多目标追踪-2019综述《Deep Learning in Video Multi-Object Tracking: A Survey》
《Deep Learning in Video Multi-Object Tracking: A Survey》 论文链接
近期开始研究多目标追踪,因此先找了一篇比较新的2019年综述性论文入门。
本论文着眼于single-camera videos and 2D data. 将MOT通用算法归纳为4个步骤,并分别介绍了Deep Learning在各步骤中的应用,给出了典型论文以供读者进一步阅读学习。
文章目录
- 1 Introduction
- 2 MOT: algorithms, metrics and datasets
-
- 2.1 Introduction to MOT algorithms
- 2.2 Metrics
- 2.3 benchmark datasets
- 3 Deep learning in MOT
-
- 3.1 DL in detection step
- 3.2 DL in feature extraction and motion prediction
- 3.3 DL in affinity computation
- 3.4 DL in Association/Tracking step
- 4 Analysis and comparisons
-
- 4.1 Setup and organization
- 4.2 Discussion of the results
-
- 4.2.1 General observations
- 4.2.2 Best approaches in the four MOT steps
- 4.2.3 Other trends in top-performing algorithms
- 5 Conclusion and future directions
1 Introduction
多目标追踪(MOT, multi-object tracking) 是指输入一段视频,在没有任何对目标的先验知识(外形或数量)的前提下,追踪其中一类或多类物体的运动轨迹。比如常见的行人追踪,车辆追踪。
与 单目标追踪(SOT) 不同,MOT不仅需要输出每一帧中每个目标的bounding box,还需要对每个box标注target ID,以此来区分 intra-class objects.
此外,SOT有对目标外形的先验知识,因为训练集会给出一段视频第一帧的bounding box,而MOT则没有。因此SOT多采用相关滤波的方法,而MOT目前多采用 tracking by detection 的方法(后文详细讲)。
MOT的困难之处在于
- various occlusions 遮挡问题,尤其在拥挤环境中
- interactions between objects 容易导致同类物体的ID标注错误
2 MOT: algorithms, metrics and datasets
2.1 Introduction to MOT algorithms
目前主流的MOT算法是 tracking by detection, 先通过常规目标检测方法提取一系列bounding box,再根据前后帧间的关系,将含有相同目标的bbox分配相同的ID。目前目标检测的质量已经比较好,因此MOT算法常被认为是一种assignment problem,即如何将匹配对应的bbox。
MOT算法可以分为batch和online两类。batch tracking algorithms可以同时利用过去/当前/将来的帧信息来对当前帧进行检测,而online tracking algorithms只能利用过去/当前的帧信息来检测当前帧。
需要特别注意,online不等于real-time,real-time一定是online的,但绝大部分online算法还太慢,不足以支持real-time environment. 尤其是应用了深度学习的算法,往往都计算密集。
主流MOT算法可以被归结为以下4个步骤:
- detection stage: 找到bounding box
- feature extraction/motion prediction stage: 对detection结果区域提取特征; 可选的,motion predictor 预测每个被追踪物体下一帧的位置
- affinity stage: 计算每一对detection之间特征的相似度
- association stage: 根据相似度匹配相同的目标,并标注相同ID
2.2 Metrics
MOT常用评价标准包括metrics defined by Wu and Nevatia, CLEAR MOT metrics, ID metrics三种.
classical metrics
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Mostly Tracked (MT) | 至少80%帧数被正确追踪的目标数量 |
| Fragments | (一段真实轨迹可能被多个追踪片段共同组成)至多覆盖真实轨迹80%帧的片段的数量 |
| Mostly Lost (ML) | 少于20%帧数被正确追踪的目标数量 |
| False trajectories | 不能对应到真实目标的预测轨迹的数量 |
| ID switches | 目标被正确追踪,但ID被错误改变的次数 |
CLEAR MOT metrics
通过IoU(和continuity constraint)来进行ground truth和predictions的对应,并计算FP/FN/Fragm/IDSW。其中Fragm是fragments总数量,IDSW是ID switches总数量。
通常使用以下两个评价标准。
M O T A = 1 − F N + F P + I D S W G T ∈ ( − ∞ , 1 ] MOTA=1-\frac{FN+FP+IDSW}{GT} \in(-\infty,1] MOTA=1−GTFN+FP+IDSW∈(−∞,1]
GT是ground truth boxes的数量
M O T P = ∑ t , i d t , i ∑ t c t MOTP=\frac{\sum_{t,i}{d_{t,i}}}{\sum_t{c_t}} MOTP=∑tct∑t,idt,i
c t c_t ct是第t帧中能正确匹配的目标数量, d t , i d_{t,i} dt,i是检测目标 i i i与其对应gt目标的IoU.
MOTA被用于检测tracking的质量,而MOTP更关注detection的质量,即bounding box的精确程度(IoU).
ID scores
ID score其实是对CLEAR MOT metrics的补充,它将检测轨迹对应于能与它匹配最大帧数的ground truth object。通过二分图算法来得出IDTP/IDFP/IDFN,并计算以下分数:

2.3 benchmark datasets
- MOT challenge :行人检测
- KITTY : 行人和车辆检测,moving camera,通过在城市里开车收集
- UA-DETRAC tracking benchmark :车辆检测,static camera,通过交通监控收集
3 Deep learning in MOT
3.1 DL in detection step
detection的精度可以极大影响整个目标追踪算法的效果,因此许多数据集都提供了公开的detection结果供大家使用,使各个算法之间的性能对比可以更公平。不过,有一些算法集成了一些独特的detection算法,借此提高tracking performance.
- faster RCNN
Simple Online and Realtime Tracking (SORT) algorithm 2016 IEEE ICIP,第一个使用CNN做行人目标检测
<-highlight
Multiple object tracking with high performance detection and appearance feature 2016 ECCV,modified faster-RCNN with skip-pooling and multi-region features,SOTA on MOT16 - SSD
Automatic individual pig detection and tracking in pig farms 2019 Sensors,DCF based online tracking method with HOG and Color Names feature to predict tag-boxes,refine bbox by DCF
Joint detection and online multi-object tracking 2018 CVPR,refine SSD detection results by other steps in tracking algorithm,use affinity scores to replace NMS in SSD<-highlight
Multi-object tracking with correlation filter for autonomous vehicle 2018 Sensors,use a CNN-based Correlation Filter(CCF) to allow SSD to generate more accurate bbox by cropped RoI - other use of CNNs in the detection step
Instance flow based online multiple object tracking 2017 IEEE ICIP,obtain instance-aware semantic segmentation map in current frame by Multi-task Network Cascade,then use optical flow to predict the position and shape in the next frame.
<- 适合 moving camera
3.2 DL in feature extraction and motion prediction
-
auto-encoders
Learning deep features for multiple object tracking by using a multi-task learning strategy 2014 IEEE ICIP,第一个提出在MOT算法中应用deep learning方法,use auto-encoders to refine visual features. 它提出feature refinement可以极大提高tracking模型的效果。
-
CNNs as visual feature extractors
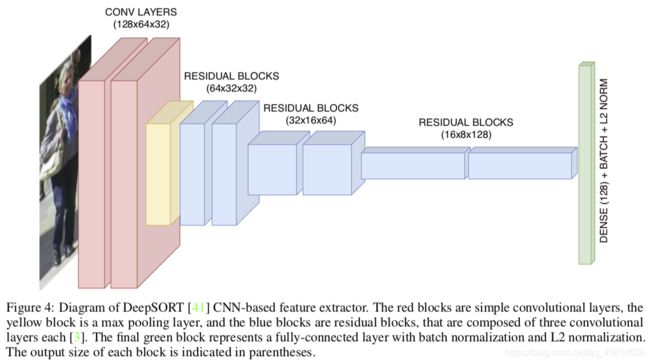
-> use pre-trained CNN to extract features.DeepSORT: Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric 2017 IEEE ICIP,extract feature vectors by custom residual CNN, add cosine distance of vectors to affinity scores. 克服了原SORT算法的主要弱点,即 ID Switch太多。
An Automatic Tracking Method for Multiple Cells Based on Multi-Feature Fusion 2018 IEEE Access,可以区分移动快/慢的目标,对不同的目标采用不同的相似度计算准则 -
Siamese networks 孪生神经网络 参考资料
孪生神经网络包含两个共享参数的相同子网,输入两张相似图片,目标是判断两张图片中是否包含相同object,为达到该目的,卷积层将会学到具有区分性的特征。

Similarity mapping with enhanced siamese network for multi-object tracking 2016 NIPS,train Siamese network with contrastive loss, take two images/ their IoU score/ their ratio as input
Tracking persons-of-interest via adaptive discriminative features 2016 ECCV,SymTriplet loss 三胞胎网络
Multi-object tracking with quadruplet convolutional neural networks 2017 CVPR,四胞胎网络,考虑detection之间的时序距离
Online multi-target tracking with tensor- based high-order graph matching 2018 ICPR,三胞胎网络 triplet based on Mask R-CNN
Eliminating exposure bias and loss-evaluation mismatch in multiple object tracking 2019 CVPR,ReID triplet CNN + bidirectional LSTM
Online multi-object tracking with dual matching attention networks 2018 ECCV,spatial attention networks(SAN) + bidirectional LSTM,通过注意力机制来排除bbox中的背景部分。这整个网络可以在ECO进行hard example mining丢失目标时,从遮挡条件下恢复检测。<- highlight -
more complex approaches for visual feature extraction
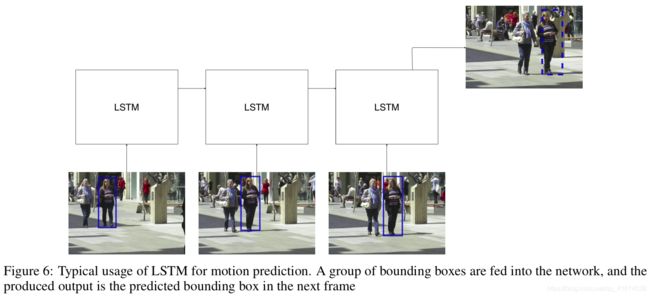
Learning to track multiple cues with long-term dependencies 2017 ICCV,使用三种RNN来计算多类特征(appearance + motion + interactions),将输出的特征再传入一个LSTM来计算affinity. 论文发表时在MOT15和MOT16达到SOTA.
<- highlight
Online multi-object tracking by decision making 2015 ICCV,前一篇论文与该论文整体算法相似,本论文用了Markov Decision Processes(MDP) based framework
A directed sparse graphical model for multi-target tracking 2018 CVPR,减少相似度计算复杂度。通过用隐马尔可夫模型预测物体接下去几帧的位置,只对检测结果中足够靠近HMM预测的detections计算相似度。 -
CNNs for motion prediction: correlation filters
Hierarchical convolutional features for visual tracking 2015 ICCV,correlation filter, whose output is a response map for the tracked object & an estimation of the new position of the object in the next frame
3.3 DL in affinity computation
许多模型计算由CNN提取出的tracklet和detection的特征间距离,作为相似性度量。以下介绍其他一些直接使用深度模型来计算相似性的方法,这些方法不需要人为预定义特征间的distance metric。主要可以分为LSTM和CNN两大类。
-
RNN and LSTMs
Online multi-target tracking using recurrent neural networks 2017 AAAI,首次提出用深度网络来计算相似度,end-to-end learning approach for online MOT. 运行速度快(165FPS),未使用appearance features
<- highlight

-
Siamese LSTMs
An online and flexible multi-object tracking framework using long short-term memory 2018 CVPR. 第一步,计算IoU作为affinity measures,捕获short reliable tracklets;第二步,将motion/appearance feature作为输入,用Siamese LSTM计算affinity。
-
Bidirectional LSTMs
Online multi-object tracking with dual matching attention networks 参考3.2节孪生神经网络
-
Use of LSTMs in MHT frameworks
Multiple Hypothesis Tracking(MHT): 为每个候选目标建立一个潜在跟踪假设的树,这样可以为数据关联问题提供一个系统的解决方法。计算每一个跟踪的概率,然后选出最有可能的跟踪组合。Multiple hypothesis tracking revisited 2015 ICCV. 回顾经典的基于tracking-by-detection框架的多假设跟踪算法,提出MHT-DAM (Multiple Hypothesis Tracking with Discriminative Appearance Modeling)
Eliminating exposure bias and loss-evaluation mismatch in multiple object tracking 2019 CVPR. 在一个MHT的变种算法中,使用LSTM来计算tracklet scores,并且循环迭代式进行剪枝和增枝,最终选出最有可能的跟踪组合。该论文核心贡献是提出并解决了两个应用RNN于MOT时常见的问题,loss-evaluation mismatch和exposure bias。该算法在多个数据集上达到最高的IDF1,但是MOTA不是最优。<-highlight -
CNNs for affinity computation
Multiple people tracking by lifted multicut and person re-identification 2017 CVPR. A novel graph-based formulation that links and clusters person hypotheses over time by solving an instance of a minimum cost lifted multi-cut problem. SOTA on MOT16.
<-highlight -
Siamese CNNs
Siamese CNNs 是一种常用的计算相似度的方法。不同于3.2节中提到用它得到两张图的feature vector,再计算特征向量的距离;这里直接使用Siamese CNN的网络输出作为相似度。
3.4 DL in Association/Tracking step
相对于上述其他步骤而言,在association步骤中深度学习的应用比较少。传统算法,如Hungarian algorithm依然被广泛使用。以下介绍3种被尝试用在association步骤中的深度学习算法。
- RNNs
Online multi-target tracking using recurrent neural networks 参考3.3节
- Deep Multi-Layer Perception
Joint detection and online multi-object tracking 参考3.1节
- Deep Reinforcement Learning agents
Multi-agent reinforcement learning for multi-object tracking 2018 ICAAMS
Collaborative deep reinforcement learning for multi-object tracking 2018 ECCV<-highlight
4 Analysis and comparisons
4.1 Setup and organization
为了公平的对比,只展示了在MOTChallenge的整个test set上进行的实验结果。
实验首先被划分为使用了public / private detections 的两类,再进一步划分为online / batch算法。MOTA作为最主要的评价指标,算法速度一栏则不太可靠,因为这些实验结果通常没有计算detections的运行时间(这一步由于使用深度学习,往往是计算量最大的步骤),此外它们测试时使用的硬件也不同。
具体实验结果对比图请参考论文。
4.2 Discussion of the results
4.2.1 General observations
- 每个数据集上表现最好的算法都采用了private detections,证明detection质量主导了整个tracker的表现。
- batch算法的表现略微超过online算法,但online算法正在逐渐接近batch算法的效果。
- online算法的一个共同问题是更高的fragmentations数量(在遇到目标被暂时遮挡/丢失检测时,它无法使用前后帧的信息进行插值,补充中间帧的目标位置)。
- MOTA成绩可以看作是FP/FN/IDSW的归一化和。在目前实际检测中,FN比FP高一个数量级,比IDSW高两个数量级,因此FN主导了MOTA成绩。目前在使用public detections的基础上有效降低FN的策略非常少,因此使用private detections来发现之前遗漏的目标(进而降低FN)成为了提高MOTA的主要方法。
有一些尝试在public detections基础上,弥补missing detections进而降低FN的论文:
Heterogeneous association graph fusion for target association in multiple object tracking 2018 IEEE TCSVT. superpixel extraction algorithm
Real-time multiple people tracking with deeply learned candidate selection and person re-identification 2018 ICME. MOTDT: use R-FCN to integrate missing detections with new detections, best MOTA and lowest FN among online algorithms on MOT17.
Online multi-object tracking with convolutional neural networks 2017 ICIP. Employ a Particle Filter algorithm and rely on detections only to initialize new targets and to recover lost ones.
Collaborative deep reinforcement learning for multi-object tracking 参考3.4节 learn motion model of objects. The 2nd best among online methods in MOT16. - 使用gt trajectories来训练affinity networks可能会产生次优的结果,因为test-time网络接受的是一个不同的数据分布,往往包含missing/wrong detections。为解决这个问题,许多算法事实上采用的是actual detections或添加人工噪音的gt trajectories进行训练。
4.2.2 Best approaches in the four MOT steps
| steps | best approach |
|---|---|
| private detection | Faster R-CNN (SSD is faster but perform worse) |
| feature extraction | CNN to extract appearance feature (appearance是最重要的特征,但许多表现最好的算法还使用了多种其他特征来共同计算相似度,尤其重要的是motion特征,常用LSTM / Kalman Filters / Bayesian filter来提取) |
| affinity | hand-crafted distance metrics on feature vectors / Siamese CNN |
| association | - |
4.2.3 Other trends in top-performing algorithms
- SOT-based MOT
- 尽管能达到很高的MOTA,但由于tracker drift导致ID switch次数太多。
- 更高质量的detector不可避免会预测出更多FP,注意不能持续追踪假轨迹。
- a SOT tracker on private detections可能是一个不错的研究方向,目前还没有相关应用
- association步骤常被作为一个graph optimization问题来解决,batch methods基于此可以做全局优化
- minimum cost lifted multicut problem
- heterogeneous association graph fusion and correlation clustering
- bounding box的精度可以极大影响tracking的效果
- 设计一个可集成在MOT算法中的effective bounding box regressor
- batch methods可以利用前后帧的appearance信息来辅助回归更精准的bbox
5 Conclusion and future directions
共性发现
- detection quality is important
- CNNs are essential in feature extraction
- SOT trackers and global graph optimization work
未来可行的研究方向
- researching more strategies to mitigate detection errors
- applying DL to track different targets, like vehicles, animals, etc.
- investigating the robustness of current algorithms
- applying DL to guide association
- combining SOT trackers with private detections
- investigating bounding box regression
- investigating post-tracking processing