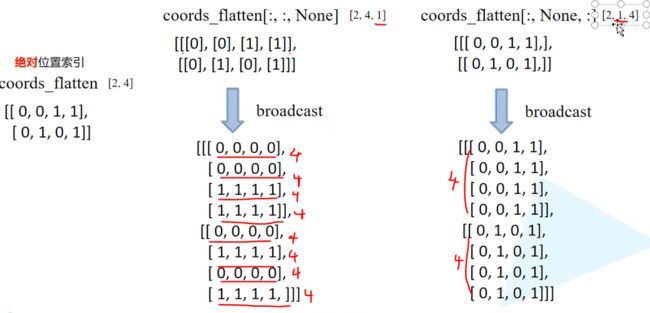
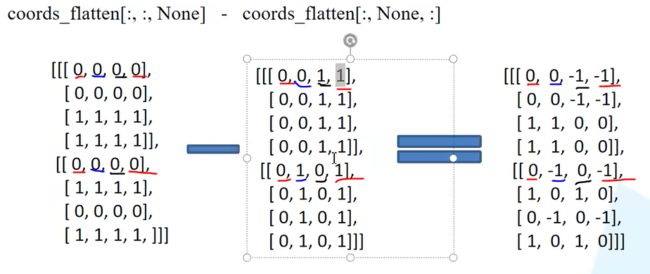
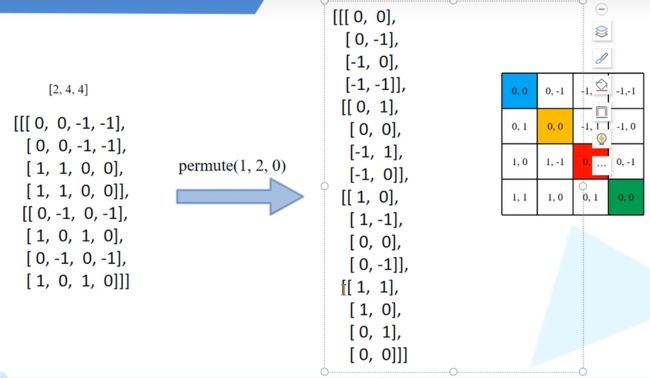
- Python密码学:cryptography库
零 度°
pythonpython密码学
在数字时代,确保数据的安全性和隐私至关重要。Python中的cryptography库是一个全面的包,为Python开发者提供了密码学原语和配方。它支持高级配方和常见密码学算法的低级接口。cryptography库概述cryptography库旨在易于使用且默认安全。它包括各种密码学操作的高级和低级API,如:对称加密非对称加密哈希函数消息认证码(MAC)数字签名密钥管理cryptography库
- Python---frozenset集合
爱听雨声的北方汉
快快乐乐学PythonPython
frozenset是set的不可变版本,因此set集合中所有能改变集合本身的方法(如add、remove、discard、xxx_update等),frozenset都不支持;set集合中不改变集合本身的方法,fronzenset都支持。frozenset的作用主要有以下两点:1、当集合元素不需要改变时,使用frozenset代替set更安全。2、当某些API需要不可变对象时,必须用frozens
- (python)保障信息安全的加密库-cryptography
Marst·Zhang
基础知识实用工具python
前言cryptography是一个广泛使用的Python加密库,提供了各种加密、哈希和签名算法的实现。它支持多种加密算法,如AES、RSA、ECC等,以及哈希函数(如SHA-256、SHA-384等)和数字签名算法(如DSA、ECDSA等).目录常见用途密码学函数主要功能优点缺点总结常见用途数据加密使用对称加密算法(如AES)对数据进行加密,确保数据在传输或存储过程中的机密性。数字签名生成和验证数
- Python if-else对缩进的要求
宇寒风暖
python编程python开发语言学习笔记
在Python中,缩进是语法的一部分,用于表示代码块的层次结构。if-else语句的代码块必须通过缩进来定义,缩进不正确会导致语法错误或逻辑错误。1.缩进的基本规则1.1缩进的作用缩进用于表示代码块的层次结构。同一代码块中的语句必须具有相同的缩进级别。缩进通常使用4个空格,这是Python官方推荐的风格。1.2示例x=10ifx>5:print("x大于5")#缩进4个空格print("这是if代
- 一文弄懂 Python assert 断言
宇寒风暖
python编程python开发语言学习笔记
在Python中,assert是一种用于调试的语句,用于检查某个条件是否为True。如果条件为False,assert会抛出AssertionError异常,并可选地输出错误信息。assert通常用于在开发阶段验证程序的假设条件,确保代码的正确性。1.assert的基本语法1.1语法assertcondition,messagecondition:需要检查的条件表达式。message:可选参数,当
- 开源项目常见问题解决方案——cryptography
周屹隽
开源项目常见问题解决方案——cryptographycryptographycryptographyisapackagedesignedtoexposecryptographicprimitivesandrecipestoPythondevelopers.项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/cr/cryptography项目基础介绍cryptography是一个
- 深度学习--概率
fantasy_arch
深度学习人工智能
1基本概率论1.1假设我们掷骰子,想知道1而不是看到另一个数字的概率,如果骰子是公司,那么所有6个结果(1..6),都有相同的可能发生,因此,我们可以说1发生的概率为1/6.然而现实生活中,对于我们从工厂收到的真实骰子,我们需要检查它是否有瑕疵,唯一的办法就是多投掷骰子,对于每个骰子观察到的[1.2...6]的概率随着投掷次数的增加,越来越接近1/6.导入必要的包%matplotlibinline
- python 利用pandas实现从CSV导出并格式化后写入.jsonl文件
风_流沙
python工具备忘录pythonpandas开发语言
你可以使用pandas库来读取CSV文件,然后通过一些格式化操作将数据转换为JSONL格式并写入文件。JSONL(JSONLines)格式是一种每行一个JSON对象的文件格式。下面是一个示例,演示了如何使用pandas读取CSV文件,处理数据并将其导出到JSONL文件中:示例代码:importpandasaspdimportjson#读取CSV文件df=pd.read_csv('data.csv'
- Python文件加密库之cryptography使用详解
Rocky006
python开发语言
概要在现代信息社会中,数据的安全性变得越来越重要。为了保护敏感信息,文件加密技术被广泛应用。Python的cryptography库提供了强大的加密功能,可以轻松实现文件加密和解密。本文将详细介绍如何使用cryptography库进行文件加密,包含具体的示例代码。cryptography库简介cryptography是Python中一个功能强大且易用的加密库,提供了对称加密、非对称加密、哈希算法、
- 【Python系列】高效Parquet数据处理策略:合并与分析实践
小团团0
python开发语言
在大数据时代,数据的存储、处理和分析变得尤为重要。Parquet作为一种高效的列存储格式,被广泛应用于大数据处理框架中,如ApacheSpark、ApacheHive等。Parquet是一个开源的列存储格式,它被设计用于支持复杂的嵌套数据结构,同时提供高效的压缩和编码方案,以优化存储空间和查询性能。以下将详细介绍如何使用Python对Parquet文件进行数据处理与合并,并提供相应的源码示例。一、
- cryptography,一个神奇的 Python 库!
Sitin涛哥
Pythonpython开发语言
更多资料获取个人网站:ipengtao.com大家好,今天为大家分享一个神奇的Python库-cryptography。Github地址:https://github.com/pyca/cryptography在当今数字化时代,信息安全越来越受到重视。数据加密是保护数据安全的重要手段之一,而Python的cryptography库提供了丰富的功能来支持各种加密算法和协议。本文将深入探讨crypto
- 深度讨论Python for循环
观智能
python开发语言
作者的其他文章推荐:强化学习再受关注!for循环使用于遍历可迭代对象的Python语句,工作原理如下:#for循环foriteminiterable:print(item)#等价于iterator=iter(iterable)#获取迭代器whileTrue:try:item=next(iterator)#获取下一个元素print(item)exceptStopIteration:break#迭代结
- Python第六章08:元组操作练习题
苹果.Python.八宝粥
python开发语言
#元组定义操作练习题"""定义一个元组,内容是:('周杰伦',11,['football','music']),记录一个学生的信息(姓名、年龄、爱好)请通元组(tuple)的功能,对其进行如下操作:1.查询其年龄所在的下标位置2.查询学生的姓名3.删除学生爱好中的football4.增加爱好:coding"""my_tuple=('周杰伦',11,['football','music'])#1.查
- Python第六章07:元组的定义和操作
苹果.Python.八宝粥
python前端开发语言
#tuple元组的定义和操作#tuple元组定义用小括号:(1,2,3,4,5),可以是不同类型元素#给变量定义元组时,写括号不写tuple:a=(1,2,3,4,5)#变量=()变量=tuple()空元组变量#tuple元组定义完成后,不可以修改,但是,如果元组中嵌套了一个列表时,元组中列表的内容可以修改#封装数据后,不希望被篡改数据,就使用元组tuple#1.定义一个元组t1=("halibo
- 利用Python爬虫获取Shopee(虾皮)商品详情:实战指南
小爬虫程序猿
python爬虫开发语言
在跨境电商领域,Shopee(虾皮)作为东南亚及台湾地区领先的电商平台,拥有海量的商品信息。无论是进行市场调研、数据分析,还是寻找热门商品,获取Shopee商品详情都是一项极具价值的任务。然而,手动浏览和整理这些信息显然是低效且容易出错的。幸运的是,通过编写Python爬虫程序,我们可以高效地完成这一任务。本文将详细介绍如何利用Python爬虫获取Shopee商品详情,并提供完整的代码示例。一、为
- Transformer 架构对比:Dense、MoE 与 Hybrid-MoE 的优劣分析
m0_74825656
面试学习路线阿里巴巴transformer架构深度学习
1.LLM基础架构类型DenseTransformerMoE(MixtureofExperts)TransformerHybrid-MoETransformer2.Transformer按照编码方式分类单向自回归模型(如早期GPT系列)双向模型(如BERT)编码器-解码器模型(如BART,T5)DenseTransformerDenseTransformer的优势是什么DenseTransform
- 在Mac M1/M2芯片上完美安装DeepCTR库:避坑指南与实战验证
ku_code_ku
机器学习macos推荐算法推荐系统
让推荐算法在AppleSilicon上全速运行概述作为推荐系统领域的最经常用的明星库,DeepCTR集成了CTR预估、多任务学习等前沿模型实现。但在AppleSilicon架构的Mac设备上,安装过程常因ARM架构适配、依赖库版本冲突等问题受阻。本文通过20+次环境搭建实测,总结出最稳定的安装方案。关键版本说明(2024年验证)组件推荐版本注意事项Python3.10.x向下兼容至3.7,但3.1
- 数据库数值函数详解
web安全工具库
数据库oraclejvm
各类资料学习下载合集https://pan.quark.cn/s/8c91ccb5a474数值函数是数据库中用于处理数值数据的函数,可以用于执行各种数学运算、统计计算等。数值函数在数据分析及处理时非常重要,能够帮助我们进行数据的聚合、计算和转换。在本篇博客中,我们将详细介绍常用的数据库数值函数,并通过Python和SQLite进行示例,帮助您理解和应用这些函数。1.数值函数的基本概念数值函数是用于
- Python中Requests的Cookies的简单使用
北条苒茗殇
python开发语言Requests
概述Python的Requests库中有一个cookies,是用于管理HTTPCookie的工具,可以像字典一样操作Cookie,支持自动处理作用域(域名、路径)和持久化,cookies是一个RequestsCookieJar的类型。一、概念1.作用自动存储服务器返回的Cookie根据请求域名和路径进行自动发送匹配的Cookie支持手动添加、修改、删除Cookie2.RequestsCookieJ
- Pytest基础使用
北条苒茗殇
pytest
概述Pytest是Python里的一个强大的测试框架,灵活易用,可以进行功能,自动化测试使用,可以与Requests,Selenium等进行结合使用,同时可以生成Html的报告。一、Pytest的基本使用在未指定Pytest的配置文件时,会对以下文件进行执行:test_*.py,如:test_1.py*_test.py,如:1_test.py会对以下的类和函数进行执行:类:以Test_开头的类,如
- Visual Studio Code官网下载地址及使用技巧(含常用的拓展插件推荐)
ITCTCSDN
vscodeide编辑器
VisualStudioCode(简称“VSCode”)是Microsoft于2015年4月发布的可运行于MacOS、Windows和Linux之上的跨平台源代码编辑器,它具有对JavaScript,TypeScript和Node.js的内置支持,并具有丰富的其他语言(例如C++,C#,Java,Python,PHP,Go)和运行时(例如.NET和Unity)扩展的生态系统。VisualStudi
- python中rmdir和rmtree的用法
Gin387
python
shutil.rmtree()是Python中shutil模块提供的一个函数,用于递归删除整个目录树(包括子目录和所有文件)。os.rmdir()(只能删除空目录)不同,shutil.rmtree()可以强制删除非空目录importshutil#删除指定目录及其所有内容shutil.rmtree('path/to/directory')
- 构建 Python 插件架构:打造灵活可扩展的模块化应用
全栈探索者chen
pythonpython架构开发语言学习机器学习程序人生插件
构建Python插件架构:打造灵活可扩展的模块化应用前言在现代软件开发中,单一的代码库往往难以满足不断变化的业务需求和多样化的扩展场景。如何设计一个应用,使其既能保持核心功能的稳定,又能轻松集成第三方功能、模块或定制化扩展?答案就是——插件架构。通过插件架构,你可以让应用具备极高的灵活性,支持动态加载、无缝扩展以及解耦维护。本文将深入探讨如何在Python中设计和构建一个插件架构。从核心概念、模块
- 31天Python入门——第11天:挑战一口气把闭包·装饰器讲明白
安然无虞
Python手把手教程python开发语言后端pyqt
你好,我是安然无虞。文章目录1.闭包扩展知识:闭包的自由变量是如何存储的2.装饰器装饰器的应用场景3.补充练习1.闭包闭包是指在一个函数内部定义的函数,并且这个内部函数可以访问外部函数的变量、参数.换句话说,闭包是一个包含了函数及其相关引用环境的组合体.在Python中,当一个函数返回了内部函数的引用时,这个内部函数可以访问并操作外部函数的局部变量,它就创建了一个闭包,即使外部函数已经执行完毕,它
- opencv python rgb转yuv_OpenCV之色彩空间与色彩空间转换
xiao fei
opencvpythonrgb转yuv
python代码:importcv2ascvsrc=cv.imread("test.jpg")cv.namedWindow("rgb",cv.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)cv.imshow("rgb",src)#RGBtoHSVhsv=cv.cvtColor(src,cv.COLOR_BGR2HSV)cv.imshow("hsv",hsv)#RGBtoYUVyuv=cv.cvtColor(sr
- 【AI大模型】搭建本地大模型GPT-NeoX:详细步骤及常见问题处理
qzw1210
gpt人工智能深度学习
搭建本地大模型GPT-NeoX:详细步骤及常见问题处理GPT-NeoX是一个开源的大型语言模型框架,由EleutherAI开发,可用于训练和部署类似GPT-3的大型语言模型。本指南将详细介绍如何在本地环境中搭建GPT-NeoX,并解决过程中可能遇到的常见问题。1.系统要求1.1硬件要求1.2软件要求操作系统:Linux(推荐Ubuntu20.04或更高版本)CUDA:11.2或更高版本Python
- Open3D 点云DBSCAN聚类算法
MelaCandy
算法聚类numpy计算机视觉图像处理3d
目录一、DBSCAN基本原理二、代码实现2.1关键函数2.2完整代码三、实现效果3.1原始点云3.2聚类后点云Open3D点云算法汇总及实战案例汇总的目录地址:Open3D点云算法与点云深度学习案例汇总(长期更新)-CSDN博客一、DBSCAN基本原理DBSCAN(Density-BasedSpatialClusteringofApplicationswithNoise)是一种基于密度的聚类算法,
- python 列表倒序输出
小琳爱分享
pythonpython
python列表倒序输出#使用reverseli1=[1,6,4,3,7,9]li2=['a','m','s','g']li1.reverse()li2.reverse()print(li1,li2)#利用list切片li1=[1,6,4,3,7,9]li2=['a','m','s','g']print(li1[::-1])print(li2[::-1])#利用算法进行转换,这里需要用到深层cop
- python怎么输出倒序
hakesashou
python基础知识pythonjava服务器
python怎么输出倒序?下面给大家介绍四种方法:创建测试列表>>> lst = [1,2,3,4,5,6]方法1:>>> lst.reverse() #reverse()反转>>> lst[6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]方法2:>>> lst1 = [i for i in reversed(lst)] #reversed只适用于与序列(列表、元组、字符串)>>> lst1[6, 5, 4,
- chatgpt赋能python:Python怎么倒序列表
aijinglingchat
ChatGptpythonchatgpt人工智能计算机
Python怎么倒序列表列表是Python中最常用的数据结构之一,但在实际使用时,有时需要将列表进行倒序排列。Python提供了多种方法来实现这个需求,本文将简要介绍这些方法以及它们的使用场景。方法1:使用reverse()函数使用列表的reverse()方法是Python中最简单直接的方法来倒序列表。该方法会将原列表倒置。lst=[1,2,3,4,5]lst.reverse()print(lst
- tomcat基础与部署发布
暗黑小菠萝
Tomcat java web
从51cto搬家了,以后会更新在这里方便自己查看。
做项目一直用tomcat,都是配置到eclipse中使用,这几天有时间整理一下使用心得,有一些自己配置遇到的细节问题。
Tomcat:一个Servlets和JSP页面的容器,以提供网站服务。
一、Tomcat安装
安装方式:①运行.exe安装包
&n
- 网站架构发展的过程
ayaoxinchao
数据库应用服务器网站架构
1.初始阶段网站架构:应用程序、数据库、文件等资源在同一个服务器上
2.应用服务和数据服务分离:应用服务器、数据库服务器、文件服务器
3.使用缓存改善网站性能:为应用服务器提供本地缓存,但受限于应用服务器的内存容量,可以使用专门的缓存服务器,提供分布式缓存服务器架构
4.使用应用服务器集群改善网站的并发处理能力:使用负载均衡调度服务器,将来自客户端浏览器的访问请求分发到应用服务器集群中的任何
- [信息与安全]数据库的备份问题
comsci
数据库
如果你们建设的信息系统是采用中心-分支的模式,那么这里有一个问题
如果你的数据来自中心数据库,那么中心数据库如果出现故障,你的分支机构的数据如何保证安全呢?
是否应该在这种信息系统结构的基础上进行改造,容许分支机构的信息系统也备份一个中心数据库的文件呢?
&n
- 使用maven tomcat plugin插件debug关联源代码
商人shang
mavendebug查看源码tomcat-plugin
*首先需要配置好'''maven-tomcat7-plugin''',参见[[Maven开发Web项目]]的'''Tomcat'''部分。
*配置好后,在[[Eclipse]]中打开'''Debug Configurations'''界面,在'''Maven Build'''项下新建当前工程的调试。在'''Main'''选项卡中点击'''Browse Workspace...'''选择需要开发的
- 大访问量高并发
oloz
大访问量高并发
大访问量高并发的网站主要压力还是在于数据库的操作上,尽量避免频繁的请求数据库。下面简
要列出几点解决方案:
01、优化你的代码和查询语句,合理使用索引
02、使用缓存技术例如memcache、ecache将不经常变化的数据放入缓存之中
03、采用服务器集群、负载均衡分担大访问量高并发压力
04、数据读写分离
05、合理选用框架,合理架构(推荐分布式架构)。
- cache 服务器
小猪猪08
cache
Cache 即高速缓存.那么cache是怎么样提高系统性能与运行速度呢?是不是在任何情况下用cache都能提高性能?是不是cache用的越多就越好呢?我在近期开发的项目中有所体会,写下来当作总结也希望能跟大家一起探讨探讨,有错误的地方希望大家批评指正。
1.Cache 是怎么样工作的?
Cache 是分配在服务器上
- mysql存储过程
香水浓
mysql
Description:插入大量测试数据
use xmpl;
drop procedure if exists mockup_test_data_sp;
create procedure mockup_test_data_sp(
in number_of_records int
)
begin
declare cnt int;
declare name varch
- CSS的class、id、css文件名的常用命名规则
agevs
JavaScriptUI框架Ajaxcss
CSS的class、id、css文件名的常用命名规则
(一)常用的CSS命名规则
头:header
内容:content/container
尾:footer
导航:nav
侧栏:sidebar
栏目:column
页面外围控制整体布局宽度:wrapper
左右中:left right
- 全局数据源
AILIKES
javatomcatmysqljdbcJNDI
实验目的:为了研究两个项目同时访问一个全局数据源的时候是创建了一个数据源对象,还是创建了两个数据源对象。
1:将diuid和mysql驱动包(druid-1.0.2.jar和mysql-connector-java-5.1.15.jar)copy至%TOMCAT_HOME%/lib下;2:配置数据源,将JNDI在%TOMCAT_HOME%/conf/context.xml中配置好,格式如下:&l
- MYSQL的随机查询的实现方法
baalwolf
mysql
MYSQL的随机抽取实现方法。举个例子,要从tablename表中随机提取一条记录,大家一般的写法就是:SELECT * FROM tablename ORDER BY RAND() LIMIT 1。但是,后来我查了一下MYSQL的官方手册,里面针对RAND()的提示大概意思就是,在ORDER BY从句里面不能使用RAND()函数,因为这样会导致数据列被多次扫描。但是在MYSQL 3.23版本中,
- JAVA的getBytes()方法
bijian1013
javaeclipseunixOS
在Java中,String的getBytes()方法是得到一个操作系统默认的编码格式的字节数组。这个表示在不同OS下,返回的东西不一样!
String.getBytes(String decode)方法会根据指定的decode编码返回某字符串在该编码下的byte数组表示,如:
byte[] b_gbk = "
- AngularJS中操作Cookies
bijian1013
JavaScriptAngularJSCookies
如果你的应用足够大、足够复杂,那么你很快就会遇到这样一咱种情况:你需要在客户端存储一些状态信息,这些状态信息是跨session(会话)的。你可能还记得利用document.cookie接口直接操作纯文本cookie的痛苦经历。
幸运的是,这种方式已经一去不复返了,在所有现代浏览器中几乎
- [Maven学习笔记五]Maven聚合和继承特性
bit1129
maven
Maven聚合
在实际的项目中,一个项目通常会划分为多个模块,为了说明问题,以用户登陆这个小web应用为例。通常一个web应用分为三个模块:
1. 模型和数据持久化层user-core,
2. 业务逻辑层user-service以
3. web展现层user-web,
user-service依赖于user-core
user-web依赖于user-core和use
- 【JVM七】JVM知识点总结
bit1129
jvm
1. JVM运行模式
1.1 JVM运行时分为-server和-client两种模式,在32位机器上只有client模式的JVM。通常,64位的JVM默认都是使用server模式,因为server模式的JVM虽然启动慢点,但是,在运行过程,JVM会尽可能的进行优化
1.2 JVM分为三种字节码解释执行方式:mixed mode, interpret mode以及compiler
- linux下查看nginx、apache、mysql、php的编译参数
ronin47
在linux平台下的应用,最流行的莫过于nginx、apache、mysql、php几个。而这几个常用的应用,在手工编译完以后,在其他一些情况下(如:新增模块),往往想要查看当初都使用了那些参数进行的编译。这时候就可以利用以下方法查看。
1、nginx
[root@361way ~]# /App/nginx/sbin/nginx -V
nginx: nginx version: nginx/
- unity中运用Resources.Load的方法?
brotherlamp
unity视频unity资料unity自学unityunity教程
问:unity中运用Resources.Load的方法?
答:Resources.Load是unity本地动态加载资本所用的方法,也即是你想动态加载的时分才用到它,比方枪弹,特效,某些实时替换的图像什么的,主张此文件夹不要放太多东西,在打包的时分,它会独自把里边的一切东西都会集打包到一同,不论里边有没有你用的东西,所以大多数资本应该是自个建文件放置
1、unity实时替换的物体即是依据环境条件
- 线段树-入门
bylijinnan
java算法线段树
/**
* 线段树入门
* 问题:已知线段[2,5] [4,6] [0,7];求点2,4,7分别出现了多少次
* 以下代码建立的线段树用链表来保存,且树的叶子结点类似[i,i]
*
* 参考链接:http://hi.baidu.com/semluhiigubbqvq/item/be736a33a8864789f4e4ad18
* @author lijinna
- 全选与反选
chicony
全选
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<title>全选与反选</title>
- vim一些简单记录
chenchao051
vim
mac在/usr/share/vim/vimrc linux在/etc/vimrc
1、问:后退键不能删除数据,不能往后退怎么办?
答:在vimrc中加入set backspace=2
2、问:如何控制tab键的缩进?
答:在vimrc中加入set tabstop=4 (任何
- Sublime Text 快捷键
daizj
快捷键sublime
[size=large][/size]Sublime Text快捷键:Ctrl+Shift+P:打开命令面板Ctrl+P:搜索项目中的文件Ctrl+G:跳转到第几行Ctrl+W:关闭当前打开文件Ctrl+Shift+W:关闭所有打开文件Ctrl+Shift+V:粘贴并格式化Ctrl+D:选择单词,重复可增加选择下一个相同的单词Ctrl+L:选择行,重复可依次增加选择下一行Ctrl+Shift+L:
- php 引用(&)详解
dcj3sjt126com
PHP
在PHP 中引用的意思是:不同的名字访问同一个变量内容. 与C语言中的指针是有差别的.C语言中的指针里面存储的是变量的内容在内存中存放的地址 变量的引用 PHP 的引用允许你用两个变量来指向同一个内容 复制代码代码如下:
<?
$a="ABC";
$b =&$a;
echo
- SVN中trunk,branches,tags用法详解
dcj3sjt126com
SVN
Subversion有一个很标准的目录结构,是这样的。比如项目是proj,svn地址为svn://proj/,那么标准的svn布局是svn://proj/|+-trunk+-branches+-tags这是一个标准的布局,trunk为主开发目录,branches为分支开发目录,tags为tag存档目录(不允许修改)。但是具体这几个目录应该如何使用,svn并没有明确的规范,更多的还是用户自己的习惯。
- 对软件设计的思考
e200702084
设计模式数据结构算法ssh活动
软件设计的宏观与微观
软件开发是一种高智商的开发活动。一个优秀的软件设计人员不仅要从宏观上把握软件之间的开发,也要从微观上把握软件之间的开发。宏观上,可以应用面向对象设计,采用流行的SSH架构,采用web层,业务逻辑层,持久层分层架构。采用设计模式提供系统的健壮性和可维护性。微观上,对于一个类,甚至方法的调用,从计算机的角度模拟程序的运行情况。了解内存分配,参数传
- 同步、异步、阻塞、非阻塞
geeksun
非阻塞
同步、异步、阻塞、非阻塞这几个概念有时有点混淆,在此文试图解释一下。
同步:发出方法调用后,当没有返回结果,当前线程会一直在等待(阻塞)状态。
场景:打电话,营业厅窗口办业务、B/S架构的http请求-响应模式。
异步:方法调用后不立即返回结果,调用结果通过状态、通知或回调通知方法调用者或接收者。异步方法调用后,当前线程不会阻塞,会继续执行其他任务。
实现:
- Reverse SSH Tunnel 反向打洞實錄
hongtoushizi
ssh
實際的操作步驟:
# 首先,在客戶那理的機器下指令連回我們自己的 Server,並設定自己 Server 上的 12345 port 會對應到幾器上的 SSH port
ssh -NfR 12345:localhost:22
[email protected]
# 然後在 myhost 的機器上連自己的 12345 port,就可以連回在客戶那的機器
ssh localhost -p 1
- Hibernate中的缓存
Josh_Persistence
一级缓存Hiberante缓存查询缓存二级缓存
Hibernate中的缓存
一、Hiberante中常见的三大缓存:一级缓存,二级缓存和查询缓存。
Hibernate中提供了两级Cache,第一级别的缓存是Session级别的缓存,它是属于事务范围的缓存。这一级别的缓存是由hibernate管理的,一般情况下无需进行干预;第二级别的缓存是SessionFactory级别的缓存,它是属于进程范围或群集范围的缓存。这一级别的缓存
- 对象关系行为模式之延迟加载
home198979
PHP架构延迟加载
形象化设计模式实战 HELLO!架构
一、概念
Lazy Load:一个对象,它虽然不包含所需要的所有数据,但是知道怎么获取这些数据。
延迟加载貌似很简单,就是在数据需要时再从数据库获取,减少数据库的消耗。但这其中还是有不少技巧的。
二、实现延迟加载
实现Lazy Load主要有四种方法:延迟初始化、虚
- xml 验证
pengfeicao521
xmlxml解析
有些字符,xml不能识别,用jdom或者dom4j解析的时候就报错
public static void testPattern() {
// 含有非法字符的串
String str = "Jamey친ÑԂ
- div设置半透明效果
spjich
css半透明
为div设置如下样式:
div{filter:alpha(Opacity=80);-moz-opacity:0.5;opacity: 0.5;}
说明:
1、filter:对win IE设置半透明滤镜效果,filter:alpha(Opacity=80)代表该对象80%半透明,火狐浏览器不认2、-moz-opaci
- 你真的了解单例模式么?
w574240966
java单例设计模式jvm
单例模式,很多初学者认为单例模式很简单,并且认为自己已经掌握了这种设计模式。但事实上,你真的了解单例模式了么。
一,单例模式的5中写法。(回字的四种写法,哈哈。)
1,懒汉式
(1)线程不安全的懒汉式
public cla