Attention学习笔记
解读Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks(SENet)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/32702350
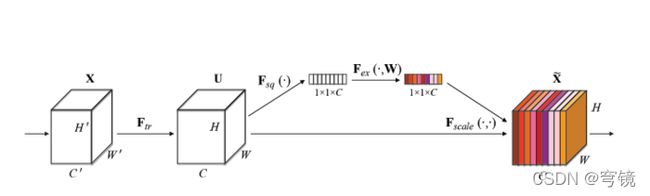
作者要利用的是通道间的相关性,而不是空间分布中的相关性,用GAP屏蔽掉空间上的分布信息能让scale的计算更加准确。
Excitation部分是用2个全连接来实现 ,第一个全连接把C个通道压缩成了C/r个通道来降低计算量(后面跟了RELU),第二个全连接再恢复回C个通道(后面跟了Sigmoid),r是指压缩的比例。作者尝试了r在各种取值下的性能 ,最后得出结论r=16时整体性能和计算量最平衡。
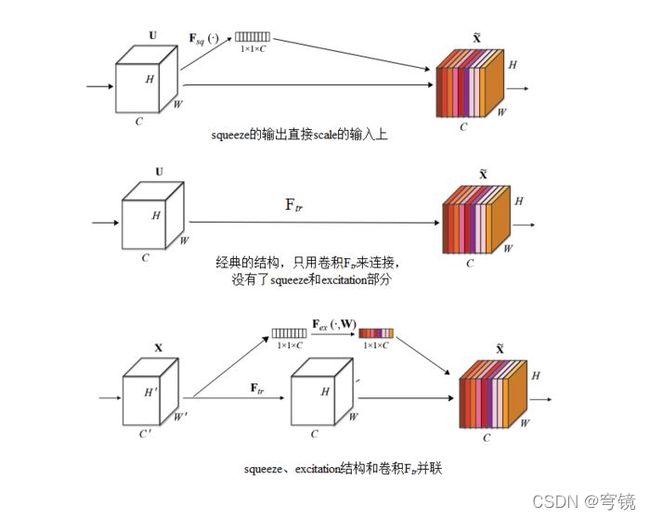
为什么要加全连接层呢?这是为了利用通道间的相关性来训练出真正的scale。一次mini-batch个样本的squeeze输出并不代表通道真实要调整的scale值,真实的scale要基于全部数据集来训练得出,而不是基于单个batch,所以后面要加个全连接层来进行训练。可以拿SE Block和下面3种错误的结构比较来进一步理解:
图2最上方的结构,squeeze的输出直接scale到输入上,没有了全连接层,某个通道的调整值完全基于单个通道GAP的结果,事实上只有GAP的分支是完全没有反向计算、没有训练的过程的,就无法基于全部数据集来训练得出通道增强、减弱的规律。
图2中间是经典的卷积结构,有人会说卷积训练出的权值就含有了scale的成分在里面,也利用了通道间的相关性,为啥还要多个SE Block?那是因为这种卷积有空间的成分在里面,为了排除空间上的干扰就得先用GAP压缩成一个点后再作卷积,压缩后因为没有了Height、Width的成分,这种卷积就是全连接了。
图2最下面的结构,SE模块和传统的卷积间采用并联而不是串联的方式,这时SE利用的是Ftr输入X的相关性来计算scale,X和U的相关性是不同的,把根据X的相关性计算出的scale应用到U上明显不合适。
理解 Deformable Convolutional Networks
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/52476083
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21997625/article/details/84899914
代码来源:
https://github.com/oeway/pytorch-deform-conv/blob/master/tests/test_deform_conv.py
插值计算处代码
def th_batch_map_offsets(input, offsets, grid=None, order=1):
"""Batch map offsets into input
Parameters
---------
input : torch.Tensor. shape = (b, s, s)
offsets: torch.Tensor. shape = (b, s, s, 2)
grid: (b*c, h*w, 2)
Returns
-------
torch.Tensor. shape = (b, s, s)
"""
batch_size = input.size(0)
input_size = [input.size(1), input.size(2)]
# (b, h*w, 2)
offsets = offsets.view(batch_size, -1, 2)
if grid is None:
# grid:(b*c, h*w, 2)
grid = th_generate_grid(batch_size, input_size, offsets.data.type(), offsets.data.is_cuda)
# (b*c, h*w, 2)
coords = offsets + grid
# (b*c, h*w)| (b*c, h*w), (b*c, h*w, c)
mapped_vals = th_batch_map_coordinates(input, coords)
return mapped_vals
def th_batch_map_coordinates(input, coords, order=1):
"""Batch version of th_map_coordinates
Only supports 2D feature maps
Parameters
----------
input : tf.Tensor. shape = (b, s, s)
coords : tf.Tensor. shape = (b, n_points, 2)
Returns
-------
tf.Tensor. shape = (b, s, s)
"""
batch_size = input.size(0)
input_size = input.size(1)
n_coords = coords.size(1)
coords = torch.clamp(coords, 0, input_size - 1)
coords_lt = coords.floor().long()
coords_rb = coords.ceil().long()
coords_lb = torch.stack([coords_lt[..., 0], coords_rb[..., 1]], 2)
coords_rt = torch.stack([coords_rb[..., 0], coords_lt[..., 1]], 2)
idx = th_repeat(torch.arange(0, batch_size), n_coords).long() ## 为batch里的每一个数据 构建n_coords个索引
idx = Variable(idx, requires_grad=False)
if input.is_cuda:
idx = idx.cuda(cfg.cuda_num)
def _get_vals_by_coords(input, coords):
indices = torch.stack([
idx, th_flatten(coords[..., 0]), th_flatten(coords[..., 1])
], 1)
inds = indices[:, 0] * input.size(1) * input.size(2) + indices[:, 1] * input.size(2) + indices[:, 2] ## 这个地方是把展平之后的tensor做定位,找到某一个位置的索引
vals = th_flatten(input).index_select(0, inds)
vals = vals.view(batch_size, n_coords)
return vals
vals_lt = _get_vals_by_coords(input, coords_lt.detach())
vals_rb = _get_vals_by_coords(input, coords_rb.detach())
vals_lb = _get_vals_by_coords(input, coords_lb.detach())
vals_rt = _get_vals_by_coords(input, coords_rt.detach())
coords_offset_lt = coords - coords_lt.type(coords.data.type())### 注意 这个地方都是小数
vals_t = coords_offset_lt[..., 0] * (vals_rt - vals_lt) + vals_lt## x轴插值
vals_b = coords_offset_lt[..., 0] * (vals_rb - vals_lb) + vals_lb## x轴插值
mapped_vals = coords_offset_lt[..., 1] * (vals_b - vals_t) + vals_t## 两个插值点再插值
return mapped_vals
1.Selective Kernel Networks
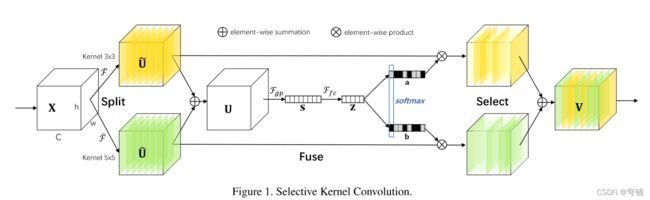
https://github.com/TeodorPoncu/selective-kernel-conv/blob/main/selective_conv.py
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
class SelectiveConv(nn.Module):
"""
Implementation of the Selective Convolution Layer used in Selective Kernel Networks
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1903.06586.pdf
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels: int, out_channels: int, groups: int, ratio: int = 16, paths: int = 2):
super(SelectiveConv, self).__init__()
self.reduced_dim = max(out_channels // ratio, 32)
self.paths = paths
self.convs = []
for i in range(paths):
self.convs.append(nn.Sequential(*[
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, groups=groups, kernel_size=3, dilation=1 + i, padding=1 + i),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU()
]))
self.convs = nn.ModuleList(self.convs)
self.flatten = nn.Sequential(*[
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(1, 1)),
Flatten(),
])
self.compress = nn.Sequential(*[
nn.Linear(out_channels, self.reduced_dim),
nn.BatchNorm1d(self.reduced_dim),
nn.ReLU(),
])
# using a 1x1 conv for Z reprojection
self.projections = nn.ModuleList([nn.Conv2d(self.reduced_dim, out_channels, 1) for _ in range(paths)])
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):
b, _, h, w = x.shape
# pass through all convolutions
features = torch.cat([conv(x) for conv in self.convs], dim=1)
# sum features across path dimension
features = features.view(features.shape[0], self.paths, -1, h, w)
fused_x = features.sum(dim=1)
#print(fused_x.shape)
_, c, _, _ = fused_x.shape
# flatten and compress fused features
fused_flat = self.flatten(fused_x)
fused_compress = self.compress(fused_flat)
# reproject the compression in order to compute channel-wise attention scores
attention_scores = torch.cat([projection(fused_compress[:, :, None, None]) for projection in self.projections], dim=1)
# compute path-wise softmax for each channel
attention_scores = attention_scores.view(b, self.paths, c, 1, 1)
attention_scores = F.softmax(attention_scores, dim=1)
# scale features with attention and fuse them back
features = features * attention_scores
features = features.sum(dim=1)
return features
class Flatten(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Flatten, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):
return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
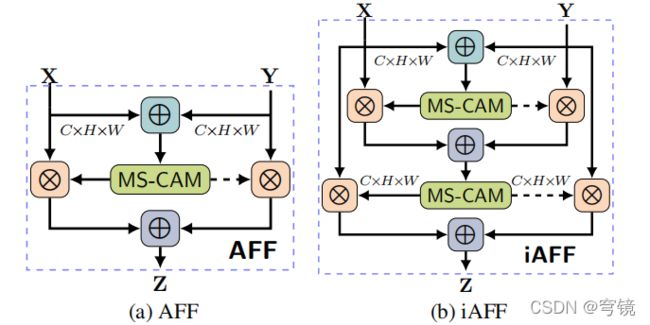
2.Iterative Attentional Feature Fusion
https://github.com/YimianDai/open-aff/tree/master/aff_pytorch

import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class DAF(nn.Module):
'''
直接相加 DirectAddFuse
'''
def __init__(self):
super(DAF, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x, residual):
return x + residual
class iAFF(nn.Module):
'''
多特征融合 iAFF
'''
def __init__(self, channels=64, r=4):
super(iAFF, self).__init__()
inter_channels = int(channels // r)
# 本地注意力
self.local_att = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(channels, inter_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inter_channels, channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channels),
)
# 全局注意力
self.global_att = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(channels, inter_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inter_channels, channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channels),
)
# 第二次本地注意力
self.local_att2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(channels, inter_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inter_channels, channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channels),
)
# 第二次全局注意力
self.global_att2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(channels, inter_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inter_channels, channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channels),
)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x, residual):
xa = x + residual
xl = self.local_att(xa)
xg = self.global_att(xa)
xlg = xl + xg
wei = self.sigmoid(xlg)
xi = x * wei + residual * (1 - wei)
xl2 = self.local_att2(xi)
xg2 = self.global_att(xi)
xlg2 = xl2 + xg2
wei2 = self.sigmoid(xlg2)
xo = x * wei2 + residual * (1 - wei2)
return xo
class AFF(nn.Module):
'''
多特征融合 AFF
'''
def __init__(self, channels=64, r=4):
super(AFF, self).__init__()
inter_channels = int(channels // r)
self.local_att = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(channels, inter_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inter_channels, channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channels),
)
self.global_att = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(channels, inter_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inter_channels, channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channels),
)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x, residual):
xa = x + residual
xl = self.local_att(xa)
xg = self.global_att(xa)
xlg = xl + xg
wei = self.sigmoid(xlg)
xo = 2 * x * wei + 2 * residual * (1 - wei)
return xo
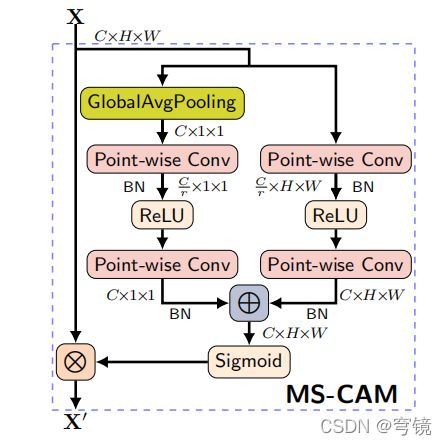
class MS_CAM(nn.Module):
'''
单特征 进行通道加权,作用类似SE模块
'''
def __init__(self, channels=64, r=4):
super(MS_CAM, self).__init__()
inter_channels = int(channels // r)
self.local_att = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(channels, inter_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inter_channels, channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channels),
)
self.global_att = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(channels, inter_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inter_channels, channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channels),
)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
xl = self.local_att(x)
xg = self.global_att(x)
xlg = xl + xg
wei = self.sigmoid(xlg)
return x * wei
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# import os
# os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = "0"
# device = torch.device("cuda:0")
#
# x, residual= torch.ones(8,64, 32, 32).to(device),torch.ones(8,64, 32, 32).to(device)
# channels=x.shape[1]
#
# model=AFF(channels=channels)
# model=model.to(device).train()
# output = model(x, residual)
# print(output.shape)
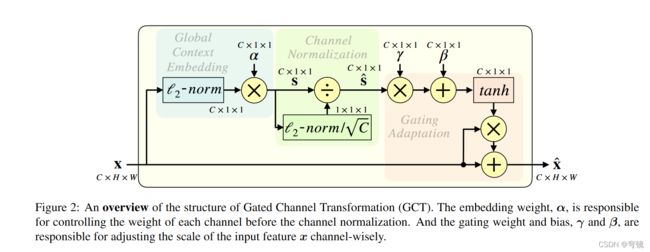
Gated Channel Transformation for Visual Recognition
https://github.com/z-x-yang/GCT/blob/68983edd87/PyTorch/GCT.py
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import math
from torch import nn
class GCT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_channels, epsilon=1e-5, mode='l2', after_relu=False):
super(GCT, self).__init__()
self.alpha = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(1, num_channels, 1, 1))
self.gamma = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_channels, 1, 1))
self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_channels, 1, 1))
self.epsilon = epsilon
self.mode = mode
self.after_relu = after_relu
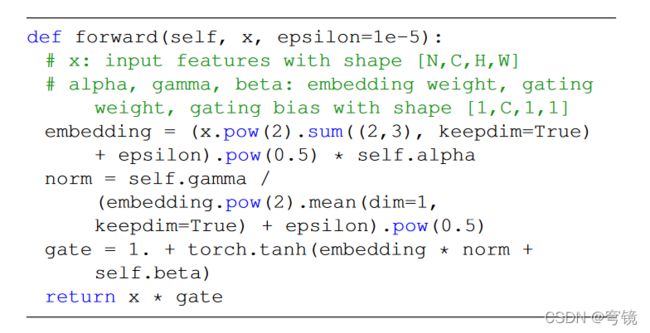
def forward(self, x):
if self.mode == 'l2':
embedding = (x.pow(2).sum((2,3), keepdim=True) + self.epsilon).pow(0.5) * self.alpha
norm = self.gamma / (embedding.pow(2).mean(dim=1, keepdim=True) + self.epsilon).pow(0.5)
elif self.mode == 'l1':
if not self.after_relu:
_x = torch.abs(x)
else:
_x = x
embedding = _x.sum((2,3), keepdim=True) * self.alpha
norm = self.gamma / (torch.abs(embedding).mean(dim=1, keepdim=True) + self.epsilon)
else:
print('Unknown mode!')
sys.exit()
gate = 1. + torch.tanh(embedding * norm + self.beta)
return x * gate