C/C++使用Quirc库解析二维码(QRcode)
C/C++使用Quirc库解析二维码
- Quirc介绍
- Quirc库使用
- 遇到的坑
- 整理的知识点
- 总结
Quirc介绍
Quirc是一个基于C/C++的一个二维码库,其在码云上的官网 https://gitee.com/mirrors/quirc?_from=gitee_search对于Quirc库是这样介绍的,简单的来概括Quirc的特点就是:简单,方便移植,识别准确率高
QR codes are a type of high-density matrix barcodes, and quirc is a library for extracting and decoding them from images. It has several features which make it a good choice for this purpose:
It is fast enough to be used with realtime video: extracting and decoding from VGA frame takes about 50 ms on a modern x86 core.
It has a robust and tolerant recognition algorithm. It can correctly recognise and decode QR codes which are rotated and/or oblique to the camera. It can also distinguish and decode multiple codes within the same image.
It is easy to use, with a simple API described in a single commented header file (see below for an overview).
It is small and easily embeddable, with no dependencies other than standard C functions.
It has a very small memory footprint: one byte per image pixel, plus a few kB per decoder object.
It uses no global mutable state, and is safe to use in a multithreaded application.
BSD-licensed, with almost no restrictions regarding use and/or modification.
The distribution comes with, in addition to the library, several test programs. While the core library is very portable, these programs have some additional dependencies as documented below.
下载好的Quirc库如图所示:lib文件加里的应用Quirc库必须的文件,demo和test文件夹里是一些例子方便用户使用。

Quirc库使用
本人主要做Alios系统下的开发,但是前辈告诉我在window下调试比较方便,且比较直观,在Alios下使用GDB调试有点不方便。因此本文使用VS2019创建项目进行开发。需要导入的文件如下图所示:
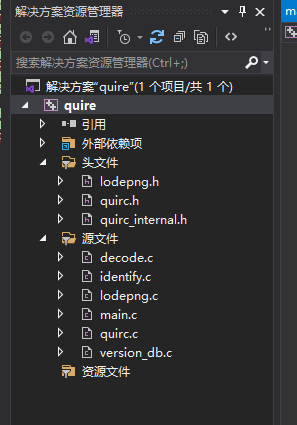
下载的Quirc源码库中,tests文件夹中有一个qrtest.c文件,这是官方给出的例子,按照这个例子进行代码编写即可。以下是自己做实验的代码
#include 到此已经可以读取二维码的内容。
遇到的坑
- VS2012环境下编译不过去
开始自己是在VS2012上做C语言开发,但是将Quirc的代码移植到VS2012上却编译不过,报语法的错误,经查证VS2012不支持C99,有一些语法不支持,自己重新装了VS2019后,这个问题得到解决。 - 文件IO遇到的一些问题
自己还在慢慢学习,之前一直在做网络部分,文件IO的处理有点生疏,犯得最离谱的错就是在处理文件的时候只用了fopen()打开文件,忘记使用fread把文件读取到缓存中,贻笑大方。
第二个是使用了feek,导致文件乱码,自己想用feek获得图片的大小,但是由于用的不熟悉导致忘记把光标复原,导致保存图片的时候,保存的不对。 - Quirc不能处理镜像
自己在window下可以读出网上下载下来的二维码,但是使用从嵌入式设备的摄像头中截取的图像却不能识别,自己做了一些实验,终于发现了问题,原来Quirc库不能识别镜像的二维码。
void rgb32_to_luma(const uint8_t* src, int src_pitch,
int w, int h,
uint8_t* dst, int dst_pitch)
{
int y;
uint8_t* gray_buf = malloc(crop_gray_size);
for (y = 0; y < h; y++) {
const uint8_t* rgb32 = src + src_pitch * y;
uint8_t* gray_index = gray_buf + y * dst_pitch;
uint8_t* mirror = dst + dst_pitch * y;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < w; i++) {
/* ITU-R colorspace assumed */
int r = (int)rgb32[2];
int g = (int)rgb32[1];
int b = (int)rgb32[0];
int sum = r * 59 + g * 150 + b * 29;
*(gray_index++) = sum >> 8;//右移8位相当于除以256,计算sum这一步是整数运算
rgb32 += 4;
mirror[w-i-1] = *(gray_index-1);//对图片进行镜像
}
}
}
自己在这个函数中首先对rgb32图像进行灰度化,然后使用指针对其图像进行了镜像,原理就是在一行中对图像的像素进行翻转。
- 在Alios下开线程的时候,程序崩溃
int QRcode_thread()
{
int ret;
aos_task_t QRcode_task_thread;
ret = aos_task_new_ext(&QRcode_task_thread, "QRcode_task", userCmdGetRGBSnapShot, NULL, 100*1024, QRcode_TASK_PRI);
if (ret != 0) {
printf("QRcode userCmdGetRGBSnapShot creation failed\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
原因是开线程分配的栈大小太小,导致程序崩溃,扩大线程栈的大小就可以了
整理的知识点
- VS2019添加lib库文件
lib和普通的源码一样,只是不能看到源码,但是库里的函数是可以直接用的,就像添加.h和.cpp文件一样,把lib文件添加到工程文件列表中去.
VS中,切换到"解决方案视图",—>选中要添加lib的工程–>点击右键–>“添加”–>“现有项”–>选择lib文件–>确定.
struct cli_command_st QRcode_cli_cmd[] = {
{ "QRcode", "QRcode test", QRcode_thread},
{ "QRstop", "QRcode test", QRcode_stop},
};
void QRcode_cli_init(void)
{
cli_register_commands(QRcode_cli_cmd,2);
}
这样就可以了,然后在主线程中调用初始化,命令行就可以使用了
-
使用git上传代码到Gitee中
写代码的时候版本控制是很重要的,下载git软件和tortoisegit软件就可以上传了,具体过程网上很多就不再说了,但是第一次上传的时候一定要用add命令,不要用commit命令,不然会少东西,有些格式的文件用commit不会自动上传。 -
图片格式的问题
图片其实就是矩阵,32rgb就是有4个通道,rgba,每个8位,一共32位。24位的就是rgb,r,g,b3个通道,每个8位,共24位。灰度图就是8位,一个字节来表示,这些知识在对图片进行处理时,如本文中的对灰度图进行镜像,是有用的。 -
代码风格的问题
网上的代码风格很多,在这里我还是准备使用在嵌入式中常用的,下划线命名法。 -
调试思路的问题
在查因为堆栈问题的时候,我调试没经验,用GDB一句句走的,但是前辈教我直接在开头添加打印,发现开头的打印就没出来,肯定是开线程的时候就出问题了,才发现是堆栈的问题,这里要好好吸收一下,调试的思想。
总结
本文介绍了Quirc库的使用方法以及自己这个月来学到的知识,这个月对指针有更加深刻的认识了,也更加熟悉文件IO,以及多线程操作,移植的Alios的机器上后Quirc正确率不错,但是太慢了要4秒一次,效率太低,通过查阅资料,Zbar的效率高,下一篇文章会介绍另一个条形码识别库Zbar的使用方法。