opencv像素遍历的三种方法
参考链接:OpenCV中高效的像素遍历方法,写出工程级像素遍历代码(贾志刚老师)
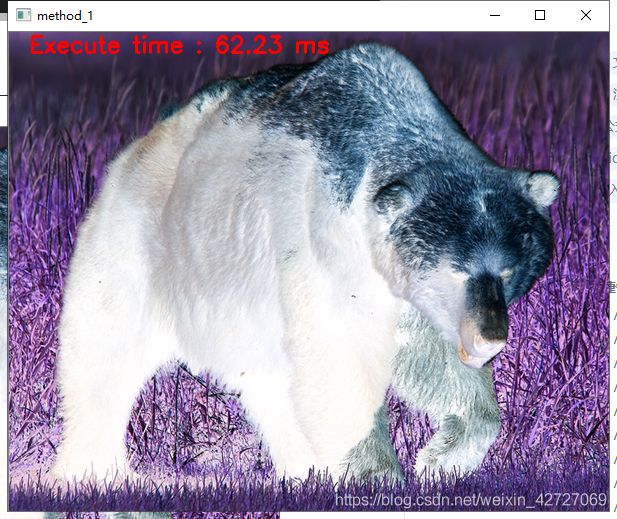
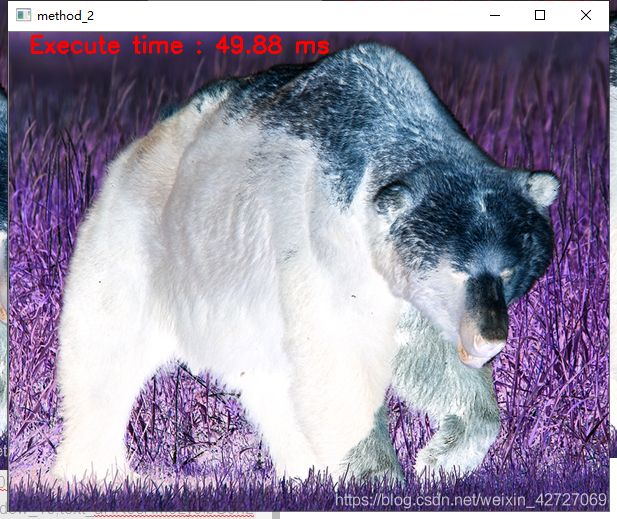
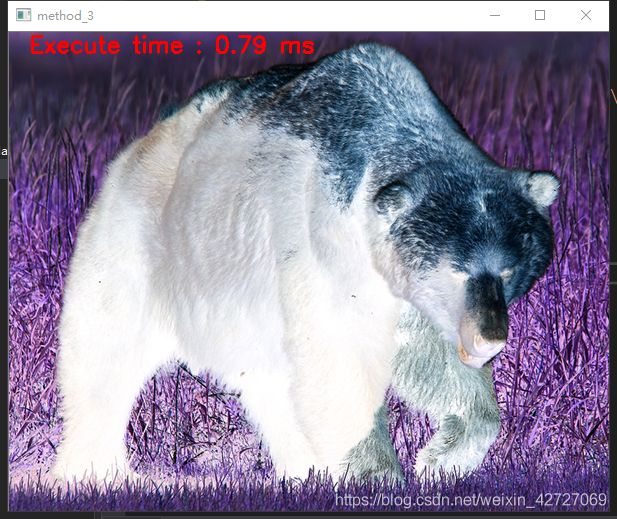
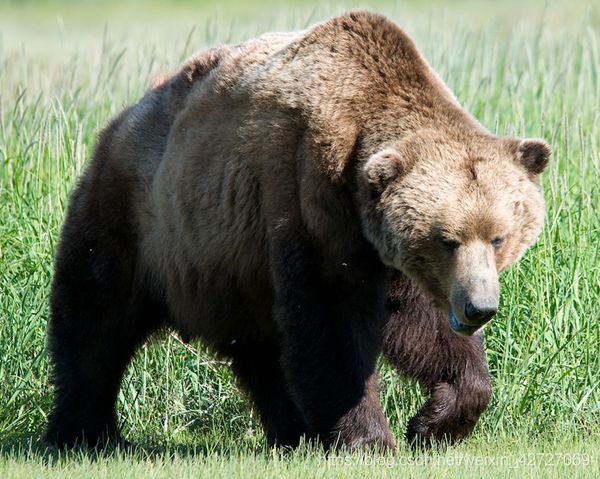
测试图片:

测试代码:
功能:遍历测试图片每个像素,对它求反向图,即 255-pix
#include 结论:
方法3效率最高,重点学习对象。
遍历像素的时候注意Mat类型,防止输出异常或者截断错误
typedef Vec<uchar, 2> Vec2b;
typedef Vec<uchar, 3> Vec3b;
typedef Vec<uchar, 4> Vec4b;
typedef Vec<short, 2> Vec2s;
typedef Vec<short, 3> Vec3s;
typedef Vec<short, 4> Vec4s;
typedef Vec<ushort, 2> Vec2w;
typedef Vec<ushort, 3> Vec3w;
typedef Vec<ushort, 4> Vec4w;
typedef Vec<int, 2> Vec2i;
typedef Vec<int, 3> Vec3i;
typedef Vec<int, 4> Vec4i;
typedef Vec<int, 6> Vec6i;
typedef Vec<int, 8> Vec8i;
typedef Vec<float, 2> Vec2f;
typedef Vec<float, 3> Vec3f;
typedef Vec<float, 4> Vec4f;
typedef Vec<float, 6> Vec6f;
typedef Vec<double, 2> Vec2d;
typedef Vec<double, 3> Vec3d;
typedef Vec<double, 4> Vec4d;
typedef Vec<double, 6> Vec6d;