SLAM14讲-ch12建图笔记
1. 单目稠密重建
遇到了一个问题,google解决了:运行ch12 单目稠密建图的程序时出现段错误(核心已转储)
不得不感叹Google比百度好用太多了。另外,在高博的Github下面有很多关于书上例程bug的讨论,遇到问题可以到这里看看。
gdb好像挺有用,挖个坑,有空来填。
1.1 单目稠密重建代码注释
针对教材中的单目稠密重建,代码量有些大,而且有些复杂,这里做简要介绍。
首先对整个单目稠密重建流程进行梳理:
- 任务使用200张图片对第1张图片上每个像素的深度值进行估计,即进行单目稠密重建。
- 读取第1张图片作为ref,后面的图片是cur,我们的任务就是对第一张图片中的深度的均值和方差进行估计更新;
- 遍历ref中所有像素,分别在各个cur中进行极线搜索和块匹配(因为这里是对所有像素点而不是特征点进行匹配,所以没有之前前端1中的特征点的描述子,此处需要确定极线位置,即极线搜索,使用深度均值的初始值来计算初始的极线位置,再不断优化深度的均值和方差;确定极线位置之后使用块匹配,此处使用3*3的窗口,计算窗口内坐标ref和cur内的像素的NCC,若NCC高于阈值,则认为匹配成功,否则匹配失败。取NCC最大的作为此次的块匹配结果,若匹配成功则将cur中对应的点作为ref中对应点的匹配)
- 根据三角化计算深度(均值)和不确定性(方差)。(难点,此处为手写而非调库,注释中有详细讲解)
- 将当前观测融合进上次估计中,并检查是否收敛(我们的目的是通过我们对cur的观测来不断优化之前的估计 μ , σ \mu,\sigma μ,σ,对应到程序里的
depth和depth_cov2各个坐标的值,先取出,再融合,实现更新的目的。)
#include 1.2 单目稠密重建讨论
- 像素梯度:像素梯度与极线平行时能精确匹配,而垂直时,匹配程度相同,无法正确匹配,故:像素梯度与极线夹角较大时,极线匹配的不确定性大;夹角较小时,匹配的不确定性变小。
- 逆深度:深度d实际上步步和Gaussian分布,而逆深度 1 d \frac{1}{d} d1比较符合。
- 图相间的变换:如果相机发生旋转,上黑下白变成上白下黑,相关性就会变成负数,无法正常匹配。为了解决这种问题,需要在块匹配前把参考帧与当前帧的运动考虑进来,在局部范围内构造一个参考帧和当前帧坐标变换的一个仿射变换(教材 P 326 − 327 P_{326-327} P326−327 12.3.4节),可以将当前帧(或参考帧)的像素进行变换,在进行块匹配,以期获得对旋转更好的效果。
- 并行化:由程序可以看出,针对每个像素的深度估计,在一个二重循环中遍历每个像素进行估计,但是每个像素估计之间是相互独立的,结果不会对对方产生影响,故此过程可以并行化,使用GPU来进行加速。
- 其他改进:
- 上述的深度估计可能在相邻的像素点间存在跳变的现象,深度估计不够平滑,可以给深度估计加上空间正则化项,使得深度图更加平滑。
- 没有显式地处理外点,只是用NCC阈值对匹配进行了筛选,当出现误匹配时对深度估计会有影响。
- 处理误匹配如均匀-高斯混合分布下的深度滤波器,将内点和外点进行区别并进行概率建模。
单目稠密重建在理论上仍有一些困难,如对环境纹理的依赖,像素梯度与极线方向的关联,这些问题很难通过工程手段来解决,所以双目和移动单目的稠密重建的地图过度依赖环境纹理和光照,不够可靠。
2. RGB-D稠密建图
2.1 点云地图
这个在我电脑上编译不通过,google半天也不知道为什么会出这个错误,先放这里。
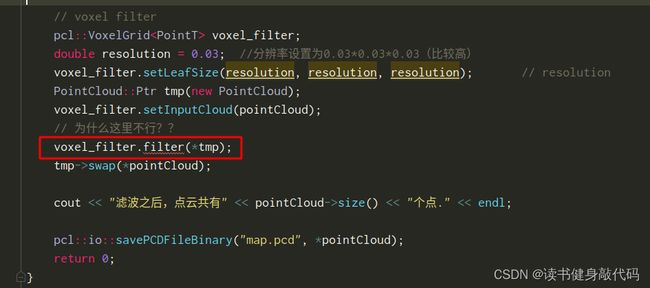
上面是在点云建图的基础上增加了一些滤波处理,包括
- 滤除深度无效的点(判断深度是否为0);
- 利用统计滤波滤除孤立点;
- 利用体素滤波进行降采样。(bug出在体素滤波这里,不知为何)
总之,点云地图作为一种初级的地图,尚无法满足定位,导航与避障,可视化和交互等功能,但是可从点云地图出发,进行进一步处理,使其满足对应的需求。
2.2 从点云重建网络
由于上面的代码没跑通,使用之前第5章的房间的点云地图来进行此部分实验。
之前的点云:

远处看还可以,但是近处看都是一系列点,没有什么实际用处,故需要进行处理。
本部分思路是先计算点云的法线,再从法线计算网格。
代码:
//
// Created by gaoxiang on 19-4-25.
//
#include 这部分代码没什么注释,看不太懂,先知道这是个什么东西,暂时略过。
重建之后如下图:
这个跟点云的对比就比较明显了,把点连成了一个个小面,原本没有表面信息的点云构建出了法线,纹理等信息了,点云地图转换成了网格地图。(这里的点云重建算法是Moving Least Square和 Greedy Projection移动最小二乘和贪心投影??)
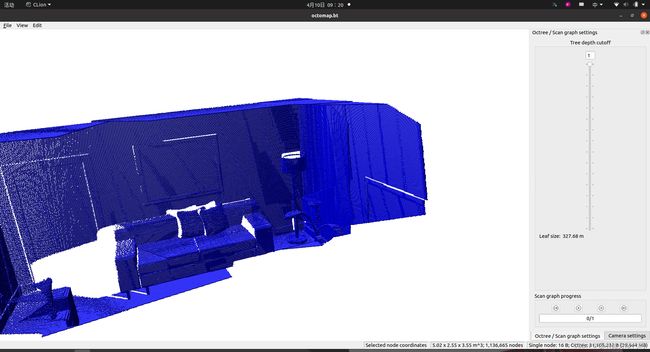
2.3 八叉树地图
需要安装octomap库和octovis可视化工具,在Ubuntu的仓库中均有。
分辨率越高,八叉树地图的文件大小越大,但地图越细致,这也符合常识。
这是0.1的分辨率的地图(有点我的世界的味道了~),这里的大小只有一个0.27M,小了快100倍(虽然可能跟分辨率确实没有什么直接关系)。
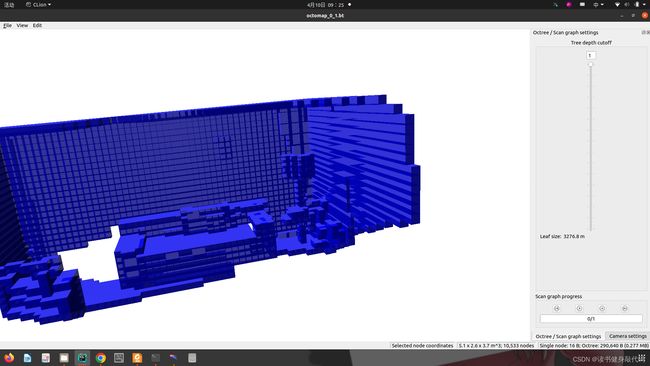
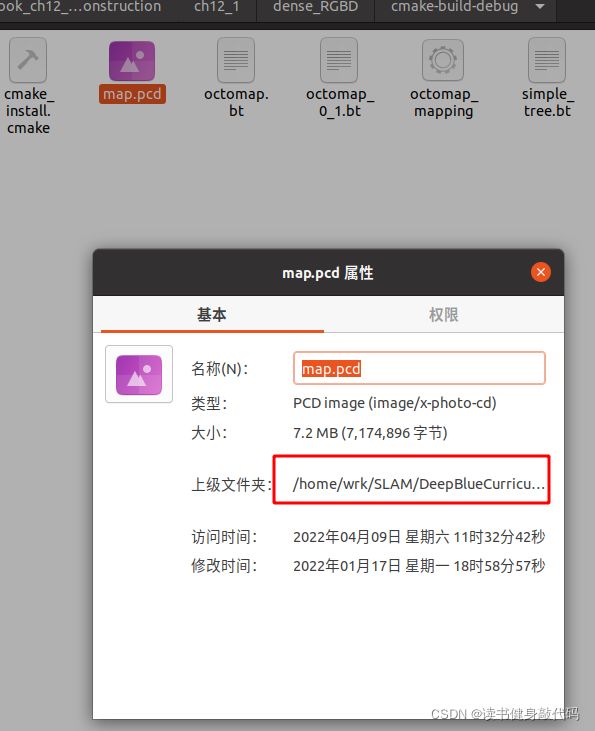
但是 确实比之前的点云地图小很多,第5章的点云地图有7.2M
3. TSDF地图和fusion系列
之前的建图中主要以定位为主,地图的拼接是作为后续加工步骤放在SLAM框架中的,是因为SLAM要求实时性,定位算法一般能够满足实时性要求(尤其是使用稀疏特征或者稀疏直接法时),而地图的表达和存储往往需要较大计算量,不适合实时处理。
当然,也存在以“建图”为主体,“定位”居于此要地位的做法,即“实时三维重建(SfM)”,都使用RGB-D图像。当地图为主要目标时,就需要使用GPU来加速计算,需要较重的计算设备,实时重建正在朝大规模、大型动态场景的重建方向发展;而SLAM超轻量级,小型化方向发展,有方案甚至放弃了建图和回环检测部分,只保留了视觉里程计。
经典的实时三维重建算法有TSDF(译为“截断符号距离函数”,有些怪怪的,还是叫TSDF吧)。与八叉树类似,TSDF是一种网格式地图,每个TSDF体素内存储了该小块与距其最近的物体表面的距离,TSDF值由负号变为正号的地方就是物体的表面。这是对于TSDF最简单的理解。
4. 小结
本章介绍了一些常见的地图形式,稀疏路标地图,稠密地图,语义地图等。对稠密地图进行了较为详细的讨论,主要包括单目稠密重建和RGB-D稠密重建,单目稠密重建需要先估计深度,介绍了高斯分布的深度滤波器,步骤是
- 假设深度服从高斯分布
- 极限搜索和块匹配(相当于特征匹配,只不过像素太多,无法计算所有的描述子)
- 三角化估计深度
- 将本次估计与之前的估计进行高斯融合
在实践环节使用200张图片迭代的方式对第一章图片的深度图进行了估计(有bug没有跑通…)。
同时在讨论部分我们讨论了单目深度估计的像素梯度问题,逆深度问题,块匹配之前的图像间的变换(解决单目的旋转问题),并行化(效率问题,各个像素见得深度估计互不影响,可以并行化),处理误匹配点的问题。且讨论了单目和双目过度依赖环境纹理和光照,不够可靠。
于是引入了RGB-D稠密重建,直接可以硬件获得较为准确的深度图,无需估计,
在RGB-D稠密重建的实践部分我们建立了点云地图,相较于第5章,我们新加入了
- 对深度的判断;
- 使用统计滤波去除孤立点;
- 使用体素滤波进行降采样以节省存储空间。
尽管进行了降采样,但是点云地图仍然较大,存储了一些不必要的细节信息(如地毯的褶皱等),于是引入了八叉树地图,可以很大程度上缩小地图所占的存储空间,其节点存储了是否被占据的信息。
到此为止的建图都是以定位为主体,建图为次要的框架,接下来介绍了以建图为主体的框架:(使用RGB-D图像的)实时三维重建。实时三维重建计算量大,需要GPU支持,网大规模发展,介绍了一种典型的实时三维重建地图形式:TSDF。
需要说明,本讲介绍的地图偏重于度量地图,而拓扑地图形式和SLAM研究差别较大,没有展开讨论(目前对拓扑地图还不是非常了解)。
本章笔记完。