Pytorch ——特征图的可视化
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、torchvision.models._utils.IntermediateLayerGetter
-
- *注意:torcvision的最新版本0.13,已经取消了pretrained=True这个参数,并且打算在0.15版正式移除,如果用pretrained这个参数会出现warring警告。现在加载与训练权重的参数改成了**weights**,这样可以加载不同版本的预训练权重,比如models.ResNet18_Weights.DEFAULT,就加载默认最新的ResNet18权重文件,还有其他参数形式,具体参考官网*
- 二、示例
-
- 1.ResNet50特征图可视化
- 原图
- 特征图
- 2.AlexNet可视化
- 总结
前言
Pytroch中间层的特征图可视化,网上已经有很多教程,比如用hook钩子函数,但是代码都写得不是很清楚,所以还是自己去摸索一下。
一、torchvision.models._utils.IntermediateLayerGetter
IntermediateLayerGetter这个函数是在看DETR源码时发现的,它的作用很简单,记录我们想要的中间层的输出。看个官方给出的例子:
import torch
import torchvision
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision.models as models
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
model = torchvision.models.resnet18(weights=models.ResNet18_Weights.DEFAULT)
new_model = torchvision.models._utils.IntermediateLayerGetter(model, {'layer1': 'feat1', 'layer3': 'feat2'})
out = new_model(torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224))
print([(k, v.shape) for k, v in out.items()]) # 其中v是对应层的输出,也就是我们要得到的特征图Tensor
#输出
"[('feat1', torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56])), ('feat2', torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14]))]"
注意:torcvision的最新版本0.13,已经取消了pretrained=True这个参数,并且打算在0.15版正式移除,如果用pretrained这个参数会出现warring警告。现在加载与训练权重的参数改成了weights,这样可以加载不同版本的预训练权重,比如models.ResNet18_Weights.DEFAULT,就加载默认最新的ResNet18权重文件,还有其他参数形式,具体参考官网
这里详细说一下
#首先定义一个模型,这里直接加载models里的预训练模型
model = torchvision.models.resnet18(weights=models.ResNet18_Weights.DEFAULT)
#查看模型的各个层,
for name in model.named_children():
print(name[0])
#输出,相当于把ResNet的分成了10个层
"""
conv1
bn1
relu
maxpool
layer1
layer2
layer3
layer4
avgpool
fc"""
可以看到ResNet18的结构被分为了10个部分,和下图的网络结构是一一对应的,conv1、bn1、relu、maxpool这四个对应第一层的卷积conv1,layer1对应图中的conv2_x,也就是一个残差结构,同理layer2对应conv3_x,以此类推。
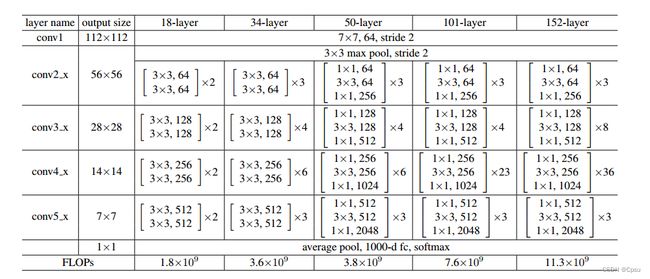
比如,我想要layer1(conv2_x)和layer2(conv3_x)的输出,那么只需要构建一个字典,{‘layer1’: ‘feat1’, ‘layer2’: ‘feat2’},feat1、feat2是我们的重命名,可以随意输入自己想要的名字。
#现在我们把model传进IntermediateLayerGetter
new_model = torchvision.models._utils.IntermediateLayerGetter(model, {'layer1': 'feat1', 'layer2': 'feat2'})
out = new_model(torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224))
print([(k,v.shape) for k,v in out.items()])
#输出
"""
[('feat1', torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56])), ('feat2', torch.Size([1, 128, 28, 28]))]
"""
二、示例
1.ResNet50特征图可视化
代码如下:
# 返回输出结果
import cv2
import torchvision
import torch
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
#定义函数,随机从0-end的一个序列中抽取size个不同的数
def random_num(size,end):
range_ls=[i for i in range(end)]
num_ls=[]
for i in range(size):
num=random.choice(range_ls)
range_ls.remove(num)
num_ls.append(num)
return num_ls
path = "test.jpg"
transformss = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
#注意如果有中文路径需要先解码,最好不要用中文
img = cv2.imread(path)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
#转换维度
img = transformss(img).unsqueeze(0)
model = torchvision.models.resnet50(weights=models.ResNet50_Weights.DEFAULT)
new_model = torchvision.models._utils.IntermediateLayerGetter(model, {'layer1': '1', 'layer2': '2',"layer3":"3"})
out = new_model(img)
tensor_ls=[(k,v) for k,v in out.items()]
#这里选取layer2的输出画特征图
v=tensor_ls[1][1]
#取消Tensor的梯度并转成三维tensor,否则无法绘图
v=v.data.squeeze(0)
print(v.shape) # torch.Size([512, 28, 28])
#随机选取25个通道的特征图
channel_num = random_num(25,v.shape[0])
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
for index, channel in enumerate(channel_num):
ax = plt.subplot(5, 5, index+1,)
plt.imshow(v[channel, :, :])
plt.savefig("feature.jpg",dpi=300)
原图
特征图
从特征图中可以看到,layer2确实已经学习到了某些特征,比如第二行第二列的特征图已经把狗的形状勾勒出来了,说明这个卷积核学习的可能是狗的颜色。

这里再展示一下ResNet第一部分(conv1)卷积层的特征图(灰度图):
2.AlexNet可视化
上面的ResNet用的是预训练模型,这里我们自己构建AlexNet。
代码如下:
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(3, 96, 11, 4, 2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2),
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(96, 256, 5, 1, 2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2),
)
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(256, 384, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2))
self.fc=nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(256*6*6, 4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 100),
)
def forward(self, x):
x=self.conv1(x)
x=self.conv2(x)
x=self.conv3(x)
output=self.fc(x.view(-1, 256*6*6))
return output
model=AlexNet()
for name in model.named_children():
print(name[0])
#同理先看网络结构
#输出
"""
conv1
conv2
conv3
fc
"""
path = "test.jpg"
transformss = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
#注意如果有中文路径需要先解码,最好不要用中文
img = cv2.imread(path)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
#转换维度
img = transformss(img).unsqueeze(0)
model = AlexNet()
## 修改这里传入的字典即可
new_model = torchvision.models._utils.IntermediateLayerGetter(model, {"conv1":1,"conv2":2,"conv3":3})
out = new_model(img)
tensor_ls=[(k,v) for k,v in out.items()]
#选取conv2的输出
v=tensor_ls[1][1]
#取消Tensor的梯度并转成三维tensor,否则无法绘图
v=v.data.squeeze(0)
print(v.shape) # torch.Size([512, 28, 28])
#随机选取25个通道的特征图
channel_num = random_num(25,v.shape[0])
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
for index, channel in enumerate(channel_num):
ax = plt.subplot(5, 5, index+1,)
plt.imshow(v[channel, :, :]) # 灰度图参数cmap="gray"
plt.savefig("feature.jpg",dpi=300)
也就是说AlexNet这里分为了4部分,三个卷积和一个全连接(其实就是我们自己定义的foward前向传播),我们想要哪层的输出改个字典就好了,new_model = torchvision.models._utils.IntermediateLayerGetter(model, {“conv1”:1,“conv2”:2,“conv3”:3}),得到的特征图如下。

plt.imshow(v[channel, :, :],cmap="gray") 加上cmap参数就可以显示灰度图

总结
IntermediateLayerGetter有一个不足就是它不能获取二级层的输出,比如ResNet的layer2,他不能获取layer2里面的卷积的输出。
