PELU激活函数的tensorflow实现(一) Parametric Exponential Linear Unit
PELU激活函数实现
-
-
- 一、PELU简介
- 二、PELU实现
-
- 1、PELU代码实现
- 2、测试PELU实现是否正确
- 3、实现PELU对 α \alpha α 求导
- 4、实现PELU对 β \beta β 求导
- 三、PELU实战应用
-
- 1、PELU 与 RELU 模型对比
- 2、实现保存和加载模型
-
一、PELU简介
激活函数 exponential linear unit (ELU) 公式如下:
ϕ ( x ) = { x if x ≥ 0 α ( exp ( x ) − 1 ) otherwise , \phi(x) = \Biggl\{ \begin{aligned} x & \;\; \text{ if } x \ge 0 \\ \alpha \left(\exp\left(x\right)- 1\right) & \;\; \text{ otherwise } \end{aligned} \Bigr. \,, ϕ(x)={xα(exp(x)−1) if x≥0 otherwise ,
其中 α \alpha α 是超参数. 该函数的实现: tf.keras.layers.ELU (点我跳转).
激活函数 parametric ELU (PELU) 是 ELU 激活函数的扩展:
ϕ ( x ) = { α β x if x ≥ 0 α ( exp ( x β ) − 1 ) otherwise , \phi(x) = \Biggl\{ \begin{aligned} \frac{\alpha}{\beta}x & \;\; \text{ if } x \ge 0 \\ \alpha \left(\exp\Bigl(\frac{x}{\beta}\Bigr)- 1\right) & \;\; \text{ otherwise } \end{aligned} \Bigr. \,, ϕ(x)={βαxα(exp(βx)−1) if x≥0 otherwise ,
主要的不同是 α , β > 0 \alpha,\beta > 0 α,β>0 是可训练的参数, ( α , β ) (\alpha, \beta) (α,β) 同时在网络中被训练。
二、PELU实现
1、PELU代码实现
tf.keras.layers.Layer可用于实现自定义的层。
参考链接:
- Making new Layers and Models via subclassing
- Custom layers
- tf.keras.layers.Layer (documentation)
实现代码如下:
import tensorflow as tf
class PELU(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, units=32):
super(PELU, self).__init__()
self.units = units
def build(self, input_shape):
# TODO: write the code here
self.alpha = self.add_weight(name = 'alpha',
shape = (self.units, ),
initializer = tf.keras.initializers.RandomUniform(minval = 0, maxval = 1, seed=None),
trainable = True,
dtype = 'float32',
constraint = tf.keras.constraints.NonNeg())
self.beta = self.add_weight(name = 'beta', shape = (self.units, ),
initializer = tf.keras.initializers.RandomUniform(minval = 0, maxval = 1, seed=None),
trainable = True,
dtype = 'float32',
constraint = tf.keras.constraints.NonNeg())
return
raise NotImplementedError("build part error !!!!!!!")
def call(self, inputs):
# TODO: write the code here
pos = (self.alpha / self.beta) * tf.nn.relu(inputs)
neg = self.alpha * (tf.exp(-tf.nn.relu(-inputs) / self.beta) - 1)
return pos + neg
raise NotImplementedError("call part error !!!!!!!!!!!")
def get_config(self):
config = {'units' : self.units}
base_config = super(PELU, self).get_config()
return dict(list(base_config.items()) + list(config.items()))
2、测试PELU实现是否正确
pelu = PELU(units=1)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_range = tf.linspace(-5, 5, 200) # An equispaced grid of 200 points in [-5, +5]
x_range = tf.cast(x_range, tf.float32) #convert type from float64 to float32
y_range = pelu(x_range) # TODO: Your code here
plt.plot(x_range.numpy(), y_range.numpy())
3、实现PELU对 α \alpha α 求导
d ϕ ( x ) d α = { x β if x ≥ 0 ( exp ( x β ) − 1 ) otherwise, \frac{d\phi(x)}{d\alpha} = \Biggl\{ \begin{aligned} \frac{x}{\beta} & \;\; \text{ if } x \ge 0 \\ \left(\exp\Bigl(\frac{x}{\beta}\Bigr)- 1\right) & \;\; \text{ otherwise,} \end{aligned} \Bigr. \, dαdϕ(x)={βx(exp(βx)−1) if x≥0 otherwise,
Note:tf.GradientTape可以用于求导,tf.reduce_all(tf.abs(x - y) < 1e-4)可用于控制小数点位数
#实现
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch(pelu.alpha)
y = pelu(x_range)
dx_da = tape.jacobian(y, pelu.alpha)
#用具体的数来测试下实现的对错
#use positive input x_range[0]
print(tf.reduce_all(tf.abs(tf.exp(x_range[0] / pelu.beta) - 1 - dx_da[0]) < 1e-4))
#use negtive input x_range[-1]
print(tf.reduce_all(tf.abs(x_range[-1] / pelu.beta - dx_da[-1]) < 1e-4))
tf.Tensor(True, shape=(), dtype=bool)
tf.Tensor(True, shape=(), dtype=bool)
4、实现PELU对 β \beta β 求导
d ϕ ( x ) d β = { − α x β 2 if x ≥ 0 α x e x β β 2 otherwise, \frac{d\phi(x)}{d\beta} = \Biggl\{ \begin{aligned} \frac{- \alpha x}{\beta ^2} & \;\; \text{ if } x \ge 0 \\ \frac{\alpha x e^{\frac{x}{\beta}}}{\beta ^2} & \;\; \text{ otherwise,} \end{aligned} \Bigr. \, dβdϕ(x)={β2−αxβ2αxeβx if x≥0 otherwise,
#实现
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch(pelu.beta)
y = pelu(x_range)
dx_db = tape.jacobian(y, pelu.beta)
#用具体的数来测试下实现的对错
# use positive input x_range[-1]
print(tf.reduce_all(tf.abs(-(pelu.alpha * x_range[-1]) / (pelu.beta ** 2) - dx_db[-1]) < 1e-4))
# use negtive input x_range[0]
g = -pelu.alpha * x_range[0] * tf.exp(x_range[0] / pelu.beta) / (pelu.beta ** 2)
print(tf.reduce_all(tf.abs(g - dx_db[0]) < 1e-4))
tf.Tensor(True, shape=(), dtype=bool)
tf.Tensor(True, shape=(), dtype=bool)
三、PELU实战应用
1、PELU 与 RELU 模型对比
- 数据集:点击此处获取该数据集的更多信息
- 下载地址:请点击此处
- PELU 和 RELU 模型的对照实验
# Load boston housing dataset
import pandas as pd
sensorless = pd.read_csv('Sensorless_drive_diagnosis.txt', header=None, sep=' ')
#处理好数据
X = sensorless.values[:, 0:-1].astype('float32')
y = sensorless.values[:, -1:].astype('int64') - 1
from sklearn import model_selection
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = model_selection.train_test_split(X, y, stratify=y)
y_train = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes=11)
#建立PELU 和 RELU模型
model_pelu = tf.keras.Sequential(layers=[
tf.keras.Input(shape = (x_train.shape[1], )),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(50),
PELU(50),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(11, activation = 'softmax')
])
model_relu = tf.keras.Sequential(layers=[
tf.keras.Input(shape = (x_train.shape[1], )),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(50),
tf.keras.layers.ReLU(50), # only different here with pelu model
tf.keras.layers.Dense(11, activation = 'softmax')
])
# 训练中修改learning rate
def schedule(epoch):
if epoch < 50:
return .001
if epoch < 300:
return .0001
if epoch < 600:
return .00001
if epoch < 900:
return .000001
else:
return .0000001
lr_scheduler = tf.keras.callbacks.LearningRateScheduler(schedule)
callbacks_list = [lr_scheduler, ]
#sgd优化器
sgd = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate = 0.001)
#编译模型
model_pelu.compile(optimizer = sgd, loss = 'categorical_crossentropy', metrics = ['acc'])
model_relu.compile(optimizer = sgd, loss = 'categorical_crossentropy', metrics = ['acc'])
# 训练 PELU 模型
history_pelu = model_pelu.fit(x_train,
y_train,
batch_size = 32,
validation_split = 0.2,
epochs = 1000,
callbacks = callbacks_list,
verbose = 0,
shuffle=True)
# 训练 RELU 模型
history_relu = model_relu.fit(x_train,
y_train,
batch_size = 32,
validation_split = 0.2,
epochs = 1000,
callbacks = callbacks_list,
verbose = 0,
shuffle=True)
# PELU 与 RELU 模型的训练损失图
plt.plot(history_relu.epoch, history_relu.history['loss'], label = 'relu loss')
plt.plot(history_pelu.epoch, history_pelu.history['loss'], label = 'pelu loss')
plt.plot(history_relu.epoch, history_relu.history['val_loss'], label = 'relu val loss')
plt.plot(history_pelu.epoch, history_pelu.history['val_loss'], label = 'pelu val loss')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.title('Train and Valid Loss Compare')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
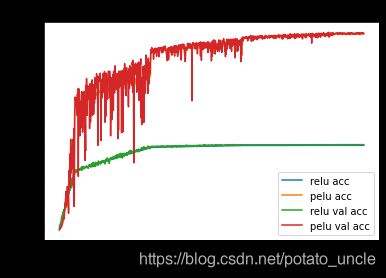
# PELU 与 RELU 模型的训练准确率图
plt.plot(history_relu.epoch, history_relu.history['acc'], label = 'relu acc')
plt.plot(history_pelu.epoch, history_pelu.history['acc'], label = 'pelu acc')
plt.plot(history_relu.epoch, history_relu.history['val_acc'], label = 'relu val acc')
plt.plot(history_pelu.epoch, history_pelu.history['val_acc'], label = 'pelu val acc')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.title('Train and Valid Accuracy Compare')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
#输出下准确率对比
import numpy as np
pre_pelu = np.argmax(model_pelu.predict(x_test), axis=-1)
pre_relu = np.argmax(model_relu.predict(x_test), axis=-1)
def get_acc(pre):
account = 0
for i in range(0, pre.shape[0]):
if pre[i] == y_test[i]:
account = account + 1
return account / len(pre)
print("Pelu model accuracy is: ", get_acc(pre_pelu))
print("Relu model accuracy is: ", get_acc(pre_relu))
Pelu model accuracy is: 0.8493984140005469
Relu model accuracy is: 0.42028985507246375
2、实现保存和加载模型
需要给PELU 实现加入 get_config / from_config 函数以保存和加载模型数据,该函数已经在上边的PELU实现里实现了
model_pelu.save('pelu_model')
del PELU # This is needed to remove any reference to PELU from memory
reloaded_model = tf.keras.models.load_model('pelu_model')
print("Original model:", model_pelu)
print("Loaded model:", reloaded_model) # Observe that the object has been dynamically recreated in absence of the configuration options
写在最后,PELU实现从实验测试中可以看出已经成功实现了,RELU准确率这么低的原因应该是是没加 normalization()层,加入之后,准确率应该和PELU 模型的准确率差不多。
求各位观众老爷点赞!!