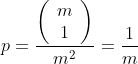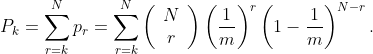Large scale evolutionary optimization using cooperative coevolution
0、论文背景
本文提出了一个新的合作协同进化框架,能够优化大规模的不可分离问题。在问题分解和协同演化中引入了一种随机分组方案和自适应加权方法。采用了一种新的微分进化算法来代替传统的进化算法。
Yang Z, Tang K, Yao X. Large scale evolutionary optimization using cooperative coevolution[J]. Information sciences, 2008, 178(15): 2985-2999.
1、具有分组和自适应加权的CC框架
该框架的关键步骤如下:
- 设置 i = 0 ,开始一个循环。
- 将一个n维的对象向量随机分割成m个子分量(s维),n = m * s。
- 使用EA优化第 i 个子组件。
- 如果 i < m,i++,回到步骤3。
- 对每个子组件施加一个权重。优化当前总体中最好、最差和随机成员的权重向量。
- 如果满足停止条件,则停止;否则,转到下一个循环的步骤1。
该方法与之前的CC最大的区别就是:
- 动态分组(随机分组)
- 框架在每个周期后使用自适应加权进行子组件之间的共适应。
自适应加权策略背后的动机是:在所有子组件相互依赖时,对它们提供协同适应。这个优化问题的维数比原始问题要低得多(m<
1.1 EACC-G的工作原理和效果
可分离函数的定义,![]() :
:
可以推出:
那么该函数就是可分离函数,否则则不是。
下面展示了在EACC-G中同时优化两个相互作用的变量的概率的一个简单例子。
首先,在每个单独的循环中,EACC-G将![]() 和
和![]() 分配到同一个子组件的概率:
分配到同一个子组件的概率:
设![]() 为EACC-G有r次循环将
为EACC-G有r次循环将![]() 和
和![]() 分配到单个子组件的概率:
分配到单个子组件的概率:
在至少k个循环中,设![]() 为EACC-G将
为EACC-G将![]() 和
和![]() 分配到单个子组件的概率:
分配到单个子组件的概率:
给定 n = 1000,s = 100,总循环数为50,我们可以得到:
P1和P2表明,EACC-G在至少一个或两个周期内优化相互作用变量方面具有相对较高的概率。换句话说,EACC-G使用简单分组策略下捕获变量相互依赖是非常有效的。
2、新的CC框架下的SaNSDE
有关SaNSDE以及实现,请参照博客:SaNSDE。
新的CC框架下的SaNSDE算法流程图如下图所示:
3、算法的实现和简单实验
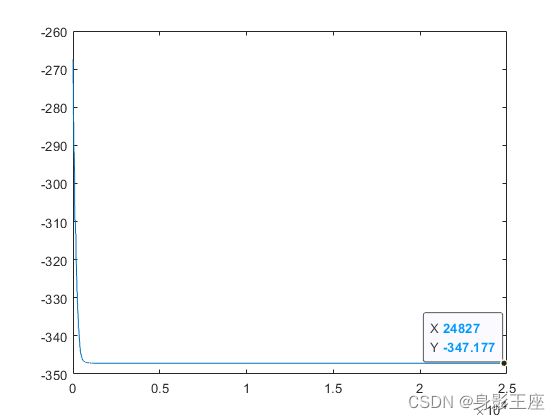
本文验证函数是CEC2008测试函数,二者总的函数估值次数均大概在2500000次。
SaNSDE实验设计代码:
clear;clc;clearvars;
addpath('CEC2008\');
% 初始化变量维度,种群数,最大迭代次数,搜索区间,F,CR
dim = 500;
popsize = 100;
maxIteration = 25000;
LB = -100 * ones(1, dim);
UB = 100 * ones(1, dim);
CR = 0.9;
% 估值次数:100*25000
[globalBest3, globalBestFitness3, FitnessHistory3] = SaNSDE(popsize, maxIteration,dim, LB, UB, @(x)benchmark_func(x,3));
plot(FitnessHistory3);
DECC_G:
clc;clear;clearvars;
addpath('CEC2008\');
global initial_flag
NS = 100; % 种群数
dim = 500; % 种群维度
s = 5; % 子空间的数目,设定为5,10
% 搜索区间:f1[-100,100],f2[-100, 100],f3[-100,100],f4[-5,5],f5[-600,600],f6[-32,32],f7[-1,1],每一维搜索区间一样
upper_bound = [100,100,100,5,600,32,1];
lower_bound = [-100,-100,-100,-5,-600,-32,-1];
best_yh = [];
for func_num = 3
initial_flag = 0; % 使initial_flag==0满足此条件,换一个函数initial_flag重置为0
% 生成num_initial个种群,并获得其评估值
sample_x = lhsdesign(NS, dim).*(upper_bound(func_num) - lower_bound(func_num)) + lower_bound(func_num).*ones(NS, dim);
sample_y = benchmark_func(sample_x,func_num);
[best_y, bestIndex] = min(sample_y); %获取全局最小值以及对应的种群
best_x = sample_x(bestIndex,:);
for i0 = 1 : 50 %迭代50次
index = randperm(dim); %随机划分子空间
for i1 = 1 : s
index1 = index(((i1 - 1) * (dim / s) + 1) : (i1 * (dim / s)));
sub_x = sample_x(:,index1);
sub_x = SaNSDE1(sub_x, sample_y, best_x, index1, 70,dim / s, lower_bound(func_num), upper_bound(func_num), @(x)benchmark_func(x,func_num));%100*70
sample_x(:,index1) = sub_x;
sample_y = benchmark_func(sample_x,func_num); %100
[best_y, bestIndex] = min(sample_y); %获取全局最小值以及对应的种群
best_x = sample_x(bestIndex,:);
end
[worse_y, worseIndex] = max(sample_y); %获取全局最大值以及对应的种群
randIndex = randi(NS);
while randIndex == bestIndex || randIndex == worseIndex
randIndex = randi(NS); % 随机获取一个值
end
% 权重向量的搜索范围[-5,5]
[sample_x(worseIndex,:),sample_y(worseIndex,:)] = NSDE(sample_x(worseIndex,:), NS, 50, s, -5, 5, 0.9, @(x)benchmark_func(x,func_num));% 50*100
[sample_x(bestIndex,:),sample_y(bestIndex,:)] = NSDE(sample_x(bestIndex,:), NS, 50, s, -5, 5, 0.9, @(x)benchmark_func(x,func_num));
[sample_x(randIndex,:),sample_y(randIndex,:)] = NSDE(sample_x(randIndex,:), NS, 50, s, -5, 5, 0.9, @(x)benchmark_func(x,func_num));
[best_y, bestIndex] = min(sample_y); %获取全局最小值以及对应的种群
best_x = sample_x(bestIndex,:);
best_yh = [best_yh;best_y];
end
end
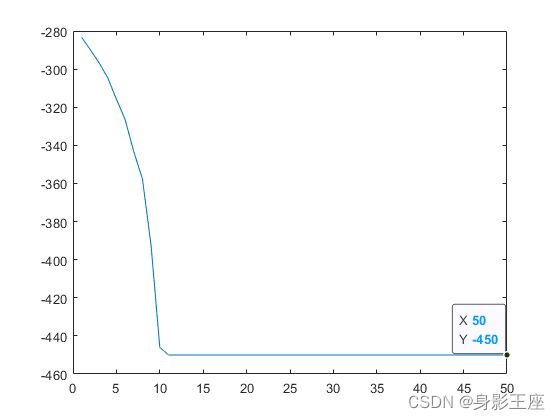
plot(best_yh);function [x1 , globalBestFitness] = NSDE(x,popsize, maxIteration,dim, LB, UB, CR, Fun)
% 种群的初始化和计算适应度值
Sol(popsize, dim) = 0; % Declare memory.
Fitness(popsize) = 0;
for i = 1:popsize
Sol(i,:) = LB+(UB-LB).* rand(1, dim);
for i0 = 1 : dim
ind = ((i0 - 1) * (size(x,2) / dim) + 1) : i0 * (size(x,2) / dim);
x(1,ind) = x(1,ind) .* Sol(i,i0);
end
Fitness(i) = Fun(x(1,:));
end
% 获得全局最优值以及对应的种群向量
[fbest, bestIndex] = min(Fitness);
globalBest = Sol(bestIndex,:);
globalBestFitness = fbest;
% 开始迭代
for time = 1:maxIteration
for i = 1:popsize
% 突变
r = randperm(popsize, 3); %在1~pop中随机选择5个数组成一个数组
r1 = rand();
if r1 > 0.5
pd = makedist('tLocationScale','mu',0,'sigma',1,'nu',1);
F = random(pd,1,1);%生成1个柯西随机数
else
F = normrnd(0.5,0.5);%生成1个高斯随机数
end
mutantPos = Sol(r(1),:) + F * (Sol(r(2),:) - Sol(r(3),:));
% 交叉
jj = randi(dim); % 选择至少一维发生交叉
for d = 1:dim
if rand() < CR || d == jj
crossoverPos(d) = mutantPos(d);
else
crossoverPos(d) = Sol(i,d);
end
end
% 检查是否越界.
crossoverPos(crossoverPos>UB) = UB;
crossoverPos(crossoverPosfunction sub_x = SaNSDE1(sub_x, sample_y, best_x, index1, maxIteration,dim, LB, UB, Fun)
% 获得全局最优值以及对应的种群向量
[~, bestIndex] = min(sample_y);
globalBest = sub_x(bestIndex,:);
% 策略学习初始化值的设置
p1 = 0.5;p3 = 0.5;
ns1 = 0;ns2 = 0;nf1 = 0;nf2 = 0;
fns1 = 0;fns2 = 0;fnf1 = 0;fnf2 = 0;
CRm = 0.5;
CRQ = normrnd(CRm,0.1,[size(sub_x,1),1]);
CRRecord = [];
RecRecord = [];
% 开始迭代
for time = 1:maxIteration
for i = 1:size(sub_x,1)
% 突变
if rand() >= p3
pd = makedist('tLocationScale','mu',0,'sigma',1,'nu',1);
F = random(pd,1,1);%生成1个柯西随机数
tag1 = 1;
else
F = normrnd(0.5,0.3);%生成1个高斯随机数
tag1 = 2;
end
if rand() <= p1
r = randperm(size(sub_x,1), 3); %策略1
mutantPos = sub_x(r(1),:) + F * (sub_x(r(2),:) - sub_x(r(3),:));%在1~pop中随机选择3个数组成一个数组
tag0 = 1;
else
r = randperm(size(sub_x,1), 2); %策略2
mutantPos = sub_x(i,:) + F * (globalBest - sub_x(i,:)) + F * (sub_x(r(1),:) - sub_x(r(2),:));
tag0 = 2;
end
% 交叉
jj = randi(dim); % 选择至少一维发生交叉
CR = CRQ(i,1);
for d = 1:dim
if rand() < CR || d == jj
crossoverPos(d) = mutantPos(d);
else
crossoverPos(d) = sub_x(i,d);
end
end
% 检查是否越界.
crossoverPos(crossoverPos>UB) = UB;
crossoverPos(crossoverPosf1,SaNSDE和CCEA_G:
f2,SaNSDE和CCEA_G:
f3,SaNSDE和CCEA_G:
从上面简单看出,CCEA_G有着不小的优势。
如有错误,还望批评指正。