基于卷积神经网络的图像去噪(入门篇)
基于卷积神经网络的图像去噪(基础篇)
基础理论知识了解
- 基于深度学习的图像去噪,区别于传统去噪,但也有一定发展历程。从浅层模型到深度模型,从含噪图像映射去噪图像到含噪图像映射噪声图像(也就是残差学习),学习发展历程,能够更好的把握当下流行的算法。个人推荐这篇文章深度学习在图像去噪方面有哪些进展
- 卷积神经网络区别于其它的神经网络,如果你不清楚神经网络的工作原理,建议看这篇深度学习之神经网络详解
一,含噪图像映射去噪图像(浅层网络模型)
- 比较好理解,输入一张含噪图像(这里是40x40x1的灰度图像块,图像块大小可变),通过神经网络提取特征与原始无噪声图像进行损失函数的计算,并通过不断优化减少损失函数,从而输出去噪后的图像。最简单的就一到三层网络,这里使用9层网络进行实验。直接上网络模型:
def get_cnn_9conv(model_path=None):
input_img = Input(shape=((None, None, 1))) # adapt this if using `channels_first` image data format
x = Conv2D(56, (5, 5), activation='relu', padding='same')(input_img)
x = Conv2D(12, (1, 1), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
x = Conv2D(12, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
x = Conv2D(12, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
x = Conv2D(12, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
x = Conv2D(12, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
x = Conv2D(56, (1, 1), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
x = Conv2D(28, (9, 9), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
decoded = Conv2D(1, (5, 5), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
autoencoder = Model(input_img, decoded)
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='sgd', loss='mean_squared_error', metrics=['accuracy', 'mean_squared_error'])
# print(autoencoder.summary())#
return autoencoder
训练集使用的是200张图像,对数据集进行扩充,得到23万张40x40大小的图像块。测试集使用的是Set12,加入的是标准差为25的加性高斯白噪声(AWGN),客观评价标准使用的是峰值信噪比(PSNR),效果比简单3层网络要好很多。
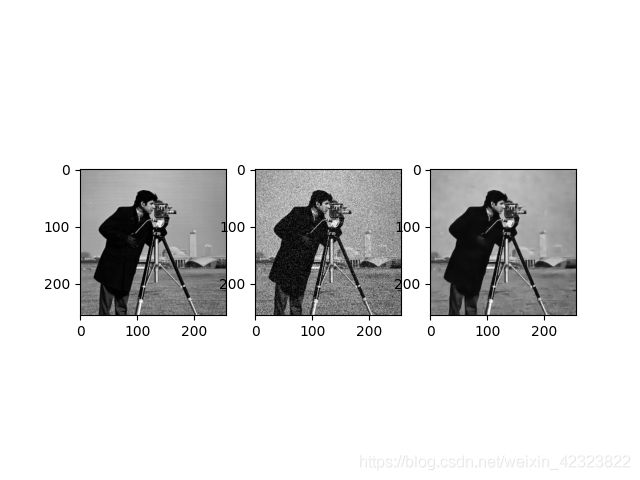

去噪后的psnr为29.10,噪声图像的psnr为20.56。两块GPU跑大概要1个小时左右(cpu就不要想了)
二,含噪图像映射去噪图像(稀疏网络模型)
同理,网络输入输出不变,共12层,只不过网络层之间的参数互相影响,因为效果没提升多少,我也没过多研究。直接上代码:
def get_gated_connections(gatePercentageFactor, inputLayer):
gateFactor = Input(tensor=K.variable([gatePercentageFactor]))
fractionG = Lambda(lambda x: x[0] * x[1])([inputLayer, gateFactor])
complement = Lambda(lambda x: x[0] - x[1])([inputLayer, fractionG])
return gateFactor, fractionG, complement
def get_cnn_architecture(weights_path=None):
input_img = Input(shape=(None, None, 1)) # adapt this if using `channels_first` image data format
x1 = Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(input_img)#180 180 64
gf1, fg1, c1 = get_gated_connections(0.1, x1)
x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(fg1)#90 90 64
x2 = Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x) #90 90 64
gf2, fg2, c2 = get_gated_connections(0.2, x2)
x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(fg2) #45 45 64
x3 = Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)#45 45 128
gf3, fg3, c3 = get_gated_connections(0.3, x3)
x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x3)#22.5 22.5 128
x4 = Conv2D(256, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)#22.5 22.5 256
gf4, fg4, c4 = get_gated_connections(0.4, x4)
x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x4)
x5 = Conv2D(512, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
gf5, fg5, c5 = get_gated_connections(0.5, x5)
x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x5)
x6 = Conv2D(1024, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x6)
y1 = Conv2DTranspose(512, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
jt4 = Add()([y1, c5])
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(jt4)
y2 = Conv2DTranspose(256, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
jt3 = Add()([y2, c4])
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(jt3)
y3 = Conv2DTranspose(128, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
jt2 = Add()([y3, c3])
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(jt2)#90 90 128
y4 = Conv2DTranspose(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)#90 90 64
jt1 = Add()([y4, c2])
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(jt1)#180 180 64
jt0 = Add()([x, c1])
y5 = Conv2DTranspose(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(jt0)#180 180 64
y6 = Conv2DTranspose(1, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(y5)#180 180 3
layers = y6
model = Model([input_img, gf1, gf2, gf3, gf4, gf5], layers)
model.compile(optimizer='sgd', loss='mean_squared_error', metrics=['accuracy'])#编译
#model.summary()
return model
测试结果如下:
 主观效果上就不是很好,这张图psnr为24.38 ,12张图平均psnr为25.13,噪声图像的psnr为20.56,可能是我代码跑的有问题。
主观效果上就不是很好,这张图psnr为24.38 ,12张图平均psnr为25.13,噪声图像的psnr为20.56,可能是我代码跑的有问题。
三,含噪图像映射噪声图像(DnCNNs残差网络模型)
这个网络模型借用的残差块的概念,将整个网络看成一个残差块,输入不变,输出的是噪声图像,将含噪图像减去噪声图像,从而得到去噪图像,效果超过传统方法,前面两个模型可以学学,DnCNNs需要深入研究。
def DnCNN(depth, filters=64, image_channels=1, use_bnorm=True):
layer_count = 0
inpt = Input(shape=(None, None, image_channels), name='input' + str(layer_count))
# 1st layer, Conv+relu
layer_count += 1
x = Conv2D(filters=filters, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(1, 1), kernel_initializer='Orthogonal', padding='same',
name='conv' + str(layer_count))(inpt)
layer_count += 1
x = Activation('relu', name='relu' + str(layer_count))(x)
# depth-2 layers, Conv+BN+relu
for i in range(depth - 2):
layer_count += 1
x = Conv2D(filters=filters, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(1, 1), kernel_initializer='Orthogonal', padding='same',
use_bias=False, name='conv' + str(layer_count))(x)
if use_bnorm:
layer_count += 1
# x = BatchNormalization(axis=3, momentum=0.1,epsilon=0.0001, name = 'bn'+str(layer_count))(x)
x = BatchNormalization(axis=3, momentum=0.0, epsilon=0.0001, name='bn' + str(layer_count))(x)
layer_count += 1
x = Activation('relu', name='relu' + str(layer_count))(x)
# last layer, Conv
layer_count += 1
x = Conv2D(filters=image_channels, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(1, 1), kernel_initializer='Orthogonal',
padding='same', use_bias=False, name='conv' + str(layer_count))(x)
layer_count += 1
x = Subtract(name='subtract' + str(layer_count))([inpt, x]) # input - noise
model = Model(inputs=inpt, outputs=x)
return model
整个残差思想就体现在这一行代码上
x = Subtract(name='subtract' + str(layer_count))([inpt, x]) # input - noise
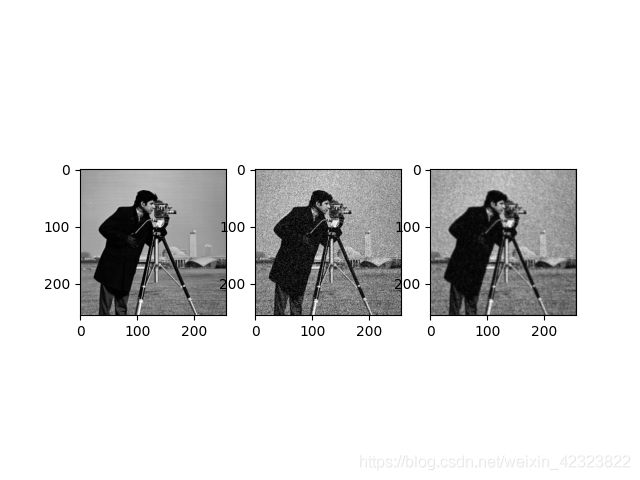
效果如下:

最左边是原始图像,中间是加入噪声强度为25的含噪图像(也就是输入图像),最右边是去噪图像(也就是输出图像)。这张图psnr为29.82 ,12张图平均psnr为29.74,噪声图像的psnr为20.56。数值是用python代码测的,用MATLAB测会更高(懂得都懂)。如果是彩色图像的话,输入输出的通道数改为3就行。
总结
因为代码都是从github上东拼西凑的,所以我把完整代码都上传到csdn上免费下载,代码下载链接在这,里面包括数据集,代码,还有训练好的模型参数(对应部分不同噪声强度,没有全部),可以直接用(代码运行环境要对),当然我也建议大家直接去github上找代码。
总的来说,初学者还是要循序渐进,一定要把网络的输入输出搞懂,要先明白网络要干什么,再去弄懂网络是怎么做到的,会更好学习一点。
`
