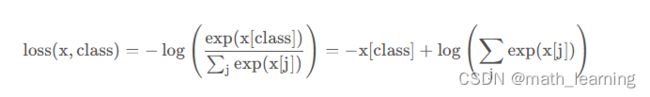对比学习(Contrastive Learning)的理解
参考网址:https://blog.csdn.net/yyhaohaoxuexi/article/details/113824125
一、Info Noise-contrastive estimation(Info NCE)
1.1 描述
InfoNCE在MoCo中被描述为:
1.2 实现
MoCo源码的\moco\builder.py中,实现如下:
# compute logits
# Einstein sum is more intuitive
# positive logits: Nx1
l_pos = torch.einsum('nc,nc->n', [q, k]).unsqueeze(-1)
# negative logits: NxK
l_neg = torch.einsum('nc,ck->nk', [q, self.queue.clone().detach()])
# logits: Nx(1+K)
logits = torch.cat([l_pos, l_neg], dim=1)
# apply temperature
logits /= self.T
# labels: positive key indicators
labels = torch.zeros(logits.shape[0], dtype=torch.long).cuda()
...
return logits, labels
这里的变量logits的意义我也查了一下:是未进入softmax的概率
这段代码根据注释即可理解:l_pos表示正样本的得分,l_neg表示所有负样本的得分,logits表示将正样本和负样本在列上cat起来之后的值。值得关注的是,labels的数值,是根据logits.shape[0]的大小生成的一组zero。也就是大小为batch_size的一组0。
接下来看损失函数部分,\main_moco.py:
# define loss function (criterion) and optimizer
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda(args.gpu)
...
# compute output
output, target = model(im_q=images[0], im_k=images[1])
loss = criterion(output, target)
这里直接对输出的
logits和生成的labels计算交叉熵,然后就是模型的loss。这里就是让我不是很理解的地方。先将疑惑埋在心里~
二、HCL
2.1 描述
在文章《Contrastive Learning with Hard Negative Samples》中描述到,使用负样本的损失函数为:
其实本质上适合InfoNCE一个道理,都是mean(-log(正样本的得分/所有样本的得分))。
2.2 实现
但是在这篇文章的实现中,\image\main.py:
def criterion(out_1,out_2,tau_plus,batch_size,beta, estimator):
# neg score
out = torch.cat([out_1, out_2], dim=0)
neg = torch.exp(torch.mm(out, out.t().contiguous()) / temperature)
old_neg = neg.clone()
mask = get_negative_mask(batch_size).to(device)
neg = neg.masked_select(mask).view(2 * batch_size, -1)
# pos score
pos = torch.exp(torch.sum(out_1 * out_2, dim=-1) / temperature)
pos = torch.cat([pos, pos], dim=0)
# negative samples similarity scoring
if estimator=='hard':
N = batch_size * 2 - 2
imp = (beta* neg.log()).exp()
reweight_neg = (imp*neg).sum(dim = -1) / imp.mean(dim = -1)
Ng = (-tau_plus * N * pos + reweight_neg) / (1 - tau_plus)
# constrain (optional)
Ng = torch.clamp(Ng, min = N * np.e**(-1 / temperature))
elif estimator=='easy':
Ng = neg.sum(dim=-1)
else:
raise Exception('Invalid estimator selected. Please use any of [hard, easy]')
# contrastive loss
loss = (- torch.log(pos / (pos + Ng) )).mean()
return loss
可以看到最后计算loss的公式是:
loss = (- torch.log(pos / (pos + Ng) )).mean()
的确与我上文中的理解相同,可是为什么这样的实现,没有用到全0的label呢?
三、文字解释
既然是同一种方法的两种实现,已经理解了第二种实现(HCL)。那么,问题就出在了:不理解第一种实现的label为何要这样生成? 于是乎,查看交叉熵的计算方式:
交叉熵的label的作用是:将label作为索引,来取得 x x x中的项( x [ c l a s s ] x[class] x[class]),因此,这些项就是label。而倘若label是全0的项,那么其含义为: x x x中的第一列为label(正样本),其他列就是负样本。然后带入公式(3)中计算,即可得到交叉熵下的loss值。
而对于HCL的实现方式,是直接将InfoNCE拆解开来,使用正样本的得分和负样本的得分来计算。
四、代码解释
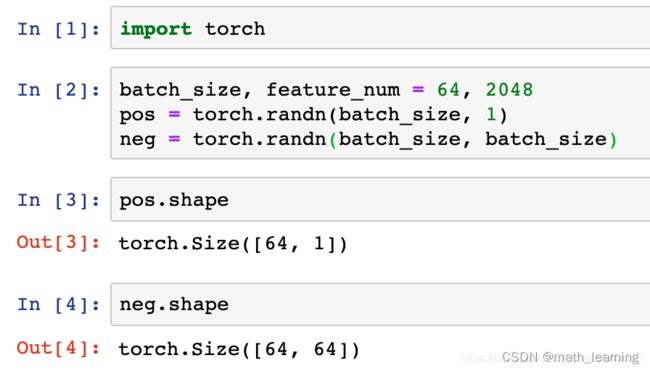
首先,生成pos得分和neg的得分:
注意,这里省略了生成的特征,直接生成了得分,
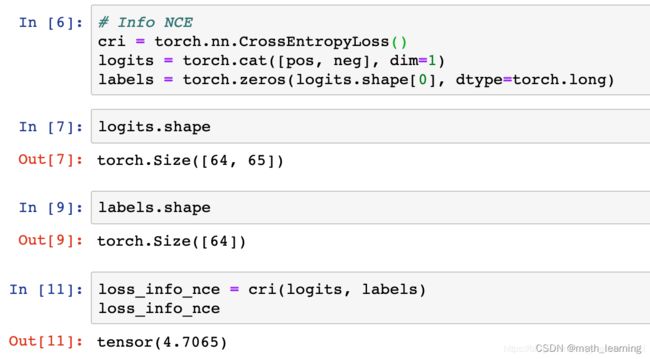
4.1 Info NCE
4.2 HCL
嗒哒~两者的结果“一模一样”(取值范围导致最后一位不太一样)