GCN变体-graphSAGE
参考材料:深入浅出图神经网络,graphSAGE详解,B站GCN实战讲解
GraphSAGE从两个方面对GCN做了改动。
一方面是通过采样邻居的策略将GCN由全图(full batch)的训练方式改造成以节点为中心的小批量(mini batch)训练方式,这使得大规模图数据的分布式训练成为可能;
另一方面是该算法对聚合邻居的操作进行了拓展,提出了替换GCN操作的几种新的方式。
采样邻居
指定每个节点在第k层的邻居采样倍率为Sk,即每个节点采样的一阶邻居总数不超过Sk
采样的总结点数:
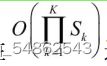
对节点采样,GraphSAGE选择了均匀分布,事实上根据工程效率或者数据的业务背景,我们可以采用其他形式的分布来替代均匀分布
聚合邻居
1、平均/加和(mean/sum)聚合算子。

2、池化(pooling)聚合算子
算法流程
基本思路是先将小批集合B内的中心节点聚合操作所要涉及的k阶子图一次性全部遍历出来,然后在这些节点上进行K次聚合操作的迭代式计算。

我的理解:
1-7行表示将所有的minbatch选择出来,这里要注意越往里层数越大,所以可以理解为从中心节点,向外扩展k层,选取k层的minibatch
8-15行表示,迭代进行特征重构,从外向内。对每一层,先经过聚合函数,然后拼接构造新的特征,在进行归一化最终得到新特征
代码实现
sampling采样,返回的是每一层的样本点的index
import numpy as np
#一阶采样
def sampling(src_nodes, sample_num, neighbor_table):
"""根据源节点采样指定数量的邻居节点,注意使用的是有放回的采样;
某个节点的邻居节点数量少于采样数量时,采样结果出现重复的节点
Arguments:
src_nodes {list, ndarray} -- 源节点列表
sample_num {int} -- 需要采样的节点数
neighbor_table {dict} -- 节点到其邻居节点的映射表
Returns:
np.ndarray -- 采样结果构成的列表
"""
results = []
for sid in src_nodes:
# 从节点的邻居中进行有放回地进行采样
res = np.random.choice(neighbor_table[sid], size=(sample_num, ))
results.append(res)
return np.asarray(results).flatten() #先将results转换为ndarry,然后.flatten返回一个一维数组
#多阶采样
def multihop_sampling(src_nodes, sample_nums, neighbor_table):
"""根据源节点进行多阶采样
Arguments:
src_nodes {list, np.ndarray} -- 源节点id
sample_nums {list of int} -- 每一阶需要采样的个数
neighbor_table {dict} -- 节点到其邻居节点的映射
Returns:
[list of ndarray] -- 每一阶采样的结果
"""
sampling_result = [src_nodes]# 存储每一层的节点,
for k, hopk_num in enumerate(sample_nums):
hopk_result = sampling(sampling_result[k], hopk_num, neighbor_table)
sampling_result.append(hopk_result)
return sampling_result
**邻居聚合方式实现,**具体实现方法在forward函数中
所有邻居加和进行一个线性变换
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.nn.init as init
#邻居聚合(对应伪代码11行)
class NeighborAggregator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim,
use_bias=False, aggr_method="mean"):
"""聚合节点邻居
Args:
input_dim: 输入特征的维度
output_dim: 输出特征的维度
use_bias: 是否使用偏置 (default: {False})
aggr_method: 邻居聚合方式 (default: {mean})
"""
super(NeighborAggregator, self).__init__()
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.output_dim = output_dim
self.use_bias = use_bias
self.aggr_method = aggr_method
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(input_dim, output_dim))
if self.use_bias:
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(self.output_dim))
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight)
if self.use_bias:
init.zeros_(self.bias)
def forward(self, neighbor_feature):
if self.aggr_method == "mean":
aggr_neighbor = neighbor_feature.mean(dim=1)#按行
elif self.aggr_method == "sum":
aggr_neighbor = neighbor_feature.sum(dim=1)
elif self.aggr_method == "max":
aggr_neighbor = neighbor_feature.max(dim=1)
else:
raise ValueError("Unknown aggr type, expected sum, max, or mean, but got {}"
.format(self.aggr_method))
neighbor_hidden = torch.matmul(aggr_neighbor, self.weight)
if self.use_bias:
neighbor_hidden += self.bias
return neighbor_hidden
def extra_repr(self):
return 'in_features={}, out_features={}, aggr_method={}'.format(
self.input_dim, self.output_dim, self.aggr_method)
更新节点特征
#更新中心节点的特征
class SageGCN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim,
activation=F.relu,
aggr_neighbor_method="mean",
aggr_hidden_method="sum"):
"""SageGCN层定义
Args:
input_dim: 输入特征的维度
hidden_dim: 隐层特征的维度,
当aggr_hidden_method=sum, 输出维度为hidden_dim
当aggr_hidden_method=concat, 输出维度为hidden_dim*2
activation: 激活函数
aggr_neighbor_method: 邻居特征聚合方法,["mean", "sum", "max"]
aggr_hidden_method: 节点特征的更新方法,["sum", "concat"]
"""
super(SageGCN, self).__init__()
assert aggr_neighbor_method in ["mean", "sum", "max"]
assert aggr_hidden_method in ["sum", "concat"]
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.aggr_neighbor_method = aggr_neighbor_method
self.aggr_hidden_method = aggr_hidden_method
self.activation = activation
self.aggregator = NeighborAggregator(input_dim, hidden_dim,
aggr_method=aggr_neighbor_method)
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(input_dim, hidden_dim))
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight)
#对应伪代码12行
def forward(self, src_node_features, neighbor_node_features):
neighbor_hidden = self.aggregator(neighbor_node_features)
self_hidden = torch.matmul(src_node_features, self.weight)
if self.aggr_hidden_method == "sum":
hidden = self_hidden + neighbor_hidden
elif self.aggr_hidden_method == "concat":
hidden = torch.cat([self_hidden, neighbor_hidden], dim=1)
else:
raise ValueError("Expected sum or concat, got {}"
.format(self.aggr_hidden))
#relu函数进行激活(也可以不写)
if self.activation:
return self.activation(hidden)
else:
return hidden
def extra_repr(self):
output_dim = self.hidden_dim if self.aggr_hidden_method == "sum" else self.hidden_dim * 2
return 'in_features={}, out_features={}, aggr_hidden_method={}'.format(
self.input_dim, output_dim, self.aggr_hidden_method)
定义模型
#定义graphSage 模型
class GraphSage(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim,
num_neighbors_list):
super(GraphSage, self).__init__()
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.num_neighbors_list = num_neighbors_list
self.num_layers = len(num_neighbors_list)
#经过多个隐藏层
self.gcn = nn.ModuleList()#它是一个储存不同 module,并自动将每个 module 的 parameters 添加到网络之中的容器
self.gcn.append(SageGCN(input_dim, hidden_dim[0]))
for index in range(0, len(hidden_dim) - 2):
self.gcn.append(SageGCN(hidden_dim[index], hidden_dim[index+1]))
#最后一层不需要激活函数
self.gcn.append(SageGCN(hidden_dim[-2], hidden_dim[-1], activation=None))
def forward(self, node_features_list):# 每一层为[16,160,1600]的list
hidden = node_features_list
#迭代次数
for l in range(self.num_layers):
next_hidden = []
gcn = self.gcn[l]
for hop in range(self.num_layers - l):#对每一层进行一个聚合操作
src_node_features = hidden[hop]#取每一层的h作为原节点特征
src_node_num = len(src_node_features)#看共有几个节点
neighbor_node_features = hidden[hop + 1].view((src_node_num, self.num_neighbors_list[hop], -1))#16*10*1433
#view相当于reshape,-1表示不确定的数,src_node_num*self.num_neighbors_list[hop]* ?的矩阵
h = gcn(src_node_features, neighbor_node_features)#16*128
next_hidden.append(h)
hidden = next_hidden
return hidden[0]#hidden[0]中存储的是源节点的特征
def extra_repr(self):
return 'in_features={}, num_neighbors_list={}'.format(
self.input_dim, self.num_neighbors_list
)
主函数
#coding: utf-8
"""
基于Cora的GraphSage示例
"""
import torch
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from net import GraphSage
from data import CoraData
from sampling import multihop_sampling
from collections import namedtuple
INPUT_DIM = 1433 # 输入维度
# Note: 采样的邻居阶数需要与GCN的层数保持一致
HIDDEN_DIM = [128, 7] # 隐藏单元节点数
NUM_NEIGHBORS_LIST = [10, 10] # 每阶采样邻居的节点数
assert len(HIDDEN_DIM) == len(NUM_NEIGHBORS_LIST)
BTACH_SIZE = 16 # 批处理大小
EPOCHS = 20
NUM_BATCH_PER_EPOCH = 20 # 每个epoch循环的批次数
LEARNING_RATE = 0.01 # 学习率
DEVICE = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print("using DEVICE:"+DEVICE)
Data = namedtuple('Data', ['x', 'y', 'adjacency_dict',
'train_mask', 'val_mask', 'test_mask'])
data = CoraData().data
x = data.x / data.x.sum(1, keepdims=True) # 归一化数据,使得每一行和为1
train_index = np.where(data.train_mask)[0]
train_label = data.y
test_index = np.where(data.test_mask)[0]
model = GraphSage(input_dim=INPUT_DIM, hidden_dim=HIDDEN_DIM,
num_neighbors_list=NUM_NEIGHBORS_LIST).to(DEVICE)
print(model)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(DEVICE)
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE, weight_decay=5e-4)
def train():
model.train()
for e in range(EPOCHS):
for batch in range(NUM_BATCH_PER_EPOCH):
batch_src_index = np.random.choice(train_index, size=(BTACH_SIZE,))#从训练集中选出批处理大小的数据集
batch_src_label = torch.from_numpy(train_label[batch_src_index]).long().to(DEVICE)
batch_sampling_result = multihop_sampling(batch_src_index, NUM_NEIGHBORS_LIST, data.adjacency_dict)
batch_sampling_x = [torch.from_numpy(x[idx]).float().to(DEVICE) for idx in batch_sampling_result]
batch_train_logits = model(batch_sampling_x)
loss = criterion(batch_train_logits, batch_src_label)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward() # 反向传播计算参数的梯度
optimizer.step() # 使用优化方法进行梯度更新
print("Epoch {:03d} Batch {:03d} Loss: {:.4f}".format(e, batch, loss.item()))
test()
def test():
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
test_sampling_result = multihop_sampling(test_index, NUM_NEIGHBORS_LIST, data.adjacency_dict)
test_x = [torch.from_numpy(x[idx]).float().to(DEVICE) for idx in test_sampling_result]
test_logits = model(test_x)
test_label = torch.from_numpy(data.y[test_index]).long().to(DEVICE)
predict_y = test_logits.max(1)[1]
accuarcy = torch.eq(predict_y, test_label).float().mean().item()
print("Test Accuracy: ", accuarcy)
if __name__ == '__main__':
train()
