LSTM的手动推导与代码逐行实现
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、LSTM的手推过程
- 二、LSTM代码实现
-
- 1、PyTorch API实现
- 2、代码逐行实现LSTM
- 总结
前言
LSTM是RNN的一个优秀的变种模型,继承了大部分RNN模型的特性,同时解决了梯度反传过程由于逐步缩减而产生的梯度消失问题。在本次学习中,展示了LSTM的手动推导过程,用代码逐行模拟实现LSTM的运算过程,并与PyTorch API输出的结果验证是否一致。
一、LSTM的手推过程
- LSTM与RNN不同在于传递中多了一个memory cell,如下图所示,这是我们要手推LSTM模型的内部结构示意图。图中的遗忘门得到ft矩阵、输入门得到lt矩阵、输出门得到ot矩阵和得到gt矩阵的过程是类似的,都是先将w矩阵和v矩阵竖着拼接,乘上横着拼接的ht-1矩阵和Xt矩阵得到的;之后将ft矩阵乘上ct-1矩阵得到Scf矩阵,加上lt矩阵与gt矩阵相乘得到的Sig矩阵后,得到ct矩阵;再将ct矩阵作为tanh激活函数的输入与ot矩阵相乘得到ht矩阵,ht矩阵与参数wy矩阵相乘,得到sy矩阵;最后用softmax得到概率分布。

- 如下图所示,这是LSTM整个运算过程中需要用到的计算公式。

- 如下图所示,对参数进行初始化,将Ct-1和ht-1设为[(1@1)],Xt设为[(2&3&4)]。

- 正向运算
将初始化好的参数代入公式中,得到我们想要的输出。

- 反向运算
反向运算中的计算过程比较复杂,因此计算中要多加小心。

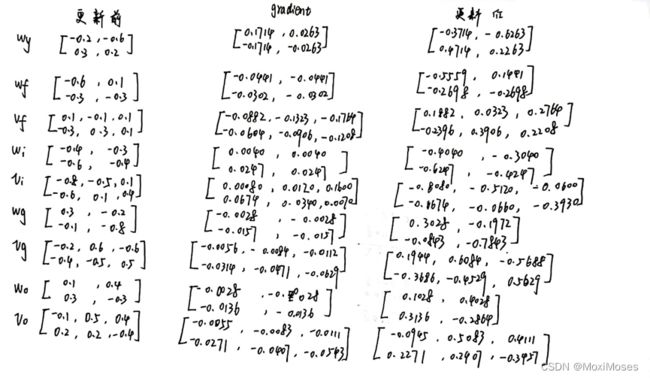
- 通过反向运算得到的gradient,更新参数。
二、LSTM代码实现
1、PyTorch API实现
首先定义一些张量,实例化对象lstm_layer,然后调用正态分布随机函数torch.randn生成input、c0和h0作为lstm_layer的输入后,得到lstm_layer的输出。
# 定义常量
bs, T, i_size, h_size = 2, 3, 4, 5
# proj_size = 3
input = torch.randn(bs, T, i_size) # 输入序列
c0 = torch.randn(bs, h_size) # 初始值,不需要训练
h0 = torch.randn(bs, h_size)
# h0 = torch.randn(bs, proj_size)
# 调用官方LSTM API
lstm_layer = nn.LSTM(i_size, h_size, batch_first=True)
# lstm_layer = nn.LSTM(i_size, h_size, batch_first=True, proj_size=proj_size)
output, (h_final, c_final) = lstm_layer(input, (h0.unsqueeze(0), c0.unsqueeze(0)))
print(output)
print(output.shape, h_final.shape, c_final.shape)
2、代码逐行实现LSTM
手写一个lstm_forward函数,手动地模拟LSTM的运算过程,并且与PyTorch LSTM API进行比较,验证输出结果。
def lstm_forward(input, initial_states, w_ih, w_hh, b_ih, b_hh):
h0, c0 = initial_states # 初始状态
bs, T, i_size = input.shape
h_size = w_ih.shape[0] // 4
prev_h = h0
prev_c = c0
batch_w_ih = w_ih.unsqueeze(0).tile(bs, 1, 1) # [bs, 4*h_size, i_size]
batch_w_hh = w_hh.unsqueeze(0).tile(bs, 1, 1) # [bs, 4*h_size, h_size]
output_size = h_size
output = torch.zeros(bs, T, output_size) # 输出序列
for t in range(T):
x = input[:, t, :] # 当前时刻的输入向量,[bs, i_size]
w_times_x = torch.bmm(batch_w_ih, x.unsqueeze(-1)) # [bs, 4*h_size, 1]
w_times_x = w_times_x.squeeze(-1) # (bs, 4*h_size)
w_times_h_prev = torch.bmm(batch_w_hh, prev_h.unsqueeze(-1)) # [bs, 4*h_size, 1]
w_times_h_prev = w_times_h_prev.squeeze(-1) # [bs, 4*h_size]
# 分别计算输入门(i)、遗忘门(f)、cell门(g)、输出门(0)
i_t = torch.sigmoid(w_times_x[:, :h_size] + w_times_h_prev[:, :h_size] + b_ih[:h_size] + b_hh[:h_size])
f_t = torch.sigmoid(w_times_x[:, h_size:2 * h_size] + w_times_h_prev[:, h_size:2 * h_size]
+ b_ih[h_size:2 * h_size] + b_hh[h_size:2 * h_size])
g_t = torch.tanh(w_times_x[:, 2 * h_size:3 * h_size] + w_times_h_prev[:, 2 * h_size:3 * h_size]
+ b_ih[2 * h_size:3 * h_size] + b_hh[2 * h_size:3 * h_size])
o_t = torch.sigmoid(w_times_x[:, 3 * h_size:4 * h_size] + w_times_h_prev[:, 3 * h_size:4 * h_size]
+ b_ih[3 * h_size:4 * h_size] + b_hh[3 * h_size:4 * h_size])
prev_c = f_t * prev_c + i_t * g_t
prev_h = o_t * torch.tanh(prev_c)
output[:, t, :] = prev_h
return output, (prev_h, prev_c)
output_custom, (h_final_custom, c_final_custom) = lstm_forward(input, (h0, c0), lstm_layer.weight_ih_l0,
lstm_layer.weight_hh_l0, lstm_layer.bias_ih_l0,
lstm_layer.bias_hh_l0)
print(output_custom)
查看输出结果以及并用torch.allclose验证手动模拟结果是否与PyTorch API一致。

总结
在本次学习中,通过对LSTM的手动推导与LSTM运算过程的代码逐行实现,了解到LSTM模型,以及加深了自己对LSTM模型的理解与推导。在上次的学习中,我学习到RNN不能处理长依赖问题,而LSTM是一种特殊的RNN,比较适用于解决长依赖问题,而且LSTM与RNN一样是链式结构,但是结构不相同,有4个input,分别指外界存储到Memory里面的值和3个gate(Input Gate、Forget Gate和Output Gate)的信号,它们都是以比较简单的方式起作用。
