ResNet网络学习笔记。
ResNet网络学习
看b站 霹雳吧啦Wz 的视频总结的学习笔记!
视频的地址
大佬的Github代码
1、ResNet详解
ResNet 网络是在2015年由微软实验室提出,斩获当年 ImageNet 竞赛中分类任务第一名,目标检测第一名。获得 COCO 数据集中目标检测第一名,图像分割第一名。
论文:《Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition》
网络中的亮点:
- 超深的网络结构。(突破1000层)
- 提出 Residual 模块。
- 使用 Batch Normalization 加速训练。(丢弃dropout)
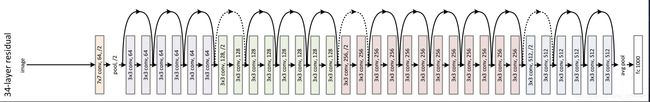
ResNet34 的网络结构图:
1.1、解决的问题
当我们的网络模型堆叠到一定深度时,会出现两个问题:
- 梯度消失或梯度爆炸。
- 退化问题:越深的网络可能比浅层的网络效果差。
如下图所示,左边图中,20层的网络的误差比56层的误差小。因此,越深的网络可能比浅层的网络效果差。
对于梯度消失或梯度爆炸的问题,原文中提出通过数据的预处理以及在网络中使用 (BN)Batch Normalization 加速训练来解决。
对于退化问题,原文中提出使用 Residual 模块来解决。
如上图所示,右图中使用了 Residual 模块,实线为测试误差,虚线为训练误差,可以看出越深层的网络误差变小了。
1.2、residual 模块介绍
接下来看一下什么是 residual 模块。
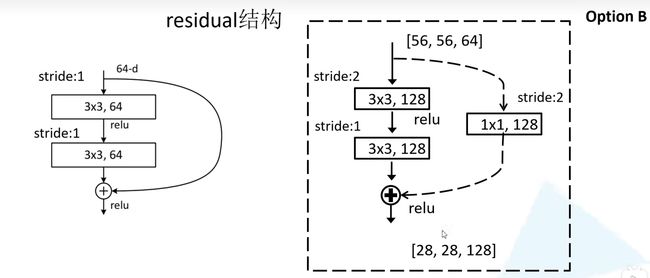
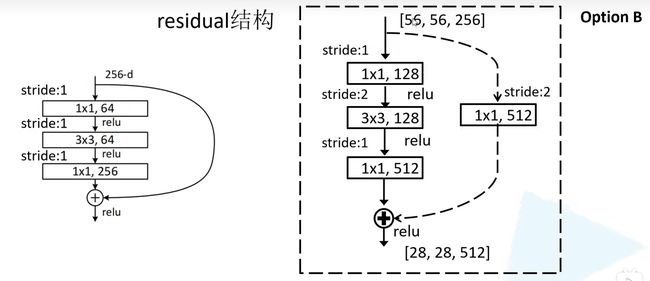
下图中分别是34层的 ResNet 和50/101/152层的 ResNet 的 residual 结构。
右边1×1的卷积核起到降维和升维的作用,同时可以减少网络的参数。
在 ResNet34 的网络结构图中我们看到,有的残差结构用的实线,有的用的虚线。
如下图所示,虚线的分支上通过1×1的卷积核进行了维度处理。
在相加操作中,需要保持维度相同。以 ResNet 18/34 为例,左边输入和输出的维度都为[56,56,64],因此可以直接进行相加操作。而右边输入的维度为[56,56,64],输出的维度为[28,28,128],因此分支上需要进行维度处理再进行相加操作。
ResNet 18/34:
ResNet 50/101/152:
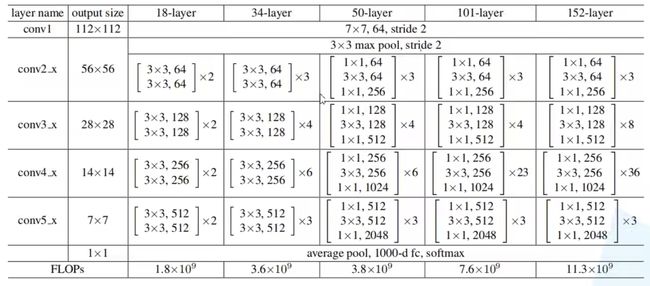
下图为不同版本的 ResNet 网络结构,表中的残差结构给出了主分支上卷积核的大小与卷积核个数,表中 ×N 表示将该残差结构堆叠N次。
对于 ResNet18/34 ,它的残差结构 conv3_x、conv4_x、conv5_x 所对应的第一层残差结构都是虚线残差结构。
对于 ResNet50/101/152 ,除了conv3_x、conv4_x、conv5_x 外,它的 conv2_x 所对应的第一层残差结构也是虚线残差结构。但是 conv2_x 只调整 channel 维度,高和宽的维度不变,而 conv3_x, conv4_x, conv5_x 的残差结构的分支上做维度处理时,不仅要调整 channel 的维度,还要将高和宽缩减为原来的一半。
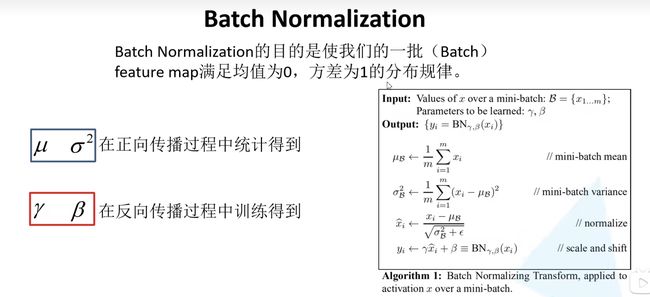
1.3、Batch Normalization
具体查看大佬的博客
1.4、迁移学习
在迁移学习中,我们希望利用源任务(Source Task)学到的知识帮助学习目标任务 (Target Task)。例如,一个训练好的图像分类网络能够被用于另一个图像相关的任务。再比如,一个网络在仿真环境学习的知识可以被迁移到真实环境的网络。迁移学习一个典型的例子就是载入训练好VGG网络,这个大规模分类网络能将图像分到1000个类别,然后把这个网络用于另一个任务,如医学图像分类。
常见的迁移学习方式:
- 载入权重后训练所有参数。
- 载入权重后只训练最后几层参数。
- 载入权重后在原网络基础上再添加一层全连接层,仅训练最后一个全连接层。
2、使用pytorch实现ResNet
2.1、model
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
# 18或34层的残差结构。
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1 # 残差结构所使用卷积核个数的一个变化,1表示是之前的一倍,没有变化。
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None, **kwargs):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False) # BatchNorm2d不需要偏置。
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.downsample = downsample # downsample为是虚线还是实线的残差结构。
def forward(self, x):
identity = x # 残差结构的分支
if self.downsample is not None: # 是否是虚线的残差结构
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
# 50、101、152层的残差结构。
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
"""
注意:原论文中,在虚线残差结构的主分支上,第一个1x1卷积层的步距是2,第二个3x3卷积层步距是1。
但在pytorch官方实现过程中是第一个1x1卷积层的步距是1,第二个3x3卷积层步距是2,
这么做的好处是能够在top1上提升大概0.5%的准确率。
可参考Resnet v1.5 https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/model-scripts/nvidia:resnet_50_v1_5_for_pytorch
"""
expansion = 4 # 卷积核个数变为原来的4倍
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None,
groups=1, width_per_group=64):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
width = int(out_channel * (width_per_group / 64.)) * groups
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=width,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # squeeze channels
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(width)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=width, out_channels=width, groups=groups,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(width)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=width, out_channels=out_channel*self.expansion, # 这里卷积核个数变为原来的4倍。
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # unsqueeze channels
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel*self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # inplace为True不影响结果,可以节省内存。
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
# 定义ResNet模型。
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
block, # 用的那种残差结构
blocks_num, # 每层的残差结构的个数
num_classes=1000, # 类别数目
include_top=True, # 表示在ResNet的基础上构建更复杂的模型,默认为true
groups=1,
width_per_group=64):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.include_top = include_top
self.in_channel = 64 # 输入的通道数为64
self.groups = groups
self.width_per_group = width_per_group
# 第一种卷积层 conv1。
# RGD图片输入的通道数为3,输出为64(卷积核的组数)。
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2,
padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, blocks_num[0]) # 对应conv2_x
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, blocks_num[1], stride=2) # 对应conv3_x
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, blocks_num[2], stride=2) # 对应conv4_x
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, blocks_num[3], stride=2) # 对应conv5_x
if self.include_top:
# 自适应采样,不管输入尺寸是多少,输出为(1, 1)。
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # output size = (1, 1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes) # 全连接层
# 初始化权重。
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
# 创建每种卷积层。
# channel为主分支卷积核的个数,block_num为卷积层的层数。
def _make_layer(self, block, channel, block_num, stride=1):
downsample = None
# 分支是否是虚线。
if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != channel * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channel, channel * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channel * block.expansion))
layers = [] # 新建一个列表,存放每一个卷积层。
# 第一层的分支为虚线,先添加进去。
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
downsample=downsample,
stride=stride,
groups=self.groups,
width_per_group=self.width_per_group))
self.in_channel = channel * block.expansion # 更新输入通道数
# 遍历剩下的层,逐个添加到列表中。
for _ in range(1, block_num): # 从1开始,因为第一层已经添加了,0表示第一层。
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
groups=self.groups,
width_per_group=self.width_per_group))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
# conv1
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x) # conv2_x
x = self.layer2(x) # conv3_x
x = self.layer3(x) # conv4_x
x = self.layer4(x) # conv5_x
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x) #池化
x = torch.flatten(x, 1) # 展平处理
x = self.fc(x) #全联接层
return x
# 定义各种类型resnet模型。
def resnet34(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth
return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet50(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet101(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnext50_32x4d(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth
groups = 32
width_per_group = 4
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],
num_classes=num_classes,
include_top=include_top,
groups=groups,
width_per_group=width_per_group)
def resnext101_32x8d(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext101_32x8d-8ba56ff5.pth
groups = 32
width_per_group = 8
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],
num_classes=num_classes,
include_top=include_top,
groups=groups,
width_per_group=width_per_group)
2.2、train
这里我们可以使用迁移学习的方式导入预训练好的模型参数。
我们输入import torchvision.models.resnet,然后点 resnet 进去查看源码中下载预训练的模型参数的地址:
model_urls = {
"resnet18": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-f37072fd.pth",
"resnet34": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-b627a593.pth",
"resnet50": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-0676ba61.pth",
"resnet101": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-63fe2227.pth",
"resnet152": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet152-394f9c45.pth",
"resnext50_32x4d": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth",
"resnext101_32x8d": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext101_32x8d-8ba56ff5.pth",
"wide_resnet50_2": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet50_2-95faca4d.pth",
"wide_resnet101_2": "https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet101_2-32ee1156.pth",
}
下载完把文件放在我们的项目目录下,进行训练:
import os
import sys
import json
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
from tqdm import tqdm
from model import resnet34
# 可以点进resnet去下载预训练的模型。
import torchvision.models.resnet
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print("using {} device.".format(device))
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224), # 中心裁剪
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])}
data_root = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "../..")) # get data root path
image_path = os.path.join(data_root, "data_set", "flower_data") # flower data set path
assert os.path.exists(image_path), "{} path does not exist.".format(image_path)
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, "train"),
transform=data_transform["train"])
train_num = len(train_dataset)
# {'daisy':0, 'dandelion':1, 'roses':2, 'sunflower':3, 'tulips':4}
flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx
cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in flower_list.items())
# write dict into json file
json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4)
with open('class_indices.json', 'w') as json_file:
json_file.write(json_str)
batch_size = 16
nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8]) # number of workers
print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw))
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=nw)
validate_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, "val"),
transform=data_transform["val"])
val_num = len(validate_dataset)
validate_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(validate_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False,
num_workers=nw)
print("using {} images for training, {} images for validation.".format(train_num,
val_num))
# 初始化模型。
net = resnet34()
# 使用迁移学习的方式进行训练。
# load pretrain weights
# download url: https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth
model_weight_path = "./resnet34-pre.pth" # 预训练模型的权重
assert os.path.exists(model_weight_path), "file {} does not exist.".format(model_weight_path)
net.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path, map_location='cpu')) # 加载预训练模型
# for param in net.parameters():
# param.requires_grad = False
# change fc layer structure
in_channel = net.fc.in_features # 全连接层输入的深度。
net.fc = nn.Linear(in_channel, 5)
net.to(device)
# define loss function
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# construct an optimizer
params = [p for p in net.parameters() if p.requires_grad]
optimizer = optim.Adam(params, lr=0.0001)
epochs = 3
best_acc = 0.0
save_path = './resNet34.pth'
train_steps = len(train_loader)
for epoch in range(epochs):
# train
net.train()# 控制网络中BatchNorm2d的状态。
running_loss = 0.0
train_bar = tqdm(train_loader, file=sys.stdout)
for step, data in enumerate(train_bar):
images, labels = data
optimizer.zero_grad()
logits = net(images.to(device))
loss = loss_function(logits, labels.to(device))
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# print statistics
running_loss += loss.item()
train_bar.desc = "train epoch[{}/{}] loss:{:.3f}".format(epoch + 1,
epochs,
loss)
# validate
net.eval() # 控制网络中BatchNorm2d的状态。
acc = 0.0 # accumulate accurate number / epoch
with torch.no_grad():
val_bar = tqdm(validate_loader, file=sys.stdout)
for val_data in val_bar:
val_images, val_labels = val_data
outputs = net(val_images.to(device))
# loss = loss_function(outputs, test_labels)
predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
acc += torch.eq(predict_y, val_labels.to(device)).sum().item()
val_bar.desc = "valid epoch[{}/{}]".format(epoch + 1,
epochs)
val_accurate = acc / val_num
print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f val_accuracy: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, running_loss / train_steps, val_accurate))
if val_accurate > best_acc:
best_acc = val_accurate
torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path)
print('Finished Training')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
2.3、test
import os
import json
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from model import resnet34
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
# load image
img_path = "../tulip.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# read class_indict
json_path = './class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
with open(json_path, "r") as f:
class_indict = json.load(f)
# create model
model = resnet34(num_classes=5).to(device)
# load model weights
weights_path = "./resNet34.pth"
assert os.path.exists(weights_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(weights_path)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights_path, map_location=device))
# prediction
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
print_res = "class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(predict_cla)],
predict[predict_cla].numpy())
plt.title(print_res)
for i in range(len(predict)):
print("class: {:10} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(i)],
predict[i].numpy()))
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()