SpringBoot系列——Starter
SpringBoot系列——Starter
- Starter
-
- SpringBoot的自动配置
- AutoConfigure
-
- 自动配置条件依赖
- Bean的参数获取
- Bean的发现
- Bean的加载
- QuickStart(自定义Starter)
-
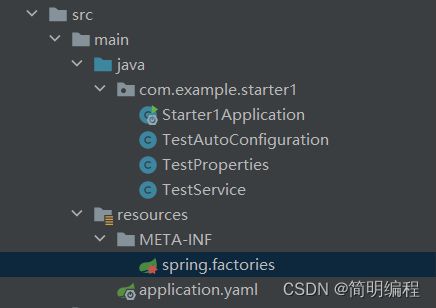
- 1.导入依赖
- 2. 创建配置属性类
- 3.创建yaml配置
- 4. 编写自动配置类
- 5.在resource下创建META-INF/spring.factories文件
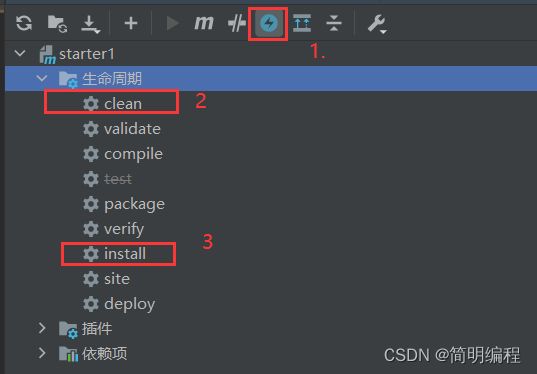
- 6.maven安装
- 7.新建一个工程导入starter
- 8.使用工程
Starter
SpringBoot在配置上相比spring要简单许多,其核心在于spring-boot-starter,在使用spring boot来搭建一个项目时,只需要引入官方提供的starter,就可以直接使用,免去了各种配置。starter简单来讲就是引入了一些相关依赖和一些初始化的配置。
Spring官方提供了很多starter,第三方也可以定义starter。为了加以区分,starter从名称上进行了如下规范:
- Spring官方提供的starter名称为: spring-boot-starter-xx
- 第三方提供的starter名称为:xxx-spring-boot-starter
SpringBoot的自动配置
自动配置,就是无须手动配置xml,自动配置并管理bean,可以简化开发过程
自动配置涉及到如下几个关键步骤:
- 基于Java代码的Bean配置
- 自动配置条件依赖
- Bean参数获取
- Bean的发现
- Bean的加载
AutoConfigure
在我们常用的Starter下我们都可以找到一个叫做XXXAutoConfigure的自动配置类,都会存在一个@Configuration注解(@org. springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
),其中写了很多的Bean
如:
@Configuration
class xxx{
@Bean
public xxx xxBean(){
}
}
- @Configuration和@Bean这两个注解一起使用就可以创建一个基于java代码的配置类,可以用来替代传统的xml配置文件。
- @Configuration注解的类可以看作是能生产让Spring loC容器管理的Bean实例的工厂
- @Bean注解的方法返回的对象可以被注册到spring容器中。
自动配置条件依赖
@ConditionalOnClass:某个class位于类路径上,才会实例化这个Bean@ConditionalOnBean:仅在当前上下文中存在某个bean时,才会实例化这个Bean@ConditionalOnExpression:当表达式为true的时候,才会实例化这个Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBean:仅在当前上下文中不存在某个bean时,才会实例化这个Bean@ConditionalOnMissingClass:某个class在类路径上不存在的时候,才会实例化这个Bean@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication:不是web应用时才会实例化这个Bean@AutoConfigureAfter:在某个bean完成自动配置后实例化这个bean@AutoConfigureBefore:在某个bean完成自动配置前实例化这个bean
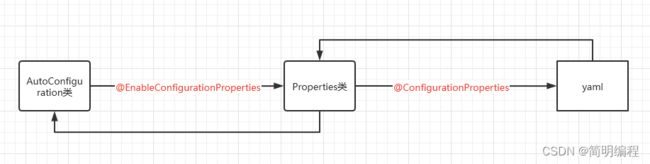
Bean的参数获取
当我们进行自动配置的时候需要获取yaml或properties文件中的配置参数,这样才能让Bean进行参数获取
例如在Mybatis中有个DataSourceAutoConfiguration的类用于进行数据源的的相关自动注入,上面有个@EnableConfigurationProperties注解设置了以DataSourceProperties这个类作为数据源的真实“映射”类@EnableConfigurationProperties(DataSourceProperties.class)
而在DataSourceProperties这个类中有个@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")的注解来获取yaml中的配置参数
Bean的发现
spring boot默认扫描启动类所在的包下的主类与子类的所有组件,但并没有包括依赖包中的类,那么依赖包中的bean是如何被发现和加载的?
我们需要从Spring Boot项目的启动类开始跟踪,在启动类上我们一般会加入@SpringBootApplication注解,其中的核心注解如下:
@SpringBootConfiguration@EnableAutoConfiguration@ComponentScan
根据源码跟踪我们会找到在SpringFactoryLoader类中有一个loadFactoryNames的方法,用于对Bean进行发现,在程序启动的时候会去查找resource/META-INFO/spring.factories这个文件进行Bean的发现
在该文件中有标识了org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure. EnableAutoConfiguration = xxxxAutoConfiguration以此来获取到自动配置类让Spring找到
Bean的加载
在Spring Boot应用中要让一个普通类交给Spring容器管理,通常有以下方法:
- 使用
@Configuration与@Bean注解 - 使用
@Controller ,@Service ,@Repository ,@Component注解标注该类并且启用@ComponentScan自动扫描 - 使用
@Import方法
其中Spring Boot实现自动配置使用的是@lmport注解这种方式,AutoConfigurationImportSelector类的selectlmports方法返回一组从META-INF/spring.factories文件中读取的bean的全类名,这样Spring Boot就可以加载到这些Bean并完成实例的创建工作。
QuickStart(自定义Starter)
1.导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
</dependency>
注意点:
我们需要删除starter中的spring-boot-maven-plugin,就是这段配置
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
2. 创建配置属性类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "shower")
public class TestProperties {
private String msg;
private int code;
}
3.创建yaml配置
shower:
code: 110
msg: test for starter
4. 编写自动配置类
@EnableConfigurationProperties(TestProperties.class)
@Configuration
public class TestAutoConfiguration {
//通过构造方法进行注入
private TestProperties testProperties;
public TestAutoConfiguration(TestProperties testProperties){
this.testProperties = testProperties;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public TestService testService(){
return new TestService(testProperties.getMsg(), testProperties.getCode());
}
}
5.在resource下创建META-INF/spring.factories文件
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.example.starter1.TestAutoConfiguration
6.maven安装
7.新建一个工程导入starter
<dependency>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>starter1</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
8.使用工程
当我们要使用的时候直接使用@Autowired注解进行注入使用即可
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private TestService testService;
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test(){
return testService.showInfo();
}
}