「C++小游戏教程」基本技巧(1)——随机化
0. 引言
小游戏中时常要用到随机数,今天就来谈谈这个所谓的“随机”。
1. 随机数 rand()
我们要使用随机数(严格意义上是伪随机)的话,C++ 中就有 rand() 来提供了这一操作。
rand() 返回值是整数。在不同系统的编译器下,返回值的范围不同,我们姑且认为足够我们使用。
设我们要获取数 x x x,逐步推导:
- 当 x ∈ [ 0 , 100 ] x\in[0,100] x∈[0,100] 时,可以写成
rand()%101; - 当 x ∈ [ 1 , 100 ] x\in[1,100] x∈[1,100] 时,可以转化为 x ′ + 1 ( x ′ ∈ [ 0 , 99 ] ) x'+1(x'\in[0,99]) x′+1(x′∈[0,99]),写成
rand()%100+1; - 当 x ∈ [ l , r ] x\in[l,r] x∈[l,r] 时,可以转化为 x ′ + l ( x ′ ∈ [ 0 , r − l ] ) x'+l(x'\in[0,r-l]) x′+l(x′∈[0,r−l]),写成
rand()%(r-l+1)+l。
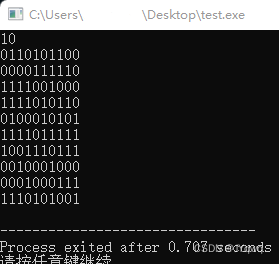
可现实总是不尽如人意:

为什么每次随机出来的序列都是一样的呢?这里我们就要讲到下面的东西了——
2. 设置随机种子 srand()
毕竟是伪随机,所以每次生成的随机序列需要有一个初始的随机种子(无符号整数),srand() 提供了这一操作。
比如设置随机种子为 114514 114514 114514,可以写成 srand(114514);。
然而——

这意味着种子要随机。
3. 时间 time()
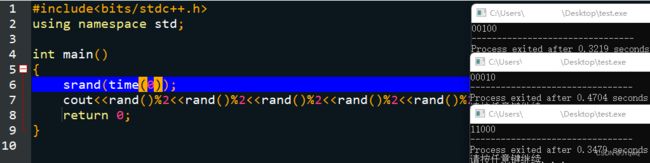
time() 返回从 1970.1.1 1970.1.1 1970.1.1 至今的秒数,参数直接填 NULL 或 0 0 0(也就是空指针)即可。
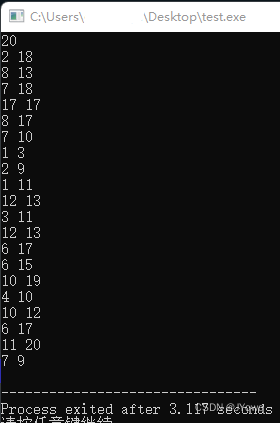
设置为种子,也就是 srand(time(0));。
效果显著:
4. 随机排列 random_shuffle()
如果有一个数组 a a a,如何让其进行随机排列呢?
C++ 有函数 random_shuffle()。
参数和用法与 sort() 类似,直接调用即可。
示例代码:
#include效果:
![]()
5. 随机基本案例
5-1. 随机 01 矩阵
给定边长 n n n,要求生成一个随机 01 矩阵。
示例代码:
#include5-2. 随机区间
给定 n n n,要求生成 n n n 个区间 [ l , r ] ( l ≤ r ) [l,r](l\le r) [l,r](l≤r),并且这些区间是 [ 1 , n ] [1,n] [1,n] 的子区间。
每次分别对于 l , r l,r l,r 随机,然后调整 l , r l,r l,r 大小位置。
示例代码:
#include5-3. 随机浮点数
给定 n n n 和 k k k,要求生成 n n n 个 [ 0 , n ] [0,n] [0,n] 的 k k k 位浮点数(不可以有后缀 0 0 0)。
分成整数部分和小数部分考虑。
整数部分生成 [ 0 , n ] [0,n] [0,n] 的整数,小数部分生成 k k k 位 [ 0 , 9 ] [0,9] [0,9] 的数(在位数允许时,可以生成一个 [ 0 , 1 0 k − 1 ] [0,10^k-1] [0,10k−1] 的整数代替小数)。
当然,要特判整数为 n n n 的情况。若小数部分 > 0 >0 >0,就不在 [ 0 , n ] [0,n] [0,n] 内了。
处理后缀 0 0 0 时,只要把其存进字符串处理即可。
示例代码:
#include5-4. 随机整数
给定 n , l , r ( l , r ∈ Z , l ≤ r ) n,l,r(l,r\in\mathbb{Z},l\le r) n,l,r(l,r∈Z,l≤r),要求生成 n n n 个整数 x ( x ∈ [ l , r ] ) x(x\in[l,r]) x(x∈[l,r])。
可能含有负数,该怎么办呢?
分三类讨论:
- 当 l ≤ r ≤ 0 l\le r\le0 l≤r≤0 时,先输出
-,然后生成 [ ∣ r ∣ , ∣ l ∣ ] [|r|,|l|] [∣r∣,∣l∣] 范围的整数。 - 当 l ≤ 0 ≤ r l\le0\le r l≤0≤r 时,先随机 t = 0 t=0 t=0 或 1 1 1 来确定符号。
- 当 t = 0 t=0 t=0 时,输出
-,生成 [ 0 , ∣ l ∣ ] [0,|l|] [0,∣l∣] 的整数。 - 当 t = 1 t=1 t=1 时,生成 [ 0 , r ] [0,r] [0,r] 的整数。
- 当 t = 0 t=0 t=0 时,输出
- 当 0 ≤ l ≤ r 0\le l\le r 0≤l≤r 时,直接生成 [ l , r ] [l,r] [l,r] 的整数。
注意以上操作中输出 -0 的情况要处理一下。
示例代码:
#include6. 后记
那这次的介绍到尾声了。有很多像模拟退火、随机调整等随机化算法,在这里不再赘述,感兴趣的读者可以查阅相关资料学习一下。随机化是游戏中重要的操作之一,相信读者已经有所收获,点个赞或者关注我一下吧,谢谢!