深度学习笔记(四)VGG14
1. 主要贡献
- 本文探究了参数总数基本不变的情况下,CNN随着层数的增加,其效果的变化。(thorough evaluation of networks of increasing depth using an architecture with very small (3×3) convolution filters, which shows that a significant improvementon the prior-art configurations can be achieved by pushing the depth to 16–19 weight layers.)
2. 前人的改进
针对原始论文ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[2]里的框架,目前主要的改进有:
-
文献[3]:utilised smaller receptive window size and smaller stride of the first convolutional layer.
-
文献[4]:dealt with training and testing the networks densely over the whole image and over multiple scales.
3. CNN网络architecture
To measure the improvement brought by the increased ConvNet depth in a fair setting, all our ConvNet layer configurations are designed using the same principles come from [1].
- CNN的输入都是224×224×3的图片.
- 输入前唯一的预处理是减去均值.
- 卷积核大小基本都是为3×3,步长为1.
- 额外的1×1的核可以被看成是输入通道的线性变换.
- 共有五个Max-Pooling层, 池化窗口大小为2×2, 步长为2.
- 所以得隐含层都使用rectification non-linearity(RELU)作为激活函数.
- 不需要添加Local Response Normalization(LRN), 因为它不提升效果反而会带来计算花费和内存花费, 增加计算时间.
- 最后一层是soft-max transform layer作为代价函数层.
4. CNN configurations
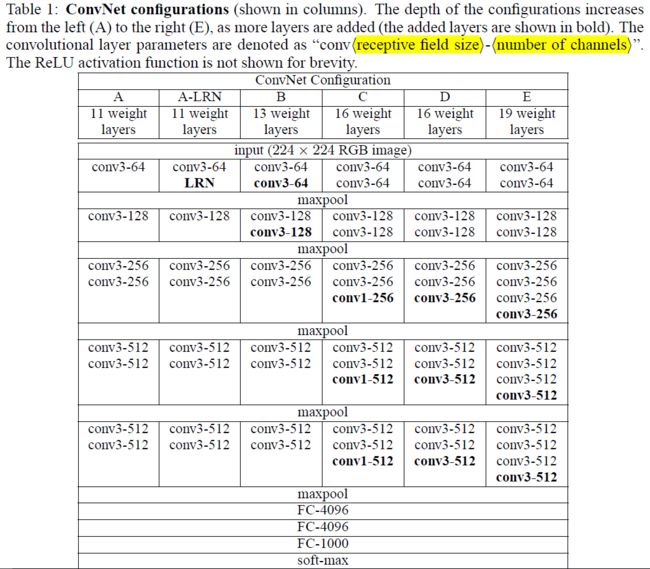
- 卷积网络的配置见表1, 按照A-E来命名. From 11 weight layers in the network A (8 conv. and 3 FC layers) to 19 weight layers in the network E (16 conv. and 3 FC layers).
- 卷积层的通道channels数目(宽度width)从64开始, 每过一个max-pooling层数量翻倍,到512为止.
5. 讨论
- 为什么论文中全程使用3×3大小的filters? 这是因为2个相连3×3大小的filters相当于一个5×5大小的filters. 同样的3个相连3×3大小的filters相当于一个7×7大小的filters.
- 那么为什么不直接用一个5×5大小的或7×7大小的呢?以7×7的为例:
首先, 三层比一层更具有判别性.(First, we incorporate three non-linearrectification layers instead of a single one, which makes the decision function more discriminative.)
其次, 假设同样的通道数C, 那么三层3×3的参数数目为3×(3×3)C×C=27C×C, 一层7×7参数数目为7×7×C×C=49C×C, 大大减少了参数数目.
- 使用1×1的卷积核可以在不影响感知域的情况下增加判别函数的非线性。该核已被用于文献Network in Network[5]网络结构。
6. 训练
除了在样本采样中使用 multiple scale之外,本文实验基本都遵循论文[2]的设置。batch size是256,momentum是0.9,正则化系数是5×10e-4,前两层全连接的dropout参数设置为0.5,learning rate初始化为10e-2,且当验证集结果不再上升时步长除以10,除三次为止。学习了370K迭代(74 epochs)时停止。(The batch size was set to 256, momentum to 0.9. The training was regularised by weight decay (the L2 penalty multiplier set to $5 · 10^{−4}$) and dropout regularisation for the first two fully-connected layers (dropout ratio set to 0.5). The learning rate was initially set to $10^{−2}$, and then decreased by a factor of 10 when the validation set accuracy stopped improving. In total, the learning rate was decreased 3 times, and the learning was stopped after 370K iterations (74 epochs).)
- 本文的网络比原来的网络[2]要更容易收敛, 这是因为
a) implicit regularisation imposed by greater depth and smaller conv. filter sizes
b) pre-initialisation of certain layers.
- 网络的权重初始化方式: 先训练浅层网络, 如图中的A网络, 得到权重参数. 然后当训练更深的网络时, 使用A中得到的参数初始化前四个卷积层和最后三个全连接层, 中间的其他层仍使用随机初始化. 在pre-initialised layers里我们不改变学习率learning rate, 允许它们在学习learning 的过程中改变. 对于随机初始化,我们在一个均值为1,方差为0.01正态分布中采样. 偏置项bias设为0.(To circumvent this problem, we began with training the configuration A (Table 1), shallow enough to be trained with random initialisation. Then, when training deeper architectures, we initialised the first four convolutional layers and the last three fullyconnected layers with the layers of net A (the intermediate layers were initialised randomly). We did not decrease the learning rate for the pre-initialised layers, allowing them to change during learning. For random initialisation (where applicable), we sampled the weights from a normal distribution with the zero mean and $10^{−2}$ variance. The biases were initialised with zero.)
- 224×224输入的获得, 将原始图片等比例缩放, 保证短边 S 大于224, 然后随机选择224×224的窗口, 为了进一步data augment, 还要考虑随机的水平翻转和RGB通道变换.
- Multi-scale Training, 多尺度的意义在于图片中的物体的尺度有变化, 多尺度可以更好的识别物体. 有两种方法进行多尺度训练:
a). 在不同的尺度下, 训练多个分类器, 参数为S, 参数的意义就是在做原始图片上的缩放时的短边长度. 论文中训练了S=256和S=384两个分类器, 其中S=384的分类器的参数使用S=256的参数进行 初始化, 且使用一个小的初始学习率10e-3.
b). 另一种方法是直接训练一个分类器, 每次数据输入时, 每张图片被重新缩放, 缩放的短边 S 随机从[min, max]中选择, 本文中使用区间[256,384], 网络参数初始化时使用S=384时的参数.
7. 测试
- 首先进行等比例缩放, 短边长度Q大于224, Q的意义与S相同, 不过S是训练集中的, Q是测试集中的参数. Q不必等于S, 相反的, 对于一个S, 使用多个Q值进行测试, 然后去平均会使效果变好.
- 然后,按照本文参考文献[4]的方式对测试数据进行测试:
a). 将全连接层转换为卷积层,第一个全连接转换为7×7的卷积,第二个转换为1×1的卷积。
b). Resulting net is applied to the whole image by convolving the filters in each layer with the full-size input. The resulting output feature map is a class score map with the number channels equal to the number of classes, and the variable spatial resolution, dependent on the input image size.
c). Finally, class score map is spatially averaged(sum-pooled) to obtain a fixed-size vector of class scores of the image.
8. 实现
- 使用C++ Caffe toolbox实现
- 支持单系统多GPU
- 多GPU把batch分为多个GPU-batch,在每个GPU上进行计算,得到子batch的梯度后,以平均值作为整个batch的梯度。
- 论文的参考文献[7]中提出了很多加速训练的方法。论文实验表明,在4-GPU的系统上,可以加速3.75倍。
9. 实验
9.1 Configuration Comparison
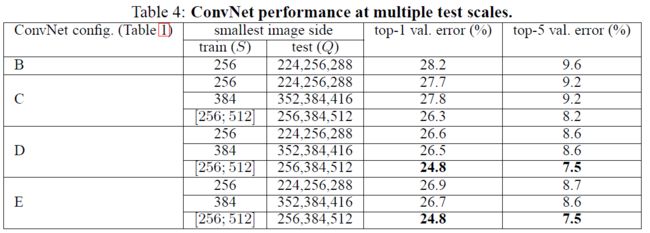
使用图1中的CNN结构进行实验,在C/D/E网络结构上进行多尺度的训练,注意的是,该组实验的测试集只有一个尺度。如下图所示:
9.2 Multi-Scale Comparison
测试集多尺度,且考虑到尺度差异过大会导致性能的下降,所以测试集的尺度Q在S的上下32内浮动。对于训练集是区间尺度的,测试集尺度为区间的最小值、最大值、中值。
9.3 Convnet Fusion
模型融合,方法是取其后验概率估计的均值。融合图3和图4中两个最好的model可以达到更好的值,融合七个model会变差。
10. Reference
[1]. Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556, 2014.
[2]. Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In NIPS, pp. 1106–1114, 2012.
[3]. Zeiler, M. D. and Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. CoRR, abs/1311.2901, 2013. Published in Proc. ECCV, 2014.
[4]. Sermanet, P., Eigen, D., Zhang, X., Mathieu, M., Fergus, R., and LeCun, Y. OverFeat: Integrated Recognition, Localization and Detection using Convolutional Networks. In Proc. ICLR, 2014.
[5]. Lin, M., Chen, Q., and Yan, S. Network in network. In Proc. ICLR, 2014.