【阿旭机器学习实战】【26】逻辑斯蒂回归----糖尿病预测实战
【阿旭机器学习实战】系列文章主要介绍机器学习的各种算法模型及其实战案例,欢迎点赞,关注共同学习交流。
本文通过构建逻辑斯蒂回归模型,对糖料病进行预测。
目录
- 1. 导入并查看数据信息
- 2. 特征工程
-
- 2.1 处理异常值
- 2.2 填充缺失值
- 3. 切分数据集并构建模型
1. 导入并查看数据信息
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
# 载入数据
data = pd.read_csv('./diabetes.csv')
data.head()
| Pregnancies | Glucose | BloodPressure | SkinThickness | Insulin | BMI | DiabetesPedigreeFunction | Age | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6 | 148 | 72 | 35 | 0 | 33.6 | 0.627 | 50 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 85 | 66 | 29 | 0 | 26.6 | 0.351 | 31 | 0 |
| 2 | 8 | 183 | 64 | 0 | 0 | 23.3 | 0.672 | 32 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 89 | 66 | 23 | 94 | 28.1 | 0.167 | 21 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 137 | 40 | 35 | 168 | 43.1 | 2.288 | 33 | 1 |
数据说明:
Pregnancies:怀孕次数
Glucose:葡萄糖测试值
BloodPressure:血压
SkinThickness:皮肤厚度
Insulin:胰岛素
BMI:身体质量指数
DiabetesPedigreeFunction:糖尿病遗传函数
Age:年龄
Outcome:糖尿病标签
# 查看数据类型
data.info()
RangeIndex: 768 entries, 0 to 767
Data columns (total 7 columns):
Pregnancies 768 non-null int64
Glucose 768 non-null float64
BloodPressure 768 non-null float64
BMI 768 non-null float64
DiabetesPedigreeFunction 768 non-null float64
Age 768 non-null int64
Outcome 768 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(4), int64(3)
memory usage: 42.1 KB
# 查看数据基本信息
data.describe()
| Pregnancies | Glucose | BloodPressure | SkinThickness | Insulin | BMI | DiabetesPedigreeFunction | Age | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 768.000000 | 768.000000 | 768.000000 | 768.000000 | 768.000000 | 768.000000 | 768.000000 | 768.000000 | 768.000000 |
| mean | 3.845052 | 120.894531 | 69.105469 | 20.536458 | 79.799479 | 31.992578 | 0.471876 | 33.240885 | 0.348958 |
| std | 3.369578 | 31.972618 | 19.355807 | 15.952218 | 115.244002 | 7.884160 | 0.331329 | 11.760232 | 0.476951 |
| min | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.078000 | 21.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 25% | 1.000000 | 99.000000 | 62.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 27.300000 | 0.243750 | 24.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 50% | 3.000000 | 117.000000 | 72.000000 | 23.000000 | 30.500000 | 32.000000 | 0.372500 | 29.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 75% | 6.000000 | 140.250000 | 80.000000 | 32.000000 | 127.250000 | 36.600000 | 0.626250 | 41.000000 | 1.000000 |
| max | 17.000000 | 199.000000 | 122.000000 | 99.000000 | 846.000000 | 67.100000 | 2.420000 | 81.000000 | 1.000000 |
# 查看数据形状
data.shape
(768, 9)
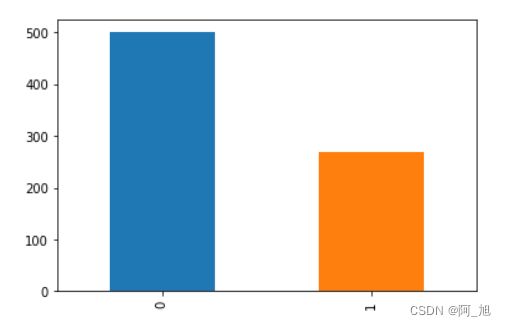
# 查看标签分布
print(data.Outcome.value_counts())
# 使用柱状图的方式画出标签个数统计
data.Outcome.value_counts().plot(kind="bar")
plt.show()
0 500
1 268
Name: Outcome, dtype: int64
# 查看两个目标分类下,各个特征的数据分布
sns.pairplot(data, hue = 'Outcome')
plt.show()
上图表明的是两种目标分类下,不用类型特征属性之间的关系,包含直方图和散点图。
其中同一特征对比时用的是直方图,不同特征对比的时候用的是散点图。
2. 特征工程
2.1 处理异常值
通过观察上图数据分布可以发现一些异常值,比如Glucose葡萄糖,BloodPressure血压,SkinThickness皮肤厚度,Insulin胰岛素,BMI身体质量指数存在0数值,但是这些数值应该是不可能出现0值的,因此我们需要将这些异常的0值进行处理。
# 将葡萄糖,血压,皮肤厚度,胰岛素,身体质量指数中的0替换为nan
colume = ['Glucose', 'BloodPressure', 'SkinThickness', 'Insulin', 'BMI']
data[colume] = data[colume].replace(0,np.nan)
# 查看数据类型
data.info()
RangeIndex: 768 entries, 0 to 767
Data columns (total 9 columns):
Pregnancies 768 non-null int64
Glucose 763 non-null float64
BloodPressure 733 non-null float64
SkinThickness 541 non-null float64
Insulin 394 non-null float64
BMI 757 non-null float64
DiabetesPedigreeFunction 768 non-null float64
Age 768 non-null int64
Outcome 768 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(6), int64(3)
memory usage: 54.1 KB
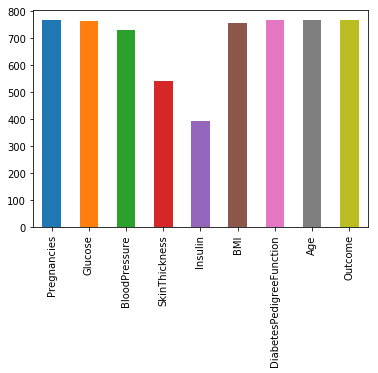
# 画出各特征非空的数值个数
data.notnull().sum().plot(kind="bar")
# 设定阀值,非空值需要超过总数量的80%以上
thresh_count = data.shape[0]*0.8
# 若某一列数据缺失的数量超过20%就会被删除
data = data.dropna(thresh=thresh_count, axis=1)
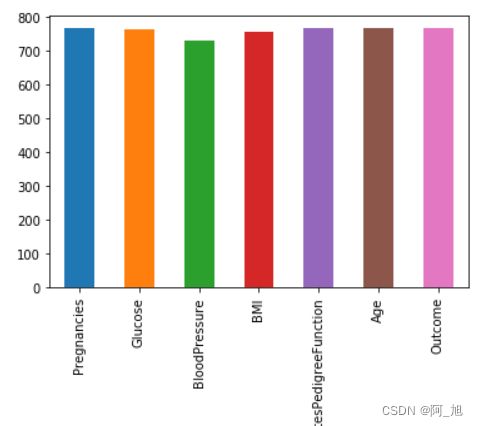
# 画出各特征非空的数值个数
data.notnull().sum().plot(kind="bar")
2.2 填充缺失值
# 导入插补库
from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer
# 此处采用均值插补的方法来填充缺失值
imr = Imputer(missing_values='NaN', strategy='mean', axis=0)
colume = ['Glucose', 'BloodPressure', 'BMI']
# 进行插补
data[colume] = imr.fit_transform(data[colume])
D:\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\ipykernel_launcher.py:7: SettingWithCopyWarning:
A value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.
Try using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead
See the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy
import sys
D:\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\indexing.py:543: SettingWithCopyWarning:
A value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.
Try using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead
See the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy
self.obj[item] = s
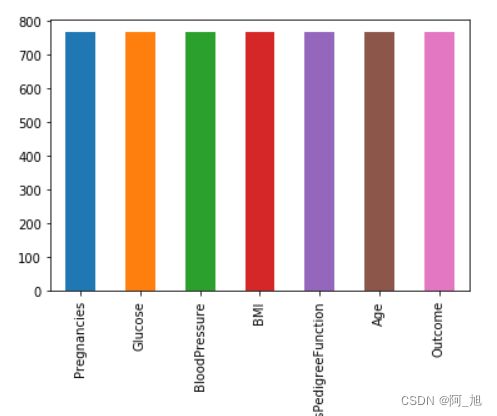
# 画出各特征非空的数值个数
data.notnull().sum().plot(kind="bar")
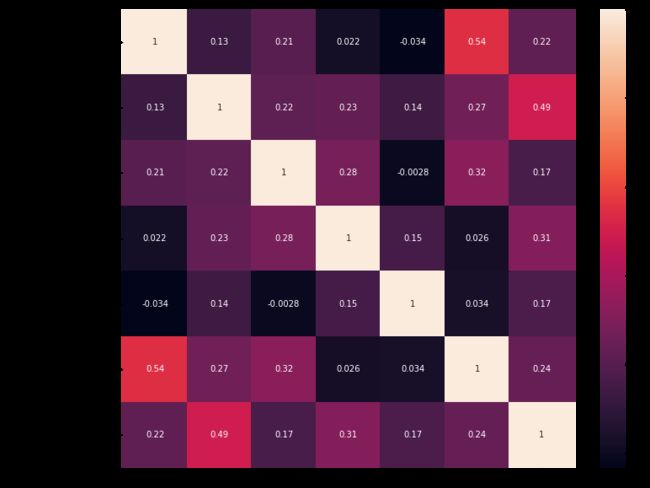
plt.figure(figsize=(12,10))
# 画热力图,数值为两个变量之间的相关系数
p=sns.heatmap(data.corr(), annot=True)
plt.show()
3. 切分数据集并构建模型
# 把数据切分为特征x和标签y
x = data.drop("Outcome",axis = 1)
y = data.Outcome
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 切分数据集,stratify=y表示切分后训练集和测试集中的数据类型的比例跟切分前y中的比例一致
# 比如切分前y中0和1的比例为1:2,切分后y_train和y_test中0和1的比例也都是1:2
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.3, stratify=y)
# 此处使用逻辑回归进行建模
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
LR = LogisticRegression()
LR.fit(x_train,y_train)
pre_result= LR.predict(x_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, pre_result))
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.78 0.91 0.84 150
1 0.76 0.52 0.62 81
avg / total 0.77 0.77 0.76 231
由上述结果,可以看出该模型的准确率约为76%,不是很高,模型还需进一步优化。
如果内容对你有帮助,感谢点赞+关注哦!
欢迎关注我的公众号:
阿旭算法与机器学习,共同学习交流。
更多干货内容持续更新中…