极智AI | 谈谈 Tengine TensorRT 后端组织流程
欢迎关注我的公众号 [极智视界],回复001获取Google编程规范
大家好,我是极智视界,本文主要谈谈 Tengine TensorRT 后端组织流程。
下面开始。
文章目录
-
-
- 1、后端斜接通用部分
- 2、后端斜接 TensorRT 实现部分
-
1、后端斜接通用部分
首先在 Tengine 工程的 examples 中找一个 trt 后端的例程切入,这里拿 tm_classification_trt 进行说明。
在 tm_classification_trt.cpp 的 main 中实现分类功能的函数如下,这里会传入算法的配置参数:
if (tengine_classify(model_file, image_file, img_h, img_w, mean, scale, loop_count, num_thread, cpu_affinity) < 0)
return -1;
进 tengine_classify 实现:
int tengine_classify(const char* model_file, const char* image_file, int img_h, int img_w, const float* mean, const float* scale, int loop_count, int num_thread, int affinity){
/* set runtime options */
struct options opt;
opt.num_thread = num_thread;
opt.cluster = TENGINE_CLUSTER_ALL;
opt.precision = TENGINE_MODE_FP32;
opt.affinity = affinity;
/* inital tengine */
if (init_tengine() != 0){
fprintf(stderr, "Initial tengine failed.\n");
return -1;
}
fprintf(stderr, "tengine-lite library version: %s\n", get_tengine_version());
/* create NVIDIA TensorRT backend */
context_t trt_context = create_context("trt", 1);
int rtt = add_context_device(trt_context, "TensorRT");
if (0 > rtt){
fprintf(stderr, "add_context_device NV TensorRT DEVICE failed.\n");
return -1;
}
/* create graph, load tengine model xxx.tmfile */
graph_t graph = create_graph(trt_context, "tengine", model_file);
if (NULL == graph){
fprintf(stderr, "Create graph failed.\n");
return -1;
}
...
};
重点看上述代码中的链接 trt 后端部分:
/* create NVIDIA TensorRT backend */
context_t trt_context = create_context("trt", 1); // 创建 trt 后端
int rtt = add_context_device(trt_context, "TensorRT"); // 斜接 trt 后端
进 add_context_device 后端斜接实现:
int add_context_device(context_t context, const char* dev_name){
struct context* ctx = (struct context*)context;
if (NULL == ctx){
TLOG_ERR("Tengine: Context pointer is null.\n");
return -1;
}
if (NULL != ctx->device){
TLOG_ERR("Tengine: Context(%s) is not multi-device collaborative.\n", ctx->name);
return -1;
}
struct device* selected_device = find_device_via_name(dev_name); // 匹配 “TensorRT”
if (NULL == selected_device){
TLOG_ERR("Tengine: Device(%s) is not found(may not registered).\n", dev_name);
return -1;
}
ctx->device = selected_device;
return 0;
}
匹配到 “TensorRT” 后端的 device 结构体指针赋给 ctx->device,这样就完成了 TensorRT 后端斜接,这一套接口对于不同的后端基本是通用的。
2、后端斜接 TensorRT 实现部分
然后到 trt 后端独特的部分,前面提到的 device 结构体实现可以链到 trt device 后端代码实现。先看一下 device 结构体的定义:
typedef struct device
{
const char* name;
struct interface* interface; //!< device scheduler operation interface
struct allocator* allocator; //!< device allocation operation interface
struct optimizer* optimizer; //!< device optimizer operation interface
struct scheduler* scheduler; //!< device scheduler
void* privacy; //!< device privacy data
} ir_device_t;
斜接到 trt 后端实现的接口在 trt_device.cc,代码如下:
static struct trt_device nv_trt_dev = {
.base = {
.name = TRT_DEVICE_NAME,
.interface = &trt_interface,
.allocator = &trt_allocator,
.optimizer = &trt_optimizer,
.scheduler = nullptr,
.privacy = nullptr,
},
};
这里主要来看 interface 接口,里面主要是网络算子的实现及网络结构的组织:
static struct interface trt_interface = {
.init = trt_dev_init,
.pre_run = trt_dev_prerun,
.run = trt_dev_run,
.post_run = trt_dev_postrun,
.async_run = nullptr,
.async_wait = nullptr,
.release_graph = nullptr,
.release_device = trt_dev_release,
};
来看 prerun,这里进行了 trt 网络执行结构的构建:
int trt_dev_prerun(struct device* dev, struct subgraph* subgraph, void* options){
subgraph->device_graph = new TensorRTEngine; // 构建 trt 网络执行结构
auto engine = (TensorRTEngine*)subgraph->device_graph;
ir_graph_t* graph = subgraph->graph;
if (nullptr != options){
struct trt_option* opt = (struct trt_option*)options;
engine->SetOption(opt);
return engine->PreRun(subgraph, opt);
}
else{
return engine->PreRun(subgraph, nullptr);}
}
进入主功能实现:
subgraph->device_graph = new TensorRTEngine;
在实例化 TensorRTEngine 类的时候也进行了 trt 网络执行结构构建,来看下 TensorRTEngine 类的定义:
class TensorRTEngine
{
public:
TensorRTEngine();
~TensorRTEngine() = default;
int PreRun(struct subgraph* subgraph, struct trt_option* opt);
int Run(struct subgraph* subgraph);
int PoseRun(struct subgraph* subgraph);
void SetOption(trt_opt_t* opt);
private:
int Build(struct subgraph* subgraph);
void SetRange(struct graph* ir_graph, uint16_t id, nvinfer1::ITensor* trt_tensor);
void SetRange(struct tensor* ir_tensor, nvinfer1::ITensor* trt_tensor);
bool check_if_input_in_map(uint16_t& id, std::map& map);
int get_type(int mode, nvinfer1::DataType& type);
private:
size_t card_id;
uint16_t tensor_swap_count;
std::map tensor_real_map;
std::map tensor_swap_map;
std::map layer_map;
std::vector io_tensors;
std::vector host_buffer;
nvinfer1::DataType precision;
private:
trt_opt_t option;
private:
bool AddTensor(struct graph* ir_graph, struct tensor* ir_tensor);
bool AddAbsVal(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddAddN(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddBatchNormNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddConcatNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddConvolutionNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddDeConvolutionNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddCropNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddDropoutNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddEltwiseLayer(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddFlattenNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddFullyConnectedNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddHardSwishNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddInstanceNormNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddInterpNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddMishNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddPadNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddPermuteNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddPoolingNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool addReLUNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddReductionNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddReshapeNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddResizeNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddTanhNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddTranspose(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddSliceNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddSoftmaxNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddSplitNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddSqueezeNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
bool AddUpSampleNode(struct graph* ir_graph, struct node* node);
private:
nvinfer1::IBuilder* builder;
nvinfer1::INetworkDefinition* network;
nvinfer1::IBuilderConfig* config;
nvinfer1::ICudaEngine* engine;
nvinfer1::IExecutionContext* context;
};
来看 TensorRTEngine::Build,这是实现网络组织构建的主要函数,里面斜接了 TensorRT 算子实现:
int TensorRTEngine::Build(struct subgraph* subgraph){
const auto cuda_status = cudaSetDevice(this->option.gpu_index);;
struct graph* ir_graph = subgraph->graph;
for (uint16_t i = 0; i < subgraph->node_num; i++){
uint16_t node_id = subgraph->node_list[i];
auto ir_node = get_ir_graph_node(ir_graph, node_id);
// 添加网络数据
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < ir_node->input_num; j++){
struct tensor* ir_tensor = get_ir_graph_tensor(ir_graph, ir_node->input_tensors[j]);
if (TENSOR_TYPE_INPUT == ir_tensor->tensor_type || TENSOR_TYPE_VAR == ir_tensor->tensor_type){
if(!AddTensor(ir_graph, ir_tensor)){
TLOG_ERR("Tengine: Cannot add input tensor(id: %d, name: %s) from node(id: %d, name: %s).\n", ir_tensor->index, ir_tensor->name, ir_node->index, ir_node->name);
return -5;}}}
}
for (uint16_t i = 0; i < subgraph->node_num; i++){
uint16_t node_id = subgraph->node_list[i];
auto ir_node = get_ir_graph_node(ir_graph, node_id);
auto op_type = ir_node->op.type;
// 添加网络算子实现
switch (op_type){
case OP_ABSVAL:
if (!AddAbsVal(ir_graph, ir_node)){
TLOG_ERR("Tengine: Cannot add AbsVal op(%d).\n", ir_node->index);
return -6;
}
break;
case OP_ADD_N:
if (!AddAddN(ir_graph, ir_node)){
TLOG_ERR("Tengine: Cannot add AddN op(%d).\n", ir_node->index);
return -6;
}
break;
case OP_BATCHNORM:
if (!AddBatchNormNode(ir_graph, ir_node)){
TLOG_ERR("Tengine: Cannot add BatchNorm op(%d).\n", ir_node->index);
return -6;
}
break;
case OP_CONST:
continue;
case OP_CONCAT:
if (!AddConcatNode(ir_graph, ir_node)){
TLOG_ERR("Tengine: Cannot add Concat op(%d).\n", ir_node->index);
return -6;
}
break;
case OP_CONV: {
if (!AddConvolutionNode(ir_graph, ir_node)){
TLOG_ERR("Tengine: Cannot add Convolution op(%d).\n", ir_node->index);
return -6;
}
break;
}
...
}
}
// 设置 output 输出
for(uint8_t i = 0; i < subgraph->output_num; i++){
struct tensor* output_tensor = get_ir_graph_tensor(ir_graph, subgraph->output_tensor_list[i]);
uint16_t output_node_id = output_tensor->producer;
nvinfer1::ILayer* layer = layer_map[output_node_id];
layer->setPrecision(nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT);
for (int j = 0; j < layer->getNbOutputs(); j++){
layer->setOutputType(j, nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT);
}
//layer->getOutput(i)->setName(output_tensor->name);
auto trt_tensor = this->tensor_real_map[this->tensor_swap_map[output_tensor->index]];
trt_tensor->setName(output_tensor->name);
this->network->markOutput(*trt_tensor);
}
}
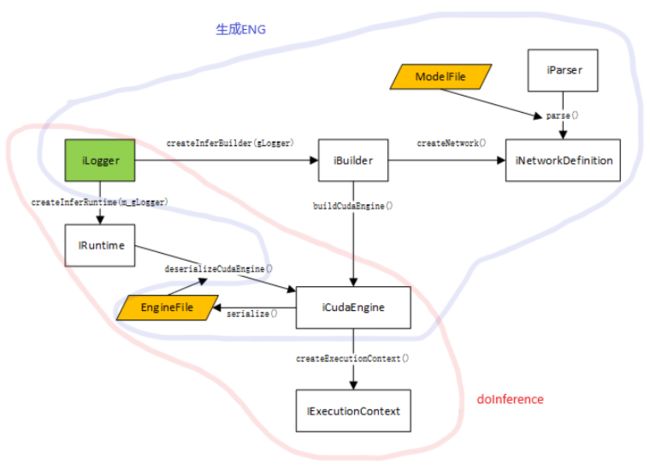
然后来看 TensorRTEngine::PreRun,这个是构建 trt 推理引擎的过程,全部逻辑如下:
这里可能没有模型序列化和反序列化的过程,不过最终目的就是为了构建 IExecutionContext:
this->context = engine->createExecutionContext();
再来看一下 Tengine trt 后端的 int8 量化操作:
case nvinfer1::DataType::kINT8:
{
if (this->builder->platformHasFastInt8()){
struct tensor* input = get_ir_graph_tensor(ir_graph, subgraph->input_tensor_list[0]);
if (nullptr != input && 1 <= input->quant_param_num){
this->config->setFlag(nvinfer1::BuilderFlag::kINT8);
this->config->setInt8Calibrator(nullptr); // 传入 TensorRT 格式 int8 校准表
this->precision = nvinfer1::DataType::kINT8;
}
else{
TLOG_ERR("Tengine: Try enable INT8, but network does not have quant params, rollback to FP32.\n");}
}
else{
TLOG_ERR("Tengine: Target inference precision(%d) is not supported, rollback.\n", opt->precision);}
break;
}
以上的量化过程可能会让你有点迷惑,没错,他这边只做了模型权重的量化,没有做激活值量化。而激活值量化的实现代码应为 this->config->setInt8Calibrator(nullptr),即要求你传入 TensorRT 格式的 int8 校准表。
这一整套下来真的就是 Tengine 和 TensorRT 的 直接斜接:
(1)没有很好利用 Tengine 量化模块的输出文件进行 TensorRT 的量化斜接,其实 Tengine 量化模块写的挺清晰的;
(2)Tengine trt 后端中 trt 实现部分相对独立,意思是可能直接把 trt 后端拿出来就是一套比较完整的 trt 推理工程,并没有很多的 Tengine 化风格,除了网络加载部分;
好了,以上分享了 Tengine TensorRT 后端组织流程,希望我的分享能对你的学习有一点帮助。
【公众号传送】
《【模型推理】谈谈 Tengine TensorRT 后端组织流程》
![]()
扫描下方二维码即可关注我的微信公众号【极智视界】,获取更多AI经验分享,让我们用极致+极客的心态来迎接AI !
![]()