MySQL 多种查询方法
这里写目录标题
-
- 查询
-
- 1、单表查询
-
- 1.选择表中的若干列
- 2.选择表中的若干元组
- 3.order by子句
- 4.聚集函数
- 5.group by分组
- 2、连接查询
-
- 1、等值与非等值连接查询
- 2、自身连接
- 3、外连接
- 4、多表连接
- 3、嵌套查询
-
- 1、带有IN谓词的子查询
- 2、带有比较运算符的子查询
- 3、带有ANY或ALL谓词的子查询
- 4、带有EXISTS谓词的子查询
- 4、集合查询
查询
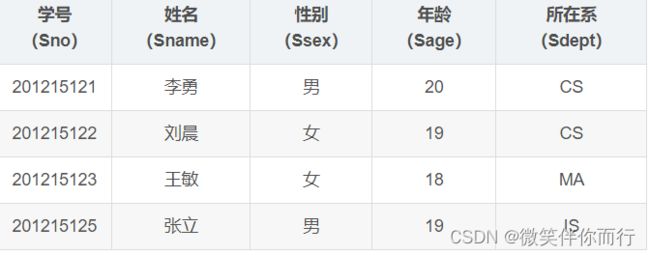
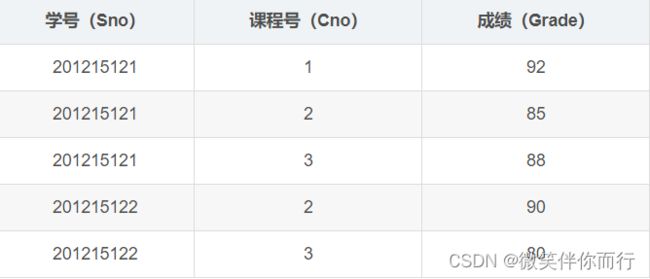
点击获取建表语句和表数据
1、单表查询
1.选择表中的若干列
1.查询指定列
select Sno,Sname from Student;
2.查询全部列
select*from Student;
3.查询经过计算的值
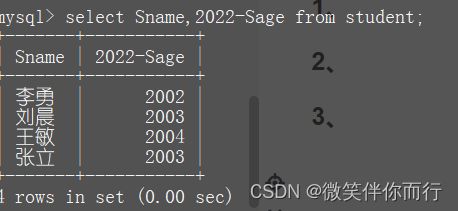
3.1、查询到同学的出生年份
select Sname,2022-Sage from student;
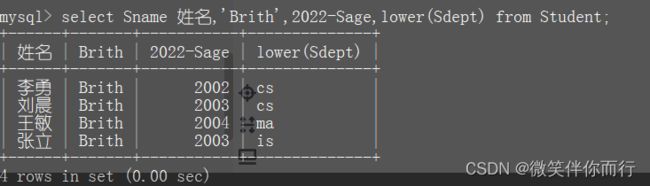
select Sname 姓名,'Brith',2022-Sage,lower(Sdept) from Student;
2.选择表中的若干元组
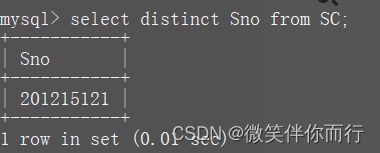
1.消除取值重复行
select distinct Sno from SC;
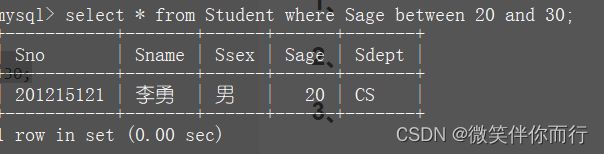
2.1、比较大小
select * from Student where Sage<20;
select * from Student where Sage between 20 and 30;
select * from Student where Sdept in ('CS','MA');
- %(百分号)代表任意长度(长度可以为0)的字符串
- _(下横线)代表任意单个字符
select * from Student where Sname like '刘%';
select * from Student where Sname like '刘_';
select * from Student where Sname not like '刘%';
select * from Student where Sname not like '刘_';
2.5、空值查询
select * from Student where Grade is null;
3.order by子句
用户可以用order by 子句对查询结果按照一个或多个属性列的升序(ASC)降序(DESC)排列,默认值升序
select * from SC order by Grade;
4.聚集函数
select count(*) from Student;
select count(Sno) from Student;
select avg(Grade) from SC;
select sum(Grade) from SC;
select max(Grade) from SC;
select min(Grade) from SC;
当聚集函数遇到空值时,除count(*)外,都跳过空值处理非空值
聚集函数只能用于select子句和group by中的having子句
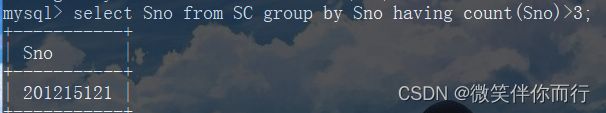
5.group by分组
select Sno,count(*) from Student group by Sno;
select Sno from SC group by Sno having count(Sno)>3;
2、连接查询
若一个查询同时涉及两个以上的表,则称之为连接查询
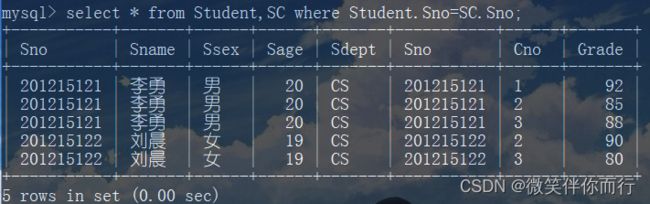
1、等值与非等值连接查询
- 连接查询的where子句中用来连接两个表的条件成为连接条件或连接谓词
- 当连接运算符为=号时,称为等值连接,使用其他运算符称为非等值连接
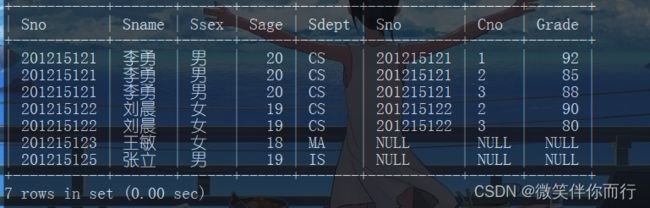
例1、查询每个学生及其选修课程的情况
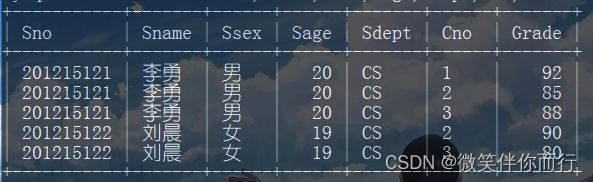
select * from Student,SC where Student.Sno=SC.Sno;
select Student.Sno,Sname,Ssex,Sage,Sdept,Cno,Grade from Student,SC where Student.Sno=SC.Sno;
2、自身连接
连接操作不仅可以在两个表之间进行,也可以时一个表与自身进行连接,称之为表的自身连接
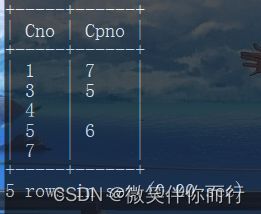
例2、查询每一门课的间接先修课(即先修课的先修课)
select first.Cno,second.Cpno from Course first,Course second where first.Cpno=second.Cno;
3、外连接
有时想以Student 表为主体列出每个学生的基本情况和选课情况。若某个学生没有选课,仍把Student的悬浮元组保存在结果关系中,而在SC表的属性上填空值NULL,这时就需要使用外连接
select * from Student left outer join SC on (Student.Sno=SC.Sno);
左外连接列出左边关系中所有元组,右外连接列出右边关系中所有的元组
4、多表连接
连接操作除了可以时两表连接、一个表与自身连接外,还可以是两个以上的表进行连接,后者通常称为多表连接。
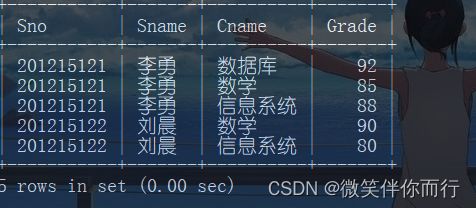
例4、查询每个学生的学号、姓名、课程名、成绩
select Student.Sno,Sname,Cname,Grade from Student,Course,Sc where Student.Sno=SC.Sno and SC.Cno=Course.Cno;
3、嵌套查询
在SQL语言中,一个select-from-where 语句称为一个查询块,将一个查询块嵌套在另一个查询块的where子句或having短语的条件中的查询称为嵌套查询例如:
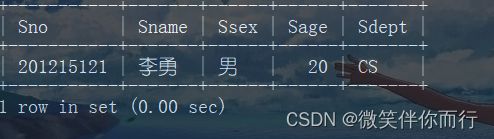
查询选修课程号为2的学生姓名
select Sname from Student where Sno in (select Sno from SC where Cno='2');
本例中,下层查询块 select sno from sc where cno=‘2’是嵌套在上层查询块select sname from student where sno in 的where条件中的,上层的查询块称为外查询或父查询,下层查询块称为内查询或子查询
子查询的select语句中不能使用 order by 子句,order by子句只能对最终查询结果排序
1、带有IN谓词的子查询
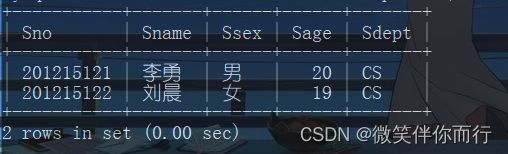
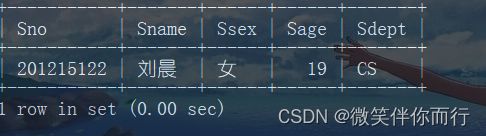
例1、查询与“刘晨”在同一个系学习的学生
select * from student where Sdept in (select Sdept from Student where Sname='刘晨');
本例中,子查询条件不依赖于父查询,称为不相关子查询
例2、查询选修了课程名为“信息系统”的学生学号和姓名
select Sno,Sname from Student where Sno in(select Sno from SC where Cno in (select Cno from Course where Cname='信息系统'));
2、带有比较运算符的子查询
带有比较运算符的子查询是指父查询与子查询之间用比较运算符进行连接。当用户明确知道内层查询返回的是单个值时,可以用>、<、=、>=、<=、!=或<>等比较运算符
例3、找出每个学生超过他自己选修课程平均成绩的课程号
select Sno,Cno from SC x where Grade>(select avg(Grade) from SC y where y.Sno=x.Sno);

x 是表SC的别名,又称为元组变量,可以用来表示SC的一个元组,内层查询是求一个学生所有选修课平均成绩的,至于是哪个学生的平均成绩要看参数x.Sno的值,而该值是与父查询相关的,因此这类查询称为相关子查询
3、带有ANY或ALL谓词的子查询
>ANY 大于子查询结果中的某个值
>ALL 大于子查询结果中的所有值
<ANY 小于子查询结果中的某个值
<ALL 小于子查询结果中的所有值
>=ANY 大于等于子查询结果中的某个值
>=ALL 大于等于子查询结果中的所有值
<=ANY 小于等于子查询结果中的某个值
<=ALL 小于等于子查询结果中的所有值
例4、查询非计算机科学系中比计算机科学系任意一个学生年龄小的学生姓名和年龄
select Sname,Sage from Student where Sage<ANY(select Sage from Student where Sdept='CS') and Sdept!='CS';
4、带有EXISTS谓词的子查询
EXISTS代表存在量词,带有EXISTS谓词的子查询不返回任何数据,只产生逻辑真值“true”或逻辑假值“false”
例5、查询所有选修了1号课程的学生姓名
select Sname from Student where exists (select * from SC where Student.Sno=SC.Sno and Cno='1');
使用存在量词exists后,若内层查询结果非空,则外层的where子句返回真值,否者返回假值
例6、查询选修了全部课程的学生姓名
SQL中没有全称量词(for all),但是可以把带有全称量词的谓词转换为等价的带有存在量词的谓词,可以将题目转换成等价的存在量词的形式:没有一门课程是他不选修的
select Sname from Student where exists (select * from Course where exists (select * from SC where SC.Sno=Student.Sno and SC.Cno=Course.Cno));
4、集合查询
集合操作主要包括并操作NUION、交操作INTERSERT和差操作EXCEPT
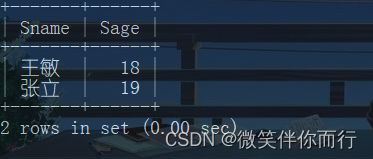
例1、查询计算机科学系的学生及年龄不大于19岁的学生
select * from Student where Sdept='CS' union select * from Student where Sage<=19;
select * from Student where Sdept='CS' intersect select * from Student where Sage<=19;
这实际上就行查询计算机科学系中年龄不大于19岁的学生
select *from Student where Sdept='CS' and Sage<=19;
例3、查询计算机科学系的学生与年龄不大于19岁的学生的差集
select * from Student where Sdept='CS' except select * from Student where Sage<=19;
这实际上就行查询计算机科学系中年龄大于19岁的学生
select *from Student where Sdept='CS' and Sage>19;