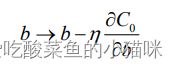pytorch实现L2正则化code(一个简单的完整模型训练代码)
L2正则化
其中,C0为原始的loss函数,C为L2正则化后的loss函数,n为样本总数;λ为一个超参数,调和loss和正则项的参数,取值在(0,1)之间,w为权重参数。
偏导数
(1)偏置b的学习规则不变,仍为
其中,η 为学习率。
(2)权重的学习规则变为:
通过因子(1-η λ/n )重新调整权重,因此L2正则化也叫权重衰减。
(3)正则化后的效果就是要神经网络倾向于学习更小的权重,其他地方都相同,可以有效减轻过拟合。
code(可直接复用)
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
torch.manual_seed(1) # 设置随机种子
n_hidden = 100 # 隐藏神经元个数
max_iter = 2000 # 最大迭代次数
disp_interval = 200 # plt展示的迭代次数间隔
lr_init = 0.01 # 学习率
# ============================ step 1/5 数据 ============================
def gen_data(num_data=10, x_range=(-1, 1)):
w = 1.5
b = 0.5
train_x = torch.linspace(x_range[0],x_range[1],num_data).unsqueeze_(1) # torch.linspace生成1*10的向量,压缩成10*1的向量
# 模型需要训练的直线:wx+b
train_y = w*train_x + b + torch.normal(0, 0.5, size=train_x.size()) # 训练集在直线wx+b基础上加入噪声
test_x = torch.linspace(x_range[0],x_range[1],num_data).unsqueeze_(1)
test_y = w*test_x + b + torch.normal(0, 0.3, size=test_x.size()) # 测试集在直线wx+b基础上加入噪声
return train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y = gen_data()
# ============================ step 2/5 模型 ============================
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, neural_num):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.linears = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(1, neural_num),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(neural_num, neural_num),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(neural_num, neural_num),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(neural_num, 1),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linears(x)
net_normal = Net(neural_num=n_hidden)
net_weight_decay = Net(neural_num=n_hidden)
# ============================ step 3/5 优化器 ============================
"""不加正则化的优化器 & 加入L2正则化参数λ(weight_decay项)的优化器"""
optim_normal = torch.optim.SGD(net_normal.parameters(), lr=lr_init, momentum=0.9)
optim_wdecay = torch.optim.SGD(net_weight_decay.parameters(), lr=lr_init, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=1e-2)
# ============================ step 4/5 损失函数 ============================
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
# ============================ step 5/5 迭代训练 ============================
for epoch in range(max_iter):
# forward
pred_normal, pred_wdecay = net_normal(train_x), net_weight_decay(train_x)
loss_normal, loss_wdecay = loss_func(pred_normal, train_y), loss_func(pred_wdecay, train_y)
# 优化器梯度清零
optim_normal.zero_grad()
optim_wdecay.zero_grad()
# 反向传播
loss_normal.backward()
loss_wdecay.backward()
optim_normal.step()
optim_wdecay.step()
if (epoch+1) % disp_interval == 0:
test_pred_normal, test_pred_wdecay = net_normal(test_x), net_weight_decay(test_x)
# 绘图
# 真实点(训练集 测试集)
plt.scatter(train_x, train_y, c='blue', s=50, alpha=0.3, label='train') # s散点面积 alpha散点透明度
plt.scatter(test_x, test_y, c='red', s=50, alpha=0.3, label='test')
# 测试集预测值 拟合的曲线,tensor->numpy格式需加入 .detach().numpy()
plt.plot(test_x, test_pred_normal.detach().numpy(), 'r-', lw=3, label='no weight decay')
plt.plot(test_x, test_pred_wdecay.detach().numpy(), 'b--', lw=3, label='weight decay')
# 训练集的loss
plt.text(-0.5, -1, 'train:no weight decay loss={:.6f}'.format(loss_normal.item()), fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'red'})
plt.text(-0.5, -1.25, 'train:weight decay loss={:.6f}'.format(loss_wdecay.item()), fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'red'})
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.title("Epoch: {}".format(epoch+1))
plt.show()
plt.close()
结果分析
当达到最大迭代次数2000时,不加权重衰减的(no weight decay的)逐渐过拟合,loss较小,完全拟合训练集数据train(蓝色点);但是对于测试集数据test(红色点)拟合效果差,模型的鲁棒性差。
加入权重衰减(weight decay)的神经网络训练效果相对较好。