YOLOV5网络结构搭建
一、基本的卷积块Conv + BN + SiLU
class Conv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True):
super(Conv, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2, eps=0.001, momentum=0.03)
self.act = SiLU() if act is True else (act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity())
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
def fuseforward(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv(x))二、残差块Bottleneck
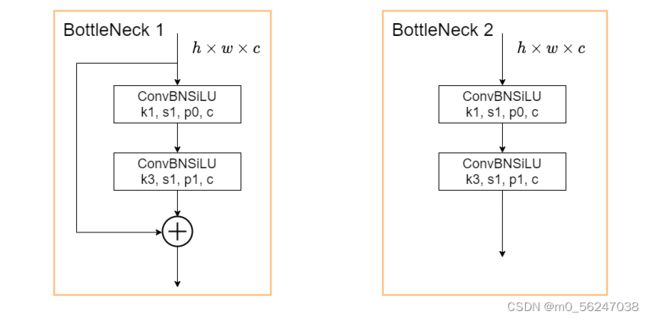
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, expansion
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1) #Bottleneck主干中第一个卷积是1*1的
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1, g=g) #第二个卷积是3*3的
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2 # shortcut为True且c1和c2相等时Bottleneck才有残差边
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))三、C3模块
class C3(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super(C3, self).__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1) #主分支中的Conv块
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1) #残差边中的Conv块
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) #Concat后的Conv块
self.m = nn.Sequential(*[Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)]) #n代表Bottleneck堆叠的次数
def forward(self, x):
# 先经过cv1,再经过Bottleneck,再与cv2的结果拼接,之后继续经过cv3
return self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), dim=1))
四、SPPF模块
class SPPF(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast (SPPF) layer for YOLOv5 by Glenn Jocher
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=5): # equivalent to SPP(k=(5, 9, 13))
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * 4, c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warning
y1 = self.m(x)
y2 = self.m(y1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)], 1))五、主干网络
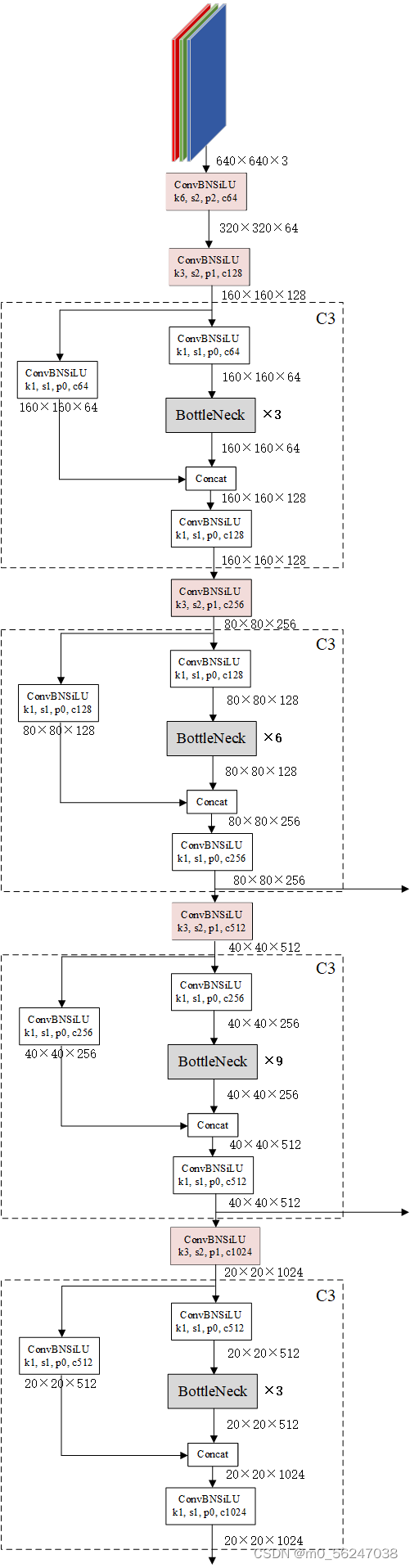
class CSPDarknet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, base_channels, base_depth, phi, pretrained):
super().__init__()
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入图片是640, 640, 3
# 初始的基本通道base_channels是64
#-----------------------------------------------#
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 完成卷积之后,320, 320, 64 -> 160, 160, 128
# 完成C3之后,160, 160, 128 -> 160, 160, 128
#-----------------------------------------------#
self.dark2 = nn.Sequential(
# 640, 640, 3 -> 320, 320, 64
Conv(3, base_channels, k=6, s=2, p=2),
# 320, 320, 64 -> 160, 160, 128
Conv(base_channels, 2 * base_channels, k=3, s=2, p=1),
# 160, 160, 128 -> 160, 160, 128
C3(base_channels * 2, base_channels * 2, base_depth),
)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 完成卷积之后,160, 160, 128 -> 80, 80, 256
# 完成C3之后,80, 80, 256 -> 80, 80, 256
# 在这里引出有效特征层80, 80, 256 进行加强特征提取网络FPN的构建
self.dark3 = nn.Sequential(
# 160, 160, 128 -> 80, 80, 256
Conv(base_channels * 2, base_channels * 4, 3, 2),
# 80, 80, 256 -> 80, 80, 256
C3(base_channels * 4, base_channels * 4, base_depth * 3),
)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 完成卷积之后,80, 80, 256 -> 40, 40, 512
# 完成C3之后,40, 40, 512 -> 40, 40, 512
# 在这里引出有效特征层40, 40, 512 进行加强特征提取网络FPN的构建
self.dark4 = nn.Sequential(
# 80, 80, 256 -> 40, 40, 512
Conv(base_channels * 4, base_channels * 8, 3, 2),
# 40, 40, 512 -> 40, 40, 512
C3(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 8, base_depth * 3),
)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 完成卷积之后,40, 40, 512 -> 20, 20, 1024
# 完成C3之后,20, 20, 1024 -> 20, 20, 1024
self.dark5 = nn.Sequential(
# 40, 40, 512 -> 20, 20, 1024
Conv(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 16, 3, 2),
# 20, 20, 1024 -> 20, 20, 1024
C3(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16, base_depth),
#SPPF(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16),
)
if pretrained:
url = {
's' : 'https://github.com/bubbliiiing/yolov5-pytorch/releases/download/v1.0/cspdarknet_s_backbone.pth',
'm' : 'https://github.com/bubbliiiing/yolov5-pytorch/releases/download/v1.0/cspdarknet_m_backbone.pth',
'l' : 'https://github.com/bubbliiiing/yolov5-pytorch/releases/download/v1.0/cspdarknet_l_backbone.pth',
'x' : 'https://github.com/bubbliiiing/yolov5-pytorch/releases/download/v1.0/cspdarknet_x_backbone.pth',
}[phi]
checkpoint = torch.hub.load_state_dict_from_url(url=url, map_location="cpu", model_dir="./model_data")
self.load_state_dict(checkpoint, strict=False)
print("Load weights from ", url.split('/')[-1])
def forward(self, x):
x = self.dark2(x)
x = self.dark3(x)
feat1 = x # 80, 80, 256
x = self.dark4(x)
feat2 = x # 40, 40, 512
x = self.dark5(x)
feat3 = x # 20, 20, 1024
return feat1, feat2, feat3
主干网络中的C3模块输入和输出的通道数是一样的,但再Neck层中前两个C3模块输出的通道数是输入通道数的一半,后两个C3模块输入和输出的通道数是一样的。C3模块的输出通道数取决于Concat后接的卷积层的通道数。
六、YOLOV5整体网络结构
![]()
class YoloBody(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, anchors_mask, num_classes, phi, backbone='cspdarknet', pretrained=False, input_shape=[640, 640]):
super(YoloBody, self).__init__()
depth_dict = {'s' : 0.33, 'm' : 0.67, 'l' : 1.00, 'x' : 1.33,}
width_dict = {'s' : 0.50, 'm' : 0.75, 'l' : 1.00, 'x' : 1.25,}
dep_mul, wid_mul = depth_dict[phi], width_dict[phi]
base_channels = int(wid_mul * 64) # 64
base_depth = max(round(dep_mul * 3), 1) # 3
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入图片是640, 640, 3
# 初始的基本通道是64
#-----------------------------------------------#
self.backbone_name = backbone
self.backbone = CSPDarknet(base_channels, base_depth, phi, pretrained)
self.upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode="nearest")
self.SPPF = SPPF(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16)
# SPPF后接的卷积层,输入为1024,输出为512,k=1,s=1,p=0
self.conv_for_feat3 = Conv(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 8, 1, 1)
# Neck中的C3模块,输入为1024,输出为512,shortcut=False即为Bottleneck2
self.conv3_for_upsample1 = C3(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 8, base_depth, shortcut=False)
# 再接一个卷积层,输入为512,输出为256,k=1,s=1,p=0
self.conv_for_feat2 = Conv(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 4, 1, 1)
# Neck中的C3模块,输入为512,输出为256,shortcut=False即为Bottleneck2
self.conv3_for_upsample2 = C3(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 4, base_depth, shortcut=False)
self.down_sample1 = Conv(base_channels * 4, base_channels * 4, 3, 2)
# Neck中的C3模块,输入为512,输出为512,shortcut=False即为Bottleneck2
self.conv3_for_downsample1 = C3(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 8, base_depth, shortcut=False)
self.down_sample2 = Conv(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 8, 3, 2)
# Neck中的C3模块,输入为1024,输出为1024,shortcut=False即为Bottleneck2
self.conv3_for_downsample2 = C3(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16, base_depth, shortcut=False)
# 80, 80, 256 => 80, 80, 3 * (5 + num_classes) => 80, 80, 3 * (4 + 1 + num_classes)
self.yolo_head_P3 = nn.Conv2d(base_channels * 4, len(anchors_mask[2]) * (5 + num_classes), 1)
# 40, 40, 512 => 40, 40, 3 * (5 + num_classes) => 40, 40, 3 * (4 + 1 + num_classes)
self.yolo_head_P4 = nn.Conv2d(base_channels * 8, len(anchors_mask[1]) * (5 + num_classes), 1)
# 20, 20, 1024 => 20, 20, 3 * (5 + num_classes) => 20, 20, 3 * (4 + 1 + num_classes)
self.yolo_head_P5 = nn.Conv2d(base_channels * 16, len(anchors_mask[0]) * (5 + num_classes), 1)
def forward(self, x):
# backbone
feat1, feat2, feat3 = self.backbone(x)
P5 = self.SPPF(feat3)
# 20, 20, 1024 -> 20, 20, 512 P5层后面会用到
P5 = self.conv_for_feat3(P5) # SPPF后接的卷积层,输入为1024,输出为512,k=1,s=1,p=0
# 20, 20, 512 -> 40, 40, 512
P5_upsample = self.upsample(P5) #上采样
# 40, 40, 512 -> 40, 40, 1024
P4 = torch.cat([P5_upsample, feat2], 1) #将P5_upsample, feat2进行拼接
# 40, 40, 1024 -> 40, 40, 512
P4 = self.conv3_for_upsample1(P4) # C3模块,输入为1024,输出为512
# 40, 40, 512 -> 40, 40, 256 P4层后面会用到
P4 = self.conv_for_feat2(P4) # 再接一个卷积层,输入为512,输出为256,k=1,s=1,p=0
# 40, 40, 256 -> 80, 80, 256
P4_upsample = self.upsample(P4) #上采样
# 80, 80, 256 cat 80, 80, 256 -> 80, 80, 512
P3 = torch.cat([P4_upsample, feat1], 1) #将P4_upsample, feat1进行拼接
# 80, 80, 512 -> 80, 80, 256 P3作为80*80预测头的输入
P3 = self.conv3_for_upsample2(P3) # C3模块,输入为512,输出为256
# 80, 80, 256 -> 40, 40, 256
P3_downsample = self.down_sample1(P3) #P3经过一个k=3,s=2的卷积层
# 40, 40, 256 cat 40, 40, 256 -> 40, 40, 512
P4 = torch.cat([P3_downsample, P4], 1) #将P3_downsample, P4进行拼接
# 40, 40, 512 -> 40, 40, 512 P4作为40*40预测头的输入
P4 = self.conv3_for_downsample1(P4) # C3模块,输入为512,输出为512
# 40, 40, 512 -> 20, 20, 512
P4_downsample = self.down_sample2(P4) #P4经过一个k=3,s=2的卷积层
# 20, 20, 512 cat 20, 20, 512 -> 20, 20, 1024
P5 = torch.cat([P4_downsample, P5], 1) #将P4_downsample, P5进行拼接
# 20, 20, 1024 -> 20, 20, 1024 P5作为20*20预测头的输入
P5 = self.conv3_for_downsample2(P5) # C3模块,输入为1024,输出为1024
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 第三个特征层 80*80
# y3=(batch_size,75,80,80)
#---------------------------------------------------#
out2 = self.yolo_head_P3(P3)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 第二个特征层 40*40
# y2=(batch_size,75,40,40)
#---------------------------------------------------#
out1 = self.yolo_head_P4(P4)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 第一个特征层 20*20
# y1=(batch_size,75,20,20)
#---------------------------------------------------#
out0 = self.yolo_head_P5(P5)
return out0, out1, out2
本文是针对yolov5_l模型推导的,base_channels=64,base_depth=3;如果按照其他模型,这两个参数会发生改变,模型各个部分的通道数以及C3中Bottleneck的堆叠次数也会发生相应改变。
reference
Pytorch 搭建自己的YoloV5目标检测平台(Bubbliiiing 源码详解 训练 预测)-Yolo Head介绍_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
YOLOv5网络详解_太阳花的小绿豆的博客-CSDN博客_yolov5网络结构详解