【PyTorch】6.1 正则化之weight_decay
目录
- 一、正则化与偏差-方差分解
-
- 1. 偏差和方差
- 2. L1正则和L2正则
- 二、PyTorch中的 L2 正则项 weight decay
-
- 1. L2 Regularization = weight decay(权值衰减)
任务简介:
了解正则化中L1和L2(weight decay);了解dropout
详细说明:
本节第一部分学习正则化的概念,正则化方法是机器学习(深度学习)中重要的方法,它目的在于减小方差。常用的正则化方法有L1和L2正则化,其中L2正则化又称为weight decay。在pytorch的优化器中就提供了weight decay的实现,本节课将学习weight decay的pytorch实现。
本节第二部分学习深度学习中常见的正则化方法——Dropout,Dropout是简洁高效的正则化方法,但需要注意其在实现过程中的权值数据尺度问题。本节将详细学习pytorch中Dropout的实现细节。
一、正则化与偏差-方差分解
正则化:提高模型的泛化能力,降低过拟合的可能 [ 1 ] ^{[1]} [1]。
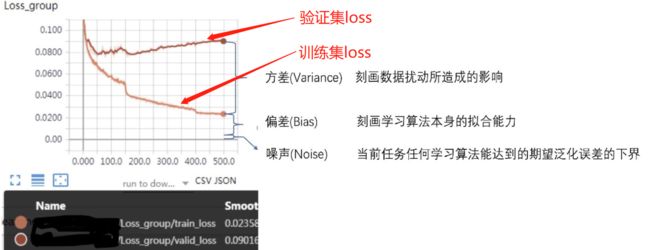
1. 偏差和方差
很好的拟合了所有的训练数据,但在验证集的表现很差,严重过拟合。
2. L1正则和L2正则
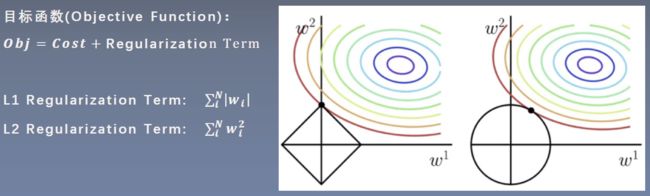
从L1正则的示例图中可以看出:当 w 1 = 0 w^1=0 w1=0 时,目标函数的值最小,此时 w 1 w^1 w1 这个权重在模型中不起作用,可以删除,达到了权值稀疏的效果。
二、PyTorch中的 L2 正则项 weight decay
1. L2 Regularization = weight decay(权值衰减)
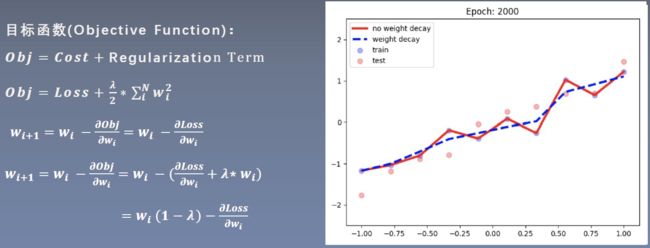
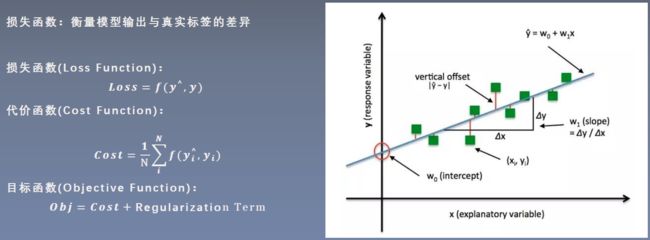
权值衰减 是一直以来经常被使用的一种抑制过拟合的方法。该方法通过在学习的过程中对大的权重进行惩罚,来抑制过拟合。很多过拟合原本就是因为权重参数取值过大才发生的。为损失函数加上权重的平方范数(L2 范数)。这样一来,就可以抑制权重变大。 λ \lambda λ 是控制正则化强度的超参数。 λ \lambda λ 设置得越大,对大的权重施加的惩罚就越重 [ 2 ] ^{[2]} [2]。
测试代码:
hello_pytorch_DIR = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)+os.path.sep+".."+os.path.sep+"..")
sys.path.append(hello_pytorch_DIR)
from tools.common_tools import set_seed
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
set_seed(1) # 设置随机种子
n_hidden = 200
max_iter = 2000
disp_interval = 200
lr_init = 0.01
# ============================ step 1/5 数据 ============================
def gen_data(num_data=10, x_range=(-1, 1)):
w = 1.5
train_x = torch.linspace(*x_range, num_data).unsqueeze_(1)
train_y = w*train_x + torch.normal(0, 0.5, size=train_x.size())
test_x = torch.linspace(*x_range, num_data).unsqueeze_(1)
test_y = w*test_x + torch.normal(0, 0.3, size=test_x.size())
return train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y = gen_data(x_range=(-1, 1))
# ============================ step 2/5 模型 ============================
class MLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, neural_num):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
self.linears = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(1, neural_num),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(neural_num, neural_num),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(neural_num, neural_num),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(neural_num, 1),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linears(x)
net_normal = MLP(neural_num=n_hidden)
net_weight_decay = MLP(neural_num=n_hidden)
# ============================ step 3/5 优化器 ============================
optim_normal = torch.optim.SGD(net_normal.parameters(), lr=lr_init, momentum=0.9)
optim_wdecay = torch.optim.SGD(net_weight_decay.parameters(), lr=lr_init, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=1e-2)
# ============================ step 4/5 损失函数 ============================
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
# ============================ step 5/5 迭代训练 ============================
writer = SummaryWriter(comment='_test_tensorboard', filename_suffix="12345678")
for epoch in range(max_iter):
# forward
pred_normal, pred_wdecay = net_normal(train_x), net_weight_decay(train_x)
loss_normal, loss_wdecay = loss_func(pred_normal, train_y), loss_func(pred_wdecay, train_y)
optim_normal.zero_grad()
optim_wdecay.zero_grad()
loss_normal.backward()
loss_wdecay.backward()
optim_normal.step()
optim_wdecay.step()
if (epoch+1) % disp_interval == 0:
# 可视化
for name, layer in net_normal.named_parameters():
writer.add_histogram(name + '_grad_normal', layer.grad, epoch)
writer.add_histogram(name + '_data_normal', layer, epoch)
for name, layer in net_weight_decay.named_parameters():
writer.add_histogram(name + '_grad_weight_decay', layer.grad, epoch)
writer.add_histogram(name + '_data_weight_decay', layer, epoch)
test_pred_normal, test_pred_wdecay = net_normal(test_x), net_weight_decay(test_x)
# 绘图
plt.scatter(train_x.data.numpy(), train_y.data.numpy(), c='blue', s=50, alpha=0.3, label='train')
plt.scatter(test_x.data.numpy(), test_y.data.numpy(), c='red', s=50, alpha=0.3, label='test')
plt.plot(test_x.data.numpy(), test_pred_normal.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=3, label='no weight decay')
plt.plot(test_x.data.numpy(), test_pred_wdecay.data.numpy(), 'b--', lw=3, label='weight decay')
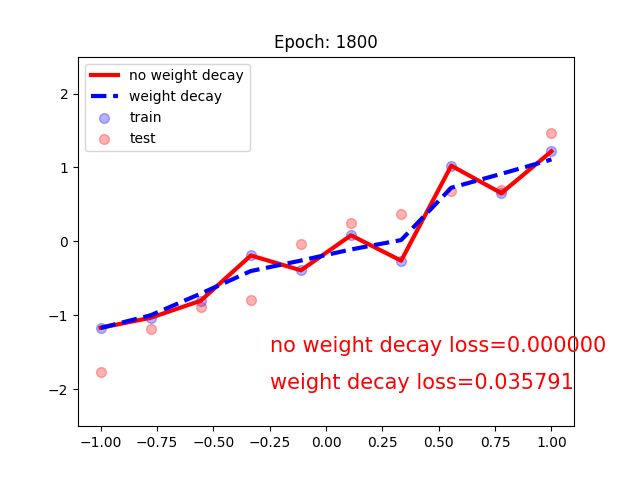
plt.text(-0.25, -1.5, 'no weight decay loss={:.6f}'.format(loss_normal.item()), fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'red'})
plt.text(-0.25, -2, 'weight decay loss={:.6f}'.format(loss_wdecay.item()), fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'red'})
plt.ylim((-2.5, 2.5))
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.title("Epoch: {}".format(epoch+1))
plt.show()
plt.close()
输出:
可以看出没有weight decay的曲线出现了过拟合的现象
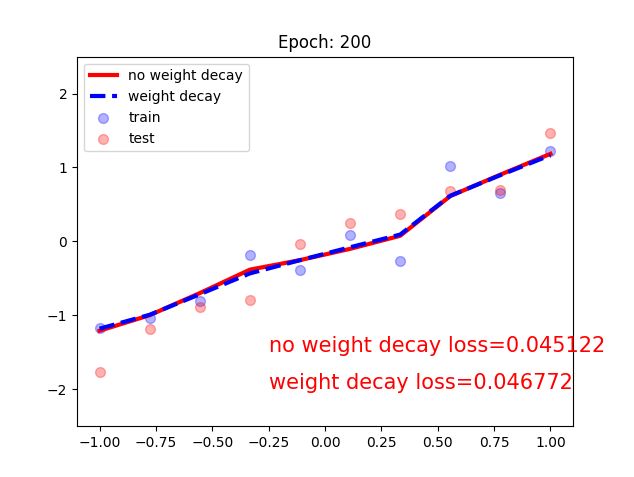
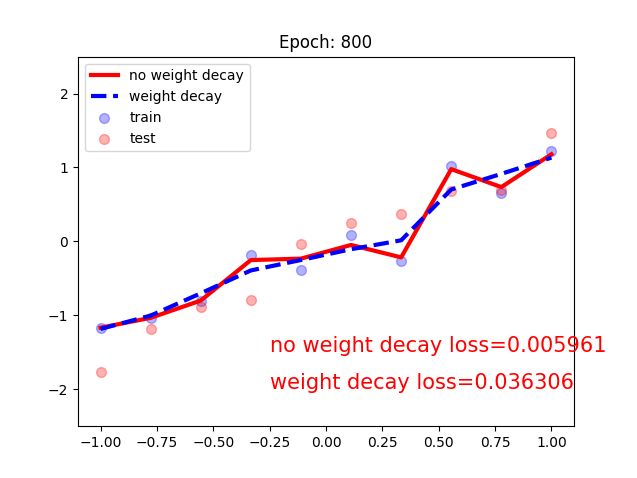
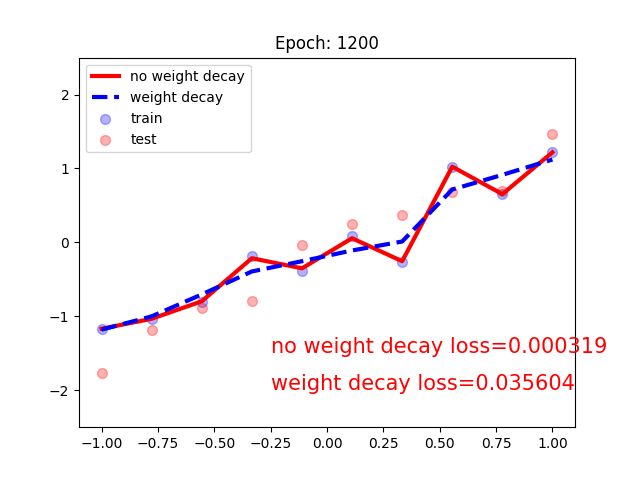
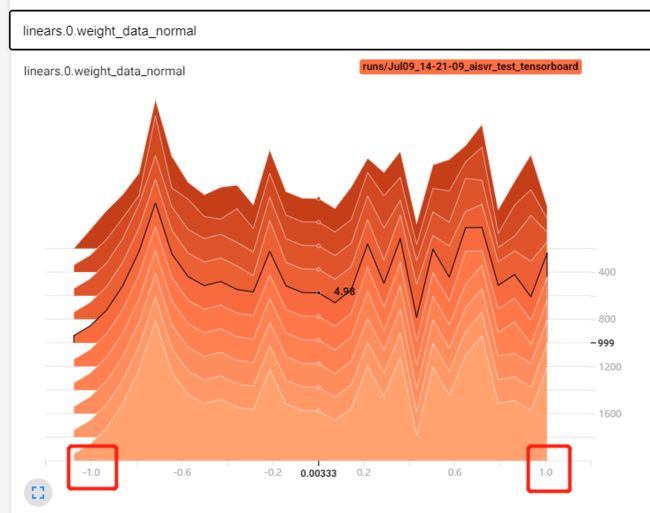
进入tensorboard:
没有L2正则化时,整个权值尺度变化不大
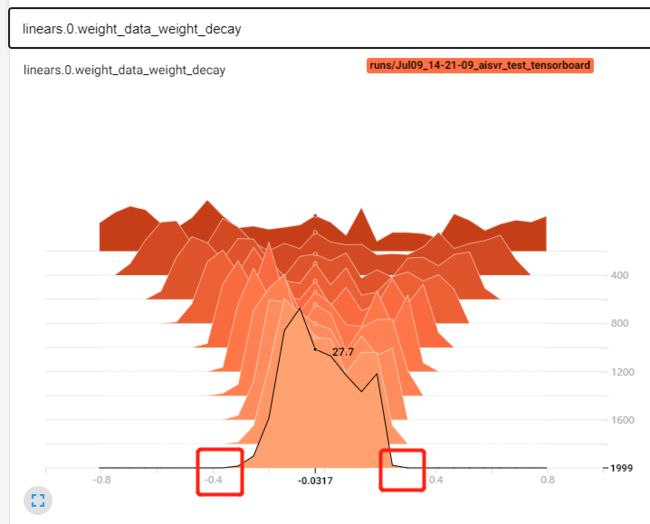
L2正则化后,整个权值的尺度不断减小
在代码optim_wdecay.step()设置断点,step into:
def step(self, closure=None):
"""Performs a single optimization step.
Arguments:
closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
and returns the loss.
"""
loss = None
if closure is not None:
loss = closure()
for group in self.param_groups:
weight_decay = group['weight_decay']
momentum = group['momentum']
dampening = group['dampening']
nesterov = group['nesterov']
for p in group['params']:
if p.grad is None:
continue
d_p = p.grad.data
if weight_decay != 0:
d_p.add_(weight_decay, p.data)
if momentum != 0:
param_state = self.state[p]
if 'momentum_buffer' not in param_state:
buf = param_state['momentum_buffer'] = torch.clone(d_p).detach()
else:
buf = param_state['momentum_buffer']
buf.mul_(momentum).add_(1 - dampening, d_p)
if nesterov:
d_p = d_p.add(momentum, buf)
else:
d_p = buf
p.data.add_(-group['lr'], d_p)
return loss
在代码的d_p.add_(weight_decay, p.data)进行权值衰减,其公式:d_p = d_p + p.data * weight_decay
在代码p.data.add_(-group['lr'], d_p)进行梯度更新
参考资料:
[1] 百面机器学习 葫芦娃 著 164页 L1正则化与稀疏性
[2] 深度学习入门:基于Python的理论与实现 斋藤康毅 著 191页 6.4正则化