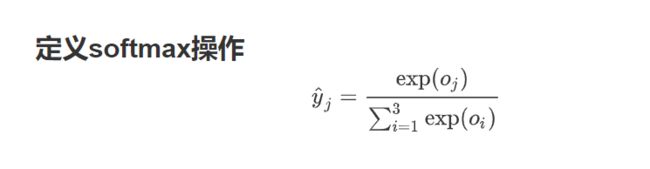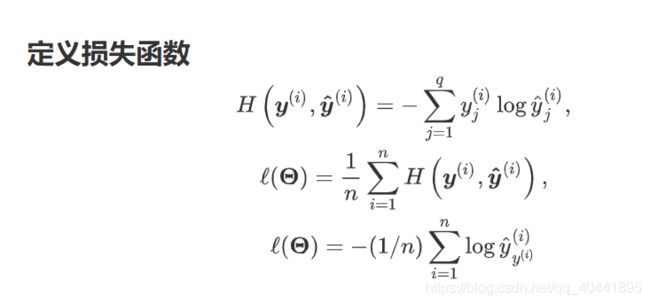softmax和分类模型
softmax和分类模型
内容包括:
- softmax回归的基本概念
- 如何获取fashion-MINIST数据集和读取数据
- softmax回归模型的从零开始,实现一个对fashion-MINIST训练集中图像数据进行分类的模型
- 使用pytorch重新实现softmax回归模型
softmax的基本概念
(1)分类问题
一个简单的图像分类问题,输入图像的高和宽均为2像素,色彩为灰度。
图像中的4像素分别记为x1,x2,x3,x4。
假设真实标签为狗、猫或者鸡,这些标签对应的离散值为y1,y2,y3。
我们通常使用离散的数值来表示类别,例如y1=1,y2=2,y3=3。
(2)权重矢量

(3)神经网络图
下图用神经网络图描绘了上面的计算。softmax回归同线性回归一样,也是一个单层神经网络。由于每个输出o1,o2,o3的计算都要依赖于所有的输入x1,x2,x3,x4,softmax回归的输出层也是一个全连接层。









# import needed package
%matplotlib inline
from IPython import display
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import time
import sys
sys.path.append("/home/kesci/input")
import d2lzh1981 as d2l
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchvision.__version__)
get dataset
mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root='/home/kesci/input/FashionMNIST2065', train=True, download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root='/home/kesci/input/FashionMNIST2065', train=False, download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
# show result
print(type(mnist_train))
print(len(mnist_train), len(mnist_test))
# 我们可以通过下标来访问任意一个样本
feature, label = mnist_train[0]
print(feature.shape, label) # Channel x Height x Width
如果不做变换输入的数据是图像,我们可以看一下图片的类型参数:
mnist_PIL = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root='/home/kesci/input/FashionMNIST2065', train=True, download=True)
PIL_feature, label = mnist_PIL[0]
print(PIL_feature)
# 本函数已保存在d2lzh包中方便以后使用
def get_fashion_mnist_labels(labels):
text_labels = ['t-shirt', 'trouser', 'pullover', 'dress', 'coat',
'sandal', 'shirt', 'sneaker', 'bag', 'ankle boot']
return [text_labels[int(i)] for i in labels]
def show_fashion_mnist(images, labels):
d2l.use_svg_display()
# 这里的_表示我们忽略(不使用)的变量
_, figs = plt.subplots(1, len(images), figsize=(12, 12))
for f, img, lbl in zip(figs, images, labels):
f.imshow(img.view((28, 28)).numpy())
f.set_title(lbl)
f.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
f.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()
X, y = [], []
for i in range(10):
X.append(mnist_train[i][0]) # 将第i个feature加到X中
y.append(mnist_train[i][1]) # 将第i个label加到y中
show_fashion_mnist(X, get_fashion_mnist_labels(y))
# 读取数据
batch_size = 256
num_workers = 4
train_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=num_workers)
test_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(mnist_test, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=num_workers)
start = time.time()
for X, y in train_iter:
continue
print('%.2f sec' % (time.time() - start))
softmax从零开始的实现
import torch
import torchvision
import numpy as np
import sys
sys.path.append("/home/kesci/input")
import d2lzh1981 as d2l
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchvision.__version__)
获取训练集数据和测试集数据
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, root='/home/kesci/input/FashionMNIST2065')
模型参数初始化
num_inputs = 784
print(28*28)
num_outputs = 10
W = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, (num_inputs, num_outputs)), dtype=torch.float)
b = torch.zeros(num_outputs, dtype=torch.float)
W.requires_grad_(requires_grad=True)
b.requires_grad_(requires_grad=True)
对多维Tensor按维度操作
X = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(X.sum(dim=0, keepdim=True)) # dim为0,按照相同的列求和,并在结果中保留列特征
print(X.sum(dim=1, keepdim=True)) # dim为1,按照相同的行求和,并在结果中保留行特征
print(X.sum(dim=0, keepdim=False)) # dim为0,按照相同的列求和,不在结果中保留列特征
print(X.sum(dim=1, keepdim=False)) # dim为1,按照相同的行求和,不在结果中保留行特征
def softmax(X):
X_exp = X.exp()
partition = X_exp.sum(dim=1, keepdim=True)
# print("X size is ", X_exp.size())
# print("partition size is ", partition, partition.size())
return X_exp / partition # 这里应用了广播机制
X = torch.rand((2, 5))
X_prob = softmax(X)
print(X_prob, '\n', X_prob.sum(dim=1))
def net(X):
return softmax(torch.mm(X.view((-1, num_inputs)), W) + b)
y_hat = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.3, 0.6], [0.3, 0.2, 0.5]])
y = torch.LongTensor([0, 2])
y_hat.gather(1, y.view(-1, 1))
def cross_entropy(y_hat, y):
return - torch.log(y_hat.gather(1, y.view(-1, 1)))
定义准确率
我们模型训练完了进行模型预测的时候,会用到我们这里定义的准确率。
def accuracy(y_hat, y):
return (y_hat.argmax(dim=1) == y).float().mean().item()
print(accuracy(y_hat, y))
# 本函数已保存在d2lzh_pytorch包中方便以后使用。该函数将被逐步改进:它的完整实现将在“图像增广”一节中描述
def evaluate_accuracy(data_iter, net):
acc_sum, n = 0.0, 0
for X, y in data_iter:
acc_sum += (net(X).argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item()
n += y.shape[0]
return acc_sum / n
print(evaluate_accuracy(test_iter, net))
训练模型
num_epochs, lr = 5, 0.1
# 本函数已保存在d2lzh_pytorch包中方便以后使用
def train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, batch_size,
params=None, lr=None, optimizer=None):
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_l_sum, train_acc_sum, n = 0.0, 0.0, 0
for X, y in train_iter:
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y).sum()
# 梯度清零
if optimizer is not None:
optimizer.zero_grad()
elif params is not None and params[0].grad is not None:
for param in params:
param.grad.data.zero_()
l.backward()
if optimizer is None:
d2l.sgd(params, lr, batch_size)
else:
optimizer.step()
train_l_sum += l.item()
train_acc_sum += (y_hat.argmax(dim=1) == y).sum().item()
n += y.shape[0]
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(test_iter, net)
print('epoch %d, loss %.4f, train acc %.3f, test acc %.3f'
% (epoch + 1, train_l_sum / n, train_acc_sum / n, test_acc))
train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, cross_entropy, num_epochs, batch_size, [W, b], lr)
模型预测
现在我们的模型训练完了,可以进行一下预测,我们的这个模型训练的到底准确不准确。 现在就可以演示如何对图像进行分类了。给定一系列图像(第三行图像输出),我们比较一下它们的真实标签(第一行文本输出)和模型预测结果(第二行文本输出)。
X, y = iter(test_iter).next()
true_labels = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(y.numpy())
pred_labels = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(net(X).argmax(dim=1).numpy())
titles = [true + '\n' + pred for true, pred in zip(true_labels, pred_labels)]
d2l.show_fashion_mnist(X[0:9], titles[0:9])
softmax的简洁实现
# 加载各种包或者模块
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import init
import numpy as np
import sys
sys.path.append("/home/kesci/input")
import d2lzh1981 as d2l
print(torch.__version__)
初始化参数和获取数据
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, root='/home/kesci/input/FashionMNIST2065')
定义网络模型
num_inputs = 784
num_outputs = 10
class LinearNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_inputs, num_outputs):
super(LinearNet, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(num_inputs, num_outputs)
def forward(self, x): # x 的形状: (batch, 1, 28, 28)
y = self.linear(x.view(x.shape[0], -1))
return y
# net = LinearNet(num_inputs, num_outputs)
class FlattenLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(FlattenLayer, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x): # x 的形状: (batch, *, *, ...)
return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
from collections import OrderedDict
net = nn.Sequential(
# FlattenLayer(),
# LinearNet(num_inputs, num_outputs)
OrderedDict([
('flatten', FlattenLayer()),
('linear', nn.Linear(num_inputs, num_outputs))]) # 或者写成我们自己定义的 LinearNet(num_inputs, num_outputs) 也可以
)
初始化模型参数
init.normal_(net.linear.weight, mean=0, std=0.01)
init.constant_(net.linear.bias, val=0)
定义损失函数
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 下面是他的函数原型
# class torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, size_average=None, ignore_index=-100, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
定义优化函数
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.1) # 下面是函数原型
# class torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=, momentum=0, dampening=0, weight_decay=0, nesterov=False)
训练
num_epochs = 5
d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, batch_size, None, None, optimizer)