深度学习模型试跑(十五):Real-ESRGAN(VS2019 trt推理部署)
目录
- 前言
- 一.模型解读
- 二.模型训练
- 三.VS2019运行C++预测
- 附一.VS2019运行C++预测
- 附二.real-esrgan代码解读
前言
超分辨率修复、重建是采用低分辨率(LR)输入并将其提高到高分辨率的任务,具体原理可以参考paddlegan原理介绍。对于在linux上如何实现trt加速该网络,这里有一篇文章详细记录了过程。
我的环境:
- Visual Studio 2019
- CUDA 11.6,cudnn 8.2
- CMake 3.17.1
- Tensorrt 8.4.1.5
一.模型解读
作者在ESRGAN(Real-ESRGAN同一作者)的基础上,又做了一些改进。这篇博文把这块改进写的很详细,想要了解原理的可以参看这篇文章解读作者的论文。
网络设计的解读,可以参考ESRGAN官方代码解读,了解整个网络结构,我这里截取部分onnx的节点图。
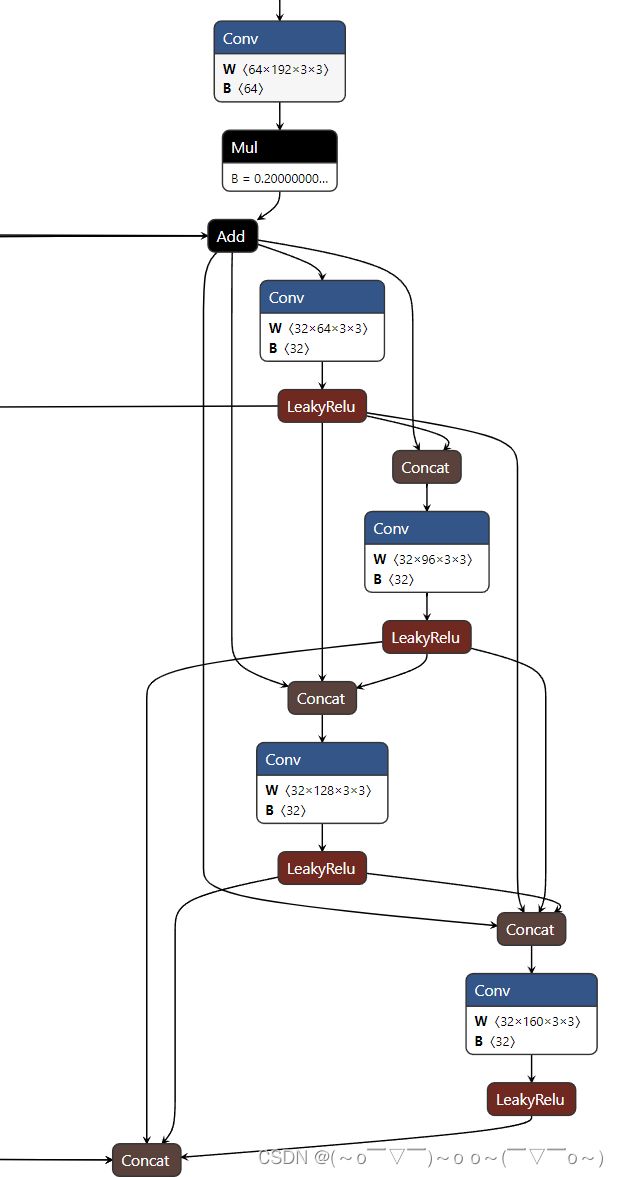
由于推理网络(就是生成器)是照搬了 ESRGAN 中的 Generator,即使用 Residual-in-residul Dense Block(RRDB),所以代码的复现还是基于ESRGAN 。
二.模型训练
我直接跳过了,试了下带不动。
三.VS2019运行C++预测
主要参照:
tensorrtx的代码
- 生成二进制序列化权重文件.wts
1)首先拷贝Real-ESRGAN官方pytorch(python)实现,我是直接下载了它的python代码,
2)然后安装各种依赖,这两步具体可参考README_CN.md。
pip install basicsr
pip install facexlib
pip install gfpgan
pip install -r requirements.txt
python setup.py develop
3)下载权重文件,在Real-ESRGAN官方pytorch(python)新建一个experiments/pretrained_models
二级目录,并将权重文件拷贝到这里面;将tensorrtx/real-esrgan/目录下的gen_wts.py脚本拷贝到 Real-ESRGAN官方pytorch下并运行
python gen_wts.py
运行成功后会生成一个real-esrgan.wts。
- 构建tensorrtx/real-esrgan工程并运行
- 转到tensorrtx/real-esrgan/目录下
- 修改CMakeLists.txt,主要将第4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12、16行改为相关库的目录,Tensorrt建议改用8开头的版本,31、67行根据我了解到的情况暂可不改。(修改 # 标记的地方)
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0)
project(real-esrgan) #1
set(OpenCV_DIR "D:\\opencv\\build") #2
set(OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS ${OpenCV_DIR}\\include) #3
set(OpenCV_LIB_DIRS ${OpenCV_DIR}\\x64\\vc15\\lib) #4
set(OpenCV_Debug_LIBS "opencv_world450d.lib") #5
set(OpenCV_Release_LIBS "opencv_world450.lib") #6
set(TRT_DIR "D:\\lbq\\TensorRT-7.2.3.4") #7
set(TRT_INCLUDE_DIRS ${TRT_DIR}\\include) #8
set(TRT_LIB_DIRS ${TRT_DIR}\\lib) #9
set(Dirent_INCLUDE_DIRS "D:\\lbq\\dirent\\include") #10
add_definitions(-std=c++14)
set(CUDA_BIN_PATH C:\\Program Files\\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\\CUDA\\v11.5)
option(CUDA_USE_STATIC_CUDA_RUNTIME OFF)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)
set(THREADS_PREFER_PTHREAD_FLAG ON)
find_package(Threads)
# setup CUDA
find_package(CUDA REQUIRED)
message(STATUS " libraries: ${CUDA_LIBRARIES}")
message(STATUS " include path: ${CUDA_INCLUDE_DIRS}")
include_directories(${CUDA_INCLUDE_DIRS})
set(CUDA_NVCC_PLAGS ${CUDA_NVCC_PLAGS};-std=c++14; -g; -G;-gencode; arch=compute_86;code=sm_86)
####
enable_language(CUDA) # add this line, then no need to setup cuda path in vs
####
include_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include) #14
include_directories(${TRT_INCLUDE_DIRS}) #12
link_directories(${TRT_LIB_DIRS}) #13
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}) #14
link_directories(${OpenCV_LIB_DIRS}) #15
include_directories(${Dirent_INCLUDE_DIRS}) #16
# -D_MWAITXINTRIN_H_INCLUDED for solving error: identifier "__builtin_ia32_mwaitx" is undefined
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++14 -Wall -Ofast -D_MWAITXINTRIN_H_INCLUDED")
# setup opencv
find_package(OpenCV QUIET
NO_MODULE
NO_DEFAULT_PATH
NO_CMAKE_PATH
NO_CMAKE_ENVIRONMENT_PATH
NO_SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PATH
NO_CMAKE_PACKAGE_REGISTRY
NO_CMAKE_BUILDS_PATH
NO_CMAKE_SYSTEM_PATH
NO_CMAKE_SYSTEM_PACKAGE_REGISTRY
)
message(STATUS "OpenCV library status:")
message(STATUS " version: ${OpenCV_VERSION}")
message(STATUS " lib path: ${OpenCV_LIB_DIRS}")
message(STATUS " Debug libraries: ${OpenCV_Debug_LIBS}")
message(STATUS " Release libraries: ${OpenCV_Release_LIBS}")
message(STATUS " include path: ${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}")
if(NOT DEFINED CMAKE_CUDA_ARCHITECTURES)
set(CMAKE_CUDA_ARCHITECTURES 86)
endif(NOT DEFINED CMAKE_CUDA_ARCHITECTURES)
add_executable(real-esrgan ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/real-esrgan.cpp ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/common.hpp
${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/preprocess.cu ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/preprocess.hpp
${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/postprocess.cu ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/postprocess.hpp
) #17
target_link_libraries(real-esrgan "nvinfer" "nvinfer_plugin") #18
target_link_libraries(real-esrgan debug ${OpenCV_Debug_LIBS}) #19
target_link_libraries(real-esrgan optimized ${OpenCV_Release_LIBS}) #20
target_link_libraries(real-esrgan ${CUDA_LIBRARIES}) #21
target_link_libraries(real-esrgan Threads::Threads)
-
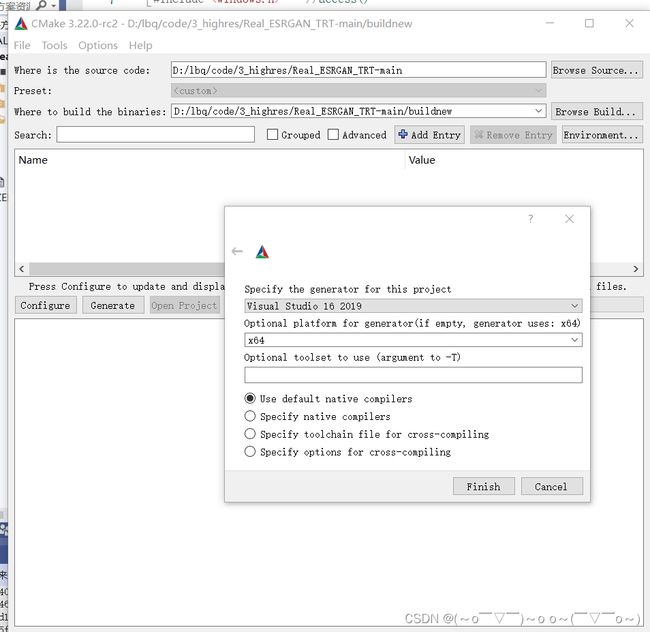
用cmake-gui打开代码,自己适配下版本,步骤跟yolov5类似。第一行填入Real_ESRGAN_TRT 目录,第三行填入Real_ESRGAN_TRT/buildnew目录。然后就是点击’Configure’、‘Generate’、‘Open Project’ 编译、生成、打开工程


-
将第一步中的real-esrgan.wts拷贝到这个Release目录下,将tensorrt中相关的dll文件如nvinfer.dll等也拷贝(软链接)到该目录下。
-
打开命令行窗口,执行real-esrgan.exe -s real-esrgan.wts real-esrgan_f32.engine ,生成对应的engine,这一步可能会花半个小时的时间,具体要看GPU。
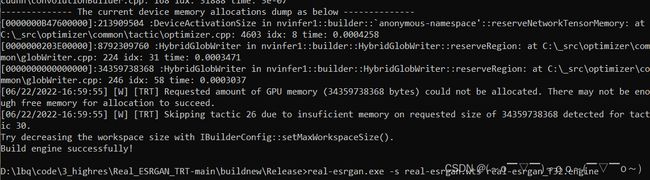
-
最后将 -d real-esrgan_f32.engine …/samples 写到VS的命令参数里,注意一定要索引到正确的目录,第一个是engine 文件所在的目录,第二个是图像所在的目录,就可以直接按F5执行程序了,图像涉密这里我就不贴出来了。
附一.VS2019运行C++预测
- 输入尺寸INPUT_H、INPUT_W、INPUT_C,其中前两项是可以根据实际需求做调整
- GPU id(DEVICE),在第9行,目前可能只支持单显卡
- BATCH_SIZE,在第10行,每次推理多少张图片
- PRECISION_MODE,推理精度,在第14行,精度越低效果越差速度越快
- VISUALIZATION,推理可视化,在第15行.
我发现对特定的图像修复还是要引用一个传统的图像修复算法做前处理,于是封装了四个传统图像增强方法在代码里,有兴趣的可以和我交流。
~~以下方式二选一,在代码257~273行;需要注意第262行是采用了传统的图像增强的方法,这一步对细胞的改善也是至关重要的;代码里一共集成了四种常用的传统的图像增强的方法均在utils.h文件里,里面的一些参数需要调节,目前采用的是伽马变换(gamma_transform)
- 静态图输入,指的是固定了输入图像的尺度(C、W、H),不可以用其它尺度的图片来推理,
- 动态图输入,即支持多种尺度的输入,目前输出结果有毛边(还未处理);~~
附二.real-esrgan代码解读
#include "cuda_utils.h"
#include "common.hpp"
#include "preprocess.hpp" // preprocess plugin
#include "postprocess.hpp" // postprocess plugin
#include "logging.h"
#include "utils.h"
#include