion-MNIST_Epoch10_Accuracy92.00%.pth"))
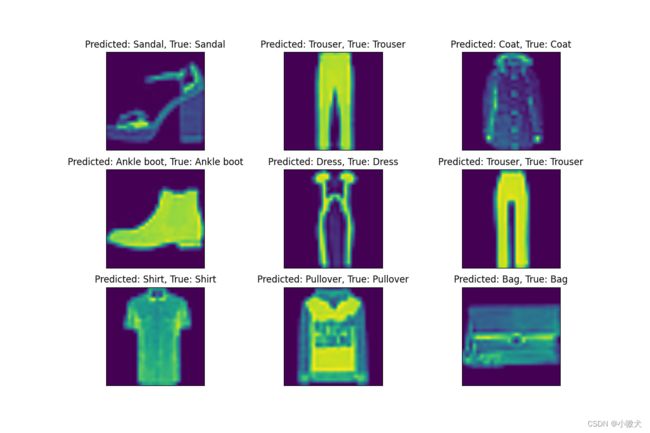
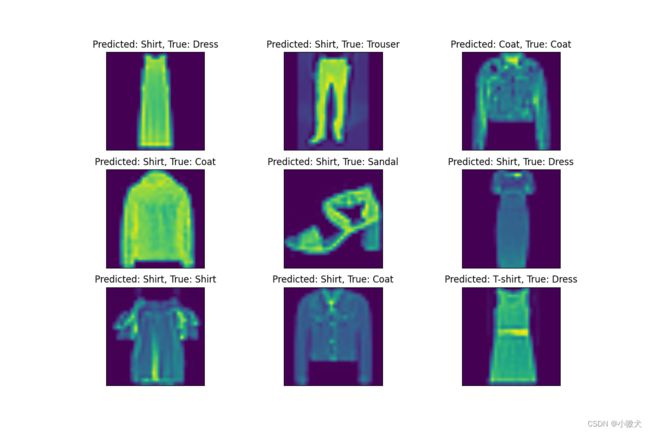
6.可视化展示
def show_predict():
# 预测结果图像可视化
net.to(device)
loader = DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=True)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
name = ['T-shirt', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat',
'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot']
for i in range(9):
(images, labels) = next(iter(loader))
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = net(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
title = f"Predicted: {name[int(predicted[0])]}, True: {name[int(labels[0])]}"
plt.subplot(3, 3, i + 1)
plt.imshow(images.cpu()[0].squeeze())
plt.title(title)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
show_predict()