Java异步编排CompletableFuture简述
Java异步编排CompletableFuture
- CompletableFuture
-
- 介绍
- 继承和实现
- 主要方法
- QuickStart
- 练习1(双线程)
- 练习(任意任务线完成执行新任务)
- 多任务编排
CompletableFuture
介绍
在Java8之后提供了一个类以帮助我们进行多线程的异步编排工作,这就是CompletableFuture类,该类优化了我们对于异步任务的掌控,使我们可以自由编排任务先后顺序,返回值,中间条件
继承和实现
该类实现了:
- Future
- CompletionStage
主要方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| allOf(CompletableFuture… cfs) | 返回当所有给定的CompletableFutures完成时完成的新CompletableFuture。如果任何给定的CompletableFutures异常完成,则返回的CompletbleFuture也会异常完成,CompletionException将此异常作为其原因。否则,给定CompletableFutures的结果(如果有)不会反映在返回的CompletableFuture中,但可以通过单独检查它们来获得。如果未提供CompletableFutures,则返回值为空的CompletableFuture。该方法的应用之一是等待一组独立的CompletableFutures完成后再继续一个程序,如:CompletableFuture。allOf(c1,c2,c3).join();。 |
| anyOf(CompletableFuture… cfs) | 返回一个新的CompletableFuture,当任何给定的CompletbleFutures完成时,该CompletableFuture将完成,结果相同。否则,如果异常完成,返回的CompletableFuture也会这样做,CompletionException将此异常作为其原因。如果未提供CompletableFutures,则返回不完整的CompletableFuture。 |
| completeAsync(Supplier supplier) | 使用给定的执行器从异步任务调用给定的Supplier函数的结果完成此CompletableFuture |
| runAsync(Runnable runnable) | 返回一个新的CompletableFuture,该任务在给定的执行器中运行给定的操作后由该任务异步完成 |
| supplyAsync(Supplier supplier, Executor executor) | 返回一个新的CompletableFuture,该任务由在给定的执行器中运行的任务异步完成,其值通过调用给定的Supplier获得,简单来说就是有返回值 |
| get() | 获取返回值 |
| whenComplete() | 上一个线程任务完成后执行新 任务以原始线程(main)进行管理 |
| whenCompleteAsync() | 上一个线程完成后执行新的任务以新线程进行管理 |
| exceptionally(Function |
处理异常信息 |
| handle( BiFunction fn) | 处理上一个任务的返回结果和异常信息在原始线程上 |
| handleAsync(BiFunction fn) | 在新线程上处理上个任务返回的结果和异常信息 |
| thenRun(Runnable action) | 执行下一个任务,并不会返回主线程,依旧以上一个线程执行,不可接收返回值,后续无返回值 |
| thenRunAsync(Runnable action) | 交由新线程来执行下一个任务,不可接收返回值,后续无返回值 |
| thenAccept(Consumer action) | 执行下一个任务,并不会返回主线程,依旧以上一个线程执行可以接收返回值,后续无返回值 |
| thenAcceptAsync(Consumer action) | 新开线程执行下一个任务,可以接收返回值,后续无返回值 |
| thenApply( Function fn) | 上一个线程继续执行新任务,可以接收上一个任务的返回值,可以向下返回结果 |
| thenApplyAsync( Function fn) | 新开一个线程继续执行新任务,可以接收上一个任务的返回值,可以向下返回结果 |
| runAfterBoth(CompletionStage other,Runnable action) | 交由原调用线程在两个线程任务线执行完毕后执行(意思是:若是任务线1完毕调用该方法,这个方法的任务就是任务线1的线程继续执行的),无法接收上个任务线的返回值 |
| runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage other,Runnable action) | 交由新线程在两个线程任务线执行完毕后执行,无法接收上个任务线的返回值 |
| thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage other,BiConsumer action) | 交由原调用线程在两个线程任务线执行完毕后执行(意思是:若是任务线1完毕调用该方法,这个方法的任务就是任务线1的线程继续执行的),可以接收上个任务线的返回值和异常信息(接收的是调用线程线的!) |
| thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage other,BiConsumer action) | 交由新线程在两个线程任务线执行完毕后执行,可以接收上个任务线的返回值和异常信息(接收的是调用线程线的!) |
| thenCombine(CompletionStage other,BiFunction fn) | 交由调用线程在两个任务线完成后进行执行新任务,可以接收两个线程线的返回值且可以返回新的返回值 |
| thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage other,BiFunction fn) | 交由新线程在两个任务线完成后进行执行新任务,可以接收两个线程线的返回值且可以返回新的返回值 |
| runAfterEither(CompletionStage other,Runnable action) | 交由调用线程在两个任务线完成后进行执行新任务,不可以接收返回值且不可以返回新的返回值 |
| runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage other,Runnable action) | 交由新线程在两个任务线完成后进行执行新任务,不可以接收返回值且不可以返回新的返回值 |
| acceptEither(CompletionStage other, Consumer action) | 交由调用线程在两个任务线完成后进行执行新任务,可以接收返回值但不可以返回新的返回值 |
| acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage other, Consumer action) | 交由新线程在两个任务线完成后进行执行新任务,可以接收返回值但不可以返回新的返回值 |
| applyToEither(CompletionStage other, Function fn) | 交由调用线程在两个任务线完成后进行执行新任务,可以接收返回值且可以返回新的返回值 |
| applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage other, Function fn) | 交由新线程在两个任务线完成后进行执行新任务,可以接收返回值且可以返回新的返回值 |
QuickStart
public class Test {
static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
5,
10,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
//无返回结果
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}, executor).whenComplete((res, exec) -> {
//res为返回结构,exec为异常信息
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "!");
});
//有返回结果,返回结果需要阻塞等待
final CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "test supply";
}, executor).whenCompleteAsync((res, exec) -> {
System.out.println("r:" + res);
System.out.println("e:" + exec);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "??");
}, executor).exceptionally((e)->{
System.out.println("e = " + e);
return "ok";
});
System.out.println(supplyAsync.get());
}
}
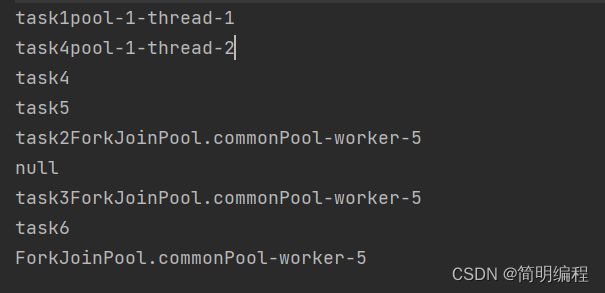
练习1(双线程)
public class Test2 {
static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
5,
10,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
public static void main(String[] args) {
final CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("task1" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}, executor).thenRunAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("task2" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenAccept((e) -> {
System.out.println(e);
System.out.println("task3" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
final CompletableFuture<Void> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("task4" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "task4";
}, executor).thenApplyAsync(res -> {
System.out.println(res);
return "task5";
}).thenAccept(res -> {
System.out.println(res);
});
future1.runAfterBothAsync(future2,()->{
System.out.println("task6");
},executor);
}
}
练习(任意任务线完成执行新任务)
public class Test3 {
static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
5,
10,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
public static void main(String[] args) {
final CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("task1" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}, executor).thenRunAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("task2" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenAccept((e) -> {
System.out.println(e);
System.out.println("task3" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
final CompletableFuture<Void> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("task4" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "task4";
}, executor).thenApplyAsync(res -> {
System.out.println(res);
return "task5";
}).thenAccept(res -> {
System.out.println(res);
});
// future1.runAfterEither(future2,()->{
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("either task");
// });
future1.runAfterEitherAsync(future2,()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("either task");
});
}
}
多任务编排
前面我们了解到双任务编排,那么大于等于3条任务线的时候我们就需要多任务编排了,主要用到anyOf和allOf方法进行,最后完成后会回到主线程
final CompletableFuture<Void> newF = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2, future3);
//用于对任务线进行阻塞,join和get都可以,看场景,单纯阻塞无返回值建议join
newF.join();
newF.get();