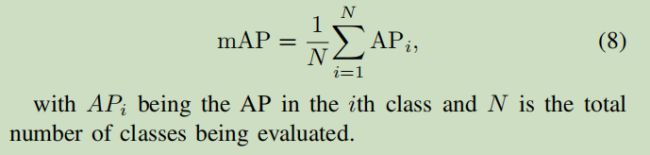目标检测评价指标 AP、mAP
目标检测中的TP、FP、FN
所有检测框都认为是Predicted Positive
所有真实框都是Ground-truth Positive
若一个检测框与一个真实框的IOU>阈值并对正确分类,则认为该检测框是一个True Positive
若一个检测框不与任何真实框IOU>阈值 或 当检测框与真实框IOU>阈值却没有正确分类时,则认为该检测框是一个False Positive
若一个真实框不与任何一个检测框匹配(即IOU>阈值且类别一致),则认为该真实框是一个False Negative
目标检测中没有True Negative的概念,因为True Negative有无数个
有了TP、FP、FN,就可以计算precision和recall
AP
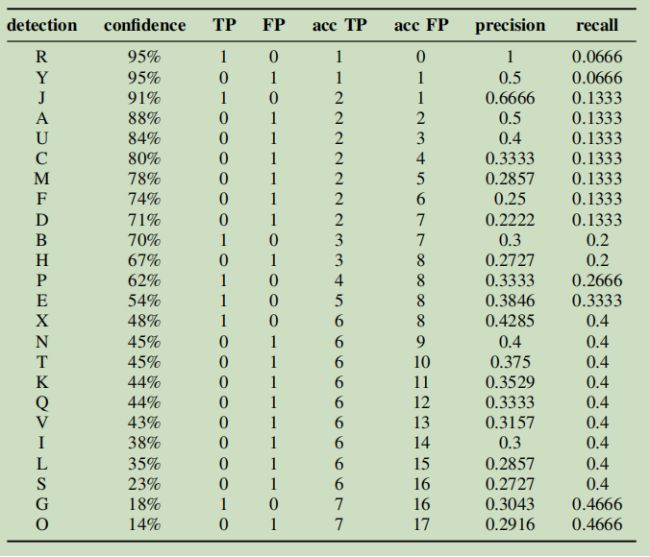
对与单类目标检测(如人脸检测),如上图,绿色框为真实框(共有15个),红色框为检测框(共有24个,A,...,Y),判断TP、FP、FN的IOU阈值设为0.3。每个检测框都有一个置信度,将所有检测框按置信度从高到低排序,可得到下表:
其中acc TP表示从头到该位置累计TP数量,acc FP表示从头到该位置累计FP数量,precision表示从头到该位置的precision,recall表示从头到该位置的recall
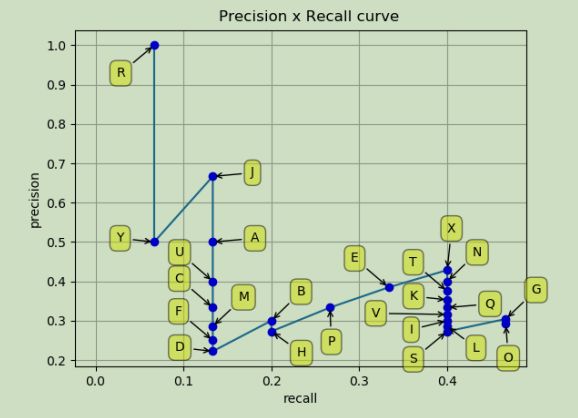
下图表示从头到尾依次加入新样本时,P和R的变化情况(P-R线):
AP有两种:
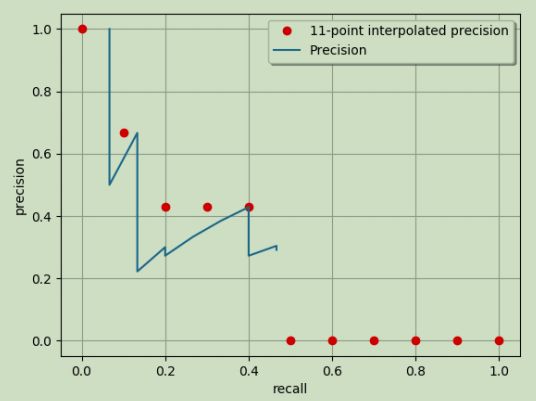
①AP_11(更常用):在上图中,将recall分别取[0, 0.1, 0.2, ..., 1]11个值,对应precision为该recall值右侧P-R线的最高值,如下图所示,红色点表示这11个(recall, precision):
AP_11就是11个红点precision的均值
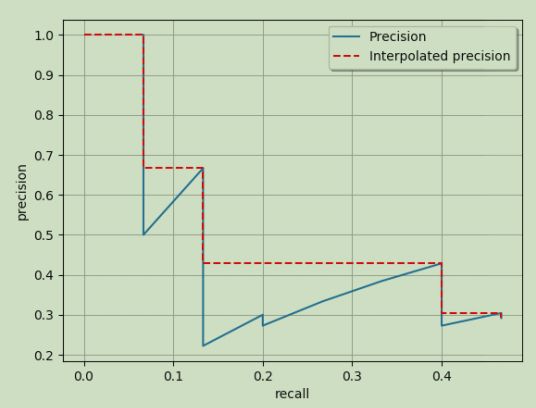
②AP_all:如下图所示,红色虚线的纵坐标从1开始单调递减,每次减小到右侧P-R线的最高值
AP_all就是红色虚线下方的面积,即:
mAP
对目标检测中的每个类计算AP,再求每个类AP的平均值,如下图所示:
在COCO竞赛中,AP就是指mAP
![]()
代码:
# --------------------------------------------------------
# Fast/er R-CNN
# Licensed under The MIT License [see LICENSE for details]
# Written by Bharath Hariharan
# --------------------------------------------------------
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
import cPickle
import numpy as np
def parse_rec(filename):
""" Parse a PASCAL VOC xml file """
tree = ET.parse(filename)
objects = []
for obj in tree.findall('object'):
obj_struct = {}
obj_struct['name'] = obj.find('name').text
obj_struct['pose'] = obj.find('pose').text
obj_struct['truncated'] = int(obj.find('truncated').text)
obj_struct['difficult'] = int(obj.find('difficult').text)
bbox = obj.find('bndbox')
obj_struct['bbox'] = [int(bbox.find('xmin').text),
int(bbox.find('ymin').text),
int(bbox.find('xmax').text),
int(bbox.find('ymax').text)]
objects.append(obj_struct)
return objects
def voc_ap(rec, prec, use_07_metric=False):
""" ap = voc_ap(rec, prec, [use_07_metric])
Compute VOC AP given precision and recall.
If use_07_metric is true, uses the
VOC 07 11 point method (default:False).
"""
if use_07_metric:
# 11 point metric
ap = 0.
for t in np.arange(0., 1.1, 0.1):
if np.sum(rec >= t) == 0:
p = 0
else:
p = np.max(prec[rec >= t])
ap = ap + p / 11.
else:
# correct AP calculation
# first append sentinel values at the end
mrec = np.concatenate(([0.], rec, [1.]))
mpre = np.concatenate(([0.], prec, [0.]))
# compute the precision envelope
for i in range(mpre.size - 1, 0, -1):
mpre[i - 1] = np.maximum(mpre[i - 1], mpre[i])
# to calculate area under PR curve, look for points
# where X axis (recall) changes value
i = np.where(mrec[1:] != mrec[:-1])[0]
# and sum (\Delta recall) * prec
ap = np.sum((mrec[i + 1] - mrec[i]) * mpre[i + 1])
return ap
def voc_eval(detpath,
annopath,
imagesetfile,
classname,
cachedir,
ovthresh=0.5,
use_07_metric=False):
"""rec, prec, ap = voc_eval(detpath,
annopath,
imagesetfile,
classname,
[ovthresh],
[use_07_metric])
Top level function that does the PASCAL VOC evaluation.
detpath: Path to detections
detpath.format(classname) should produce the detection results file.
annopath: Path to annotations
annopath.format(imagename) should be the xml annotations file.
imagesetfile: Text file containing the list of images, one image per line.
classname: Category name (duh)
cachedir: Directory for caching the annotations
[ovthresh]: Overlap threshold (default = 0.5)
[use_07_metric]: Whether to use VOC07's 11 point AP computation
(default False)
"""
# assumes detections are in detpath.format(classname)
# assumes annotations are in annopath.format(imagename)
# assumes imagesetfile is a text file with each line an image name
# cachedir caches the annotations in a pickle file
# first load gt
if not os.path.isdir(cachedir):
os.mkdir(cachedir)
cachefile = os.path.join(cachedir, 'annots.pkl')
# read list of images
with open(imagesetfile, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
imagenames = [x.strip() for x in lines]
if not os.path.isfile(cachefile):
# load annots
recs = {}
for i, imagename in enumerate(imagenames):
recs[imagename] = parse_rec(annopath.format(imagename))
if i % 100 == 0:
print 'Reading annotation for {:d}/{:d}'.format(
i + 1, len(imagenames))
# save
print 'Saving cached annotations to {:s}'.format(cachefile)
with open(cachefile, 'w') as f:
cPickle.dump(recs, f)
else:
# load
with open(cachefile, 'r') as f:
recs = cPickle.load(f)
# extract gt objects for this class
class_recs = {}
npos = 0
for imagename in imagenames:
R = [obj for obj in recs[imagename] if obj['name'] == classname]
bbox = np.array([x['bbox'] for x in R])
difficult = np.array([x['difficult'] for x in R]).astype(np.bool)
det = [False] * len(R)
npos = npos + sum(~difficult)
class_recs[imagename] = {'bbox': bbox,
'difficult': difficult,
'det': det}
# read dets
detfile = detpath.format(classname)
with open(detfile, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
splitlines = [x.strip().split(' ') for x in lines]
image_ids = [x[0] for x in splitlines]
confidence = np.array([float(x[1]) for x in splitlines])
BB = np.array([[float(z) for z in x[2:]] for x in splitlines])
# sort by confidence
sorted_ind = np.argsort(-confidence)
sorted_scores = np.sort(-confidence)
BB = BB[sorted_ind, :]
image_ids = [image_ids[x] for x in sorted_ind]
# go down dets and mark TPs and FPs
nd = len(image_ids)
tp = np.zeros(nd)
fp = np.zeros(nd)
for d in range(nd):
R = class_recs[image_ids[d]]
bb = BB[d, :].astype(float)
ovmax = -np.inf
BBGT = R['bbox'].astype(float)
if BBGT.size > 0:
# compute overlaps
# intersection
ixmin = np.maximum(BBGT[:, 0], bb[0])
iymin = np.maximum(BBGT[:, 1], bb[1])
ixmax = np.minimum(BBGT[:, 2], bb[2])
iymax = np.minimum(BBGT[:, 3], bb[3])
iw = np.maximum(ixmax - ixmin + 1., 0.)
ih = np.maximum(iymax - iymin + 1., 0.)
inters = iw * ih
# union
uni = ((bb[2] - bb[0] + 1.) * (bb[3] - bb[1] + 1.) +
(BBGT[:, 2] - BBGT[:, 0] + 1.) *
(BBGT[:, 3] - BBGT[:, 1] + 1.) - inters)
overlaps = inters / uni
ovmax = np.max(overlaps)
jmax = np.argmax(overlaps)
if ovmax > ovthresh:
if not R['difficult'][jmax]:
if not R['det'][jmax]:
tp[d] = 1.
R['det'][jmax] = 1
else:
fp[d] = 1.
else:
fp[d] = 1.
# compute precision recall
fp = np.cumsum(fp)
tp = np.cumsum(tp)
rec = tp / float(npos)
# avoid divide by zero in case the first detection matches a difficult
# ground truth
prec = tp / np.maximum(tp + fp, np.finfo(np.float64).eps)
ap = voc_ap(rec, prec, use_07_metric)
return rec, prec, ap
参考:
目标检测01:常用评价指标(AP、AP50、AP@50:5:95、mAP) - 黎明程序员 - 博客园
【目标检测】一、目标检测中常见的评价指标_满船清梦压星河HK的博客-CSDN博客
Sign in to GitHub · GitHub
AP,mAP计算详解(代码全解) - 知乎